Abstract
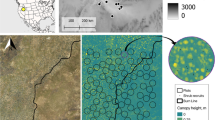
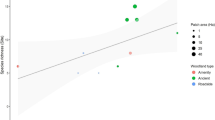
We present the results of one of the few available tests of how CORINE (CLC2000) is likely to perform as a basis for the calculation of landscape indices, for environmental monitoring over large areas. This paper investigates to what extent landscape structural indices based on this widely used European land cover database can be used to predict plant species richness in a 2,000 km2 transect in the northeast of Scotland. We investigate both statistical and map resolution issues by comparing the performance of CORINE-based common landscape indices with the same indices derived from a much more detailed geographic data set. In our case study, only shape-related indices show correlation with species richness, but effect size, important for monitoring, is small. The results highlight the area-specific and map specific nature of the performance of landscape indices for protecting plant diversity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 19:716–723. doi:10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705
Altman DG, Andersen PK (1989) Bootstrap investigation of the stability of a Cox regression model. Stat Med 8:771–783. doi:10.1002/sim.4780080702
Bailey D, Herzog F, Augenstein I, Aviron S, Billeter R, Szerencsits E et al (2007) Thematic resolution matters: indicators of landscape pattern for European agro-ecosystems. Ecol Indic 7:692–709. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2006.08.001
Baldwin DJB, Weaver K, Schnekenburger F, Perera AH (2004) Sensitivity of landscape pattern indices to input data characteristics on real landscapes: implications for their use in natural disturbance emulation. Landsc Ecol 19:255–271. doi:10.1023/B:LAND.0000030442.96122.ef
Bastian O (2000) Landscape classification in Saxony—a tool for holistic regional planning. Landsc Urban Plan 50:145–155. doi:10.1016/S0169-2046(00)00086-4
Bastian O, Kronert R, Zdeneck L (2006) Landscape diagnosis on different space and time scales—a challenge for landscape planning. Landsc Ecol 21:359–374. doi:10.1007/s10980-005-5224-1
Bera P, Prasher SO, Patel RM, Madani A, Lacroix R, Gaynor JD et al (2006) Application of MARS in simulating pesticide concentrations in soil. Trans ASAE 49:297–307
Bunce RGH, Metzger MJ, Jongman RHG, Brandt J, De Blust G, Elena-Rossello R et al (2008) A standardized procedure for surveillance and monitoring of European habitats and provision of spatial data. Landsc Ecol 23:11–25. doi:10.1007/s10980-007-9173-8
Buyantuyev A, Wu JG (2007) Effects of thematic resolution on landscape pattern analysis. Landscape Ecol 22:7–13. doi:10.1007/s10980-006-9010-5
CBD (1992) The Convention on biological diversity. http://wwwcbdint/convention/
Chown SL, van Rensburg BJ, Gaston KJ, Rodrigues ASL, van Jaarsveld AS (2003) Energy, species richness, and human population size: conservation implications at a national scale. Ecol Appl 13:1233–1241
Commission of the European Communities (1998) Communication to the council and parliament on a European community biodiversity strategy, COM (98) 42
Commission of the European Communities (2006) Halting the loss of biodiversity by 2006 and beyond—sustaining ecosystem services for human well-being http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/site/en/com/2006/com2006_0216en01.pdf
Corry RC, Nassauer JI (2005) Limitations of using landscape pattern indices to evaluate the ecological consequences of alternative plans and designs. Landsc Urban Plan 72:265–280. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2004.04.003
Council of Europe (1994) Landscape diversity strategy. http://conventions.coe.int/Treaty/EN/Reports/Html/176.htm
Council of Europe (2000) The European landscape convention. http://conventions.coe.int/Treaty/en/Treaties/Html/176.htm
Craven P, Wahba G (1979) Smoothing noisy data with spline functions. Numer Math 31:377–403. doi:10.1007/BF01404567
Dale VH, Brown S, Haeuber RA, Hobbs NT, Huntly N, Naiman RJ et al (2000) Ecological principles and guidelines for managing the use of land. Ecol Appl 10:639–670
De Clercq EM, Vandemoortele F, De Wulf RR (2006) A method for the selection of relevant pattern indices for monitoring of spatial forest cover pattern at a regional scale. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinform 8:113–125. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2005.07.002
Deutschewitz K, Lausch A, Kuhn I, Kloz S (2003) Native and alien plant species richness in relation to spatial heterogeneity on a regional scale in Germany. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 12:299–311. doi:10.1046/j.1466-822X.2003.00025.x
