Abstract
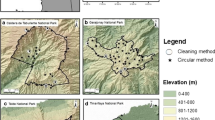
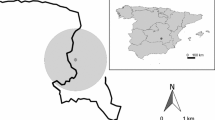
Assessing the associations between spatial patterns in population abundance and environmental heterogeneity is critical for understanding various population processes and for managing species and communities. This study evaluates responses in the abundance of the European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus), an important prey for predators of conservation concern in Mediterranean ecosystems, to environmental heterogeneity at different spatial scales. Multi-scale habitat models of rabbit abundance in three areas of Doñana, south-western Spain, were developed using a spatially extensive dataset of faecal pellet counts as an abundance index. The best models included habitat variables at the three spatial scales examined: distance from lagoons (broad scale), mean landscape shrub coverage and interspersion of pastures (home-range scale), and shrub and pasture cover (microhabitat scale). These variables may well have been related to the availability of food and refuge for the species at the different scales. However, the models’ fit to data and their predictive accuracy for an independent sample varied among the study regions. Accurate predictions in some areas showed that the combination of variables at various spatial scales can provide a reliable method for assessing the abundance of ecologically complex species such as the European rabbit over large areas. On the other hand, the models failed to identify abundance patterns in a population that suffered the strongest demographic collapse after viral epidemics, underlining the difficulty of generalizing this approach. In the latter case, factors difficult to implement in static models such as disease history and prevalence, predator regulation and others may underlie the lack of association. Habitat models can provide useful guidelines for the management of landscape attributes relevant to rabbits and help improve the conservation of Mediterranean communities. However, other influential factors not obviously related to environmental heterogeneity should also be analyzed in more detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Aars R.A. Ims (2000) ArticleTitlePopulation dynamic and genetic consequences of spatial density–dependent dispersal in patchy populations Am. Nat. 155 252–264 Occurrence Handle10.1086/303317 Occurrence Handle10686164
H. Akaike (1973) Information theory as an extension of the maximum likelihood principle B.N. Petrov F. Csaki (Eds) Second International Symposium on Information Theory Akademiai Kiado BudapestHungary 267–281
J.A. Bissonette D.J. Harrison C.D. Hargis T.G. Chapin (1997) The influence of spatial scale and scale-sensitive properties in habitat selection by American marten J.A. Bissonette (Eds) Wildlife and Landscape Ecology: Effects of Pattern and Scale Springer-Verlag New York, USA 368–385
M.S. Boyce L.L. McDonald (1999) ArticleTitleRelating populations to habitats using resource selection functions Trends Ecol. Evol. 14 268–272 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-5347(99)01593-1 Occurrence Handle10370262
J.H. Brown D.W. Mehlman G.C. Stevens (1995) ArticleTitleSpatial variation in abundance Ecology 76 2028–2043
K.P. Burnham D.R. Anderson (1998) Model Selection and Inference. A Practical Information-theoretic Approach Springer-Verlag New York, USA
J. Bustamante (1997) ArticleTitlePredictive models for lesser kestrel Falco naumanni distribution, abundance and extinction in southern Spain Biol. Conserv. 80 153–160 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-3207(96)00136-X
C. Calvete (1999) Epidemiología de enfermedad hemorrágica (VHD) y mixomatosis en el conejo silvestre (Oryctolagus cuniculus) en el Valle Medio del Ebro University of Zaragoza ZaragozaSpain
C. Calvete R. Villafuerte J. Lucientes J. Osacar (1997) ArticleTitleEffectiveness of traditional wild rabbit restocking in Spain J. Zool. 241 271–277
J.M. Chambers T.J. Hastie (1993) Statistical Models in S Chapman & Hall London, UK
B.D. Cooke (2002) ArticleTitleRabbit haemorrhagic disease: field epidemiology and the management of wild rabbit populations Rev. Sci. Tech. De L Office Int. Epizoot. 21 347–358
N.C. Coops P.C. Catling (2002) ArticleTitlePrediction of the spatial distribution and relative abundance of ground-dwelling mammals using remote sensing imagery and simulation models Landscape Ecol. 17 173–188 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1016587816997
M. Delibes F. Hiraldo (1981) The rabbit as a prey in the Iberian Mediterranean ecosystem K. Myers C.D. MacInnes (Eds) Proceedings of the World Lagomorph Conference University of Guelph Guelp, OntarioCanada 614–622
G. Dwyer S.A. Levin L. Buttel (1990) ArticleTitleA simulation model of the population dynamics and evolution of myxomatosis Ecol. Monogr. 60 423–447
J.E. Fa C.M. Sharples D.J. Bell D. DeAngelis (2001) ArticleTitleAn individual-based model of rabbit viral haemorrhagic disease in European wild rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) Ecol. Model. 144 121–138 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3800(01)00363-5
N. Fernández M. Delibes F. Palomares D.J. Mladenoff (2003) ArticleTitleIdentifying breeding habitat for the Iberian lynx: inferences from a fine-scale spatial analysis Ecol. Appl. 13 1310–1324
C. Fernández-Delgado (1997) Conservation management of an European Natural Area: Doñana National Park, Spain G.K. Meffe C.R. Carroll (Eds) Principles of Conservation Biology, 2nd ed Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers SunderlandMAUSA 458–467
M. Ferrer (1993) El águila imperial Quercus MadridSpain
R.N. Fisher A.V. Suarez T.J. Case (2002) ArticleTitleSpatial patterns in the abundance of the coastal horned lizard Conserv. Biol. 16 205–215 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-1739.2002.00326.x
C.H. Flather J.R. Sauer (1996) ArticleTitleUsing landscape ecology to test hypotheses about large-scale abundance patterns in migratory birds Ecology 77 28–35