Donohue RJ, Roderick ML, McVicar TR (2007) On the importance of including vegetation dynamics in Budyko’s hydrological model. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 11:983–995
Dramstad WE, Fjellstad WJ, Strand G-H, Mathiesen HF, Engan G, Stokland JN (2002) Development and implementation of the Norwegian programme for agricultural landscapes. J Environ Manage 63:1–15
Dunning JB, Danielson BJ, Pulliam HR (1992) Ecological processes that affect populations in complex landscapes. Oikos 65:169–175
EEA (2006) The thematic accuracy of CORINE land cover 2000. Assessment using LUCAS (land use/cover area frame statistical survey). EEA, Copenhagen, Denmark
EEA and ETC-TE (2002) CORINE Land Cover update. CLC2000 project. Technical guidelines. Final version. EEA, Denmark
Evans KL, Gaston KJ (2005) Can the evolutionary-rates hypothesis explain species energy relationships? Funct Ecol 19:899-915
Fjellstad WJ, Dramstad W,E (1999) Patterns of change in two contrasting Norwegian agricultural landscapes. Landsc Urban Plan 45:177–191
Forman RTT, Godron M (1986) Landscape Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, NY
Gaston KJ, Blackburn TM, Goldewijk KK (2003) Habitat conversion and global avian biodiversity loss. Proc R Soc Lond B 270:1293–1300
Gimona A, van der Horst D (2007) Mapping hotspots of landscape functions; a case study on farmland afforestation in Scotland. Landsc Ecol 22:1255–1264
Groom G, Mucher CA, Ihse M, Wrbka T (2006) Remote sensing in landscape ecology: experiences and perspectives in a European context. Landsc Ecol 21:391–408
Grossman YL, Ustin SL, Jacquemoud S, Sanderson EW, Schmuck G, Verdebout J (1996) Critique of stepwise multiple linear regression for the extraction of leaf biochemistry information from leaf reflectance data. Remote Sens Environ 56:182–193
Gustafson EJ (1998) Quantifying landscape spatial pattern: what is the state of the art? Ecosystems 1:143–156
Gustafson EJ, Lytle DE, Swaty R, Loehle C (2007) Simulating the cumulative effects of multiple forest management strategies on landscape measures of forest sustainability. Landsc Ecol 22:141–156
Hanski I (1991) Single-species metapopulation dynamics: concepts, models, and observations. Biol J Linn Soc 42:17–38
Haslem A, Bennet AF (2008) Countryside elements and the conservation of birds in agricultural environments. Agric Ecosyst Environ 125:191–203
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman JH (2001) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference and prediction. Springer Verlag, New York
Hawkins BA, Field R, Cornell HV, Currie DJ, Guegan JF, Kaufman DM, Kerr JT, Mittelbach GG, Obrdorff T, O'Brien EM, Porter EE, Turner JRG (2003) Energy, water, and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness. Ecology 84:3105–3117
Hernandez-Stefanoni JL (2006) The role of landscape patterns of habitat types on plant species diversity of a tropical forest in Mexico. Biodivers Conserv 15:1441–1457
Herzog F, Lausch A, Muller E, Thulke HH, Steinhardt U, Lehmann S (2001) Landscape metrics for assessment of landscape destruction and rehabilitation. Environ Manag 27:91–107
Hietala-Koivu R (1999) Agricultural landscape change: a case-study in Ylane, southwest Finland. Landsc Urban Plan 46:103–108
Hilborn R, Mangel M (1997) The ecological detective: confronting models with data. PUP, Princeton
HMSO (1995) Biodiversity, the UK action plan. London, 191pp
IRENA (2004) IRENA expert meeting on landscape and biodiversity. European environment agency, Copenhagen, Denmark. http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/dsis/landstat/library?l=/lucas/reports/landscapeandbiodiversity/_EN_1.0_&a=d
Kim KH, Pauleit S (2007) Landscape character, biodiversity and land use planning: the case of Kwangju city region, South Korea. Land Use Policy 24:264–274
Kivinen S, Luoto M, Kuussaari M, Helenius J (2005) Multi-species richness of boreal agricultural landscapes: effects of climate, biotope, soil and geographical location. J Biogeography 33:862–975
Kivinen S, Luoto M, Kuussaari M, Helenius J (2006) Multi-species richness of boreal agricultural landscapes: effects of climate, biotope, soil and geographical location. J Biogeogr 33:862–875
Leathwick JR, Rowe D, Richardson J, Elith J, Hastie T (2005) Using multivariate adaptive regression splines to predict the distributions of New Zealand’s freshwater diadromous fish. Freshw Biol 50:2034–2052
Levins R (1969) Some demographic and genetic consequences of environmental heterogeneity for biological control. Bull Entomol Soc Am 15:237–240
Li H, Wu J (2004) Use and misuse of landscape indices. Landsc Ecol 19:389–399
Luoto M (2000) Modeling of rare plant species richness by landscape variables in an agricultural areas in Finland. Plant Ecol 149:157–168
MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1967) The theory of island biogeography. Princeton University Press, NJ
Mander U, Mikk M, Kulvik M (1999) Ecological and low intensity agriculture as contributors to landscape and biological diversity. Landsc Urban Plan 46:169–177
Mander Ü, Müller F, Wrbka T (2005) Functional and structural landscape indicators: upscaling and downscaling problems. Ecol Indic 5:267–272
McGarigal K, Marks BJ (1995) FRAGSTATS: spatial pattern analysis program for quantifying landscape structure. U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service, General Technical Report PNW-351, Portland, Oregon, USA
Mortelliti A, Amori G, Sammuri G, Boitani L (2007) Factors affecting the distribution of Sorex samniticus, an endemic Italian shrew, in a heterogeneous landscape. Acta Theriol 52:75–84
Moser D, Zechmeister HG, Plutzar C, Sauberer N, Wrbka T, Grabherr G (2002) Landscape patch shape complexity as an effective measure for plant species richness in rural landscapes. Landsc Ecol 17:657–669
Moser D, Dullinger S, Englisch T, Niklfeld H, Plutzar C, Sauberer N, Zechmeister HG, Grabherr G (2005) Environmental determinants of vascular plant species richness in the Austrian Alps. J Biogeogr 32:1117–1127
Munoz J, Felicisimo AM (2004) Comparison of statistical methods commonly used in predictive modeling. J Veg Sci 15:285–292
Oja T, Alamets K, Pärnamets H (2005) Modelling bird habitat suitability based on landscape parameters at different scales. Ecological Indicators 5:314–321
Preston CD, Pearman DA, Dines TD (2002) New atlas of the British and Irish flora. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Rahbek C, Graves GR (2001) Multiscale assessment of patterns of avian species richness. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 98:4534–4539
Riitters KH, O’Neill RV, Hunsaker CT, Wickham JD, Yankee DH, Timmins SP, Jones KB, Jackson BL (1995) A factor analysis of landscape pattern and structure metrics. Landsc Ecol 10:23–39
Rosenzweig ML (1995) Species diversity in space and time. Cambridge University Press, New York, NY
Rosenzweig ML (2001) Loss of speciation rate will impoverish future diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5404–5410
Saura S, Martinez-Millan J (2001) Sensitivity of landscape pattern metrics to map spatial extent. Photogram Eng Remote Sens 67:1027–1036
Schmit C, Rousevell MDA, La Jeunesse I (2006) The limitations of spatial land use data in environmental analysis. Environ Sci Policy 9:174–188
Thomas CD et al (2004) Extinction risk from climate change. Nature 427:145–148
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Statist Soc, B Ser 58:267–288
Tischendorf L (2001) Can landscape indices predict ecological processes consistently? Landsc Ecol 16:235–254
Tress B, Tress G (2003) Scenario visualisation for participatory landscape planning—a study from Denmark. Landsc Urban Plan 64:161–178
Uuemaa E, Roosaare J, Mander U (2005) Scale dependence of landscape metrics and their indicatory value for nutrient and organic matter losses from catchments. Ecological Indicators 5:350–369
van der Horst D, Gimona A (2005) Where new farm woodlands support biodiversity action plans: a spatial multi-criteria analysis. Biol Conserv 123:421–432
Wagner HH, Wildi O, Ewald KC (2000) Additive partitioning of plant species diversity in an agricultural mosaic landscape. Landsc Ecol 15:219–227
Walters S (2007) Modeling scale-dependent landscape pattern, dispersal, and connectivity from the perspective of the organism. Landsc Ecol 22:867–881
Wascher DM (ed) (2005) European landscape character areas—typologies, cartography and indicators for the assessment of sustainable landscapes. Final ELCAI Project Report. Landscape Europe, Wageningen
Wu JG (2004) Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: scaling relations. Landsc Ecol 19:125–138
Wu JG, Shen WJ, Sun WZ, Tueller PT (2002) Empirical patterns of the effects of changing scale on landscape metrics. Landsc Ecol 17:761–782
Zechmeister HG, Moser D (2001) The influence of agricultural land-use intensity on bryophyte species richness. Biodivers Conserv 10:1609–1625
Zhang Y, Guindon B (2005) Landscape analysis of human impacts on forest fragmentation in the Great Lakes region. Can J Remote Sens 31:153–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gimona, A., Messager, P. & Occhi, M. CORINE-based landscape indices weakly correlate with plant species richness in a northern European landscape transect. Landscape Ecol 24, 53–64 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-008-9279-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-008-9279-7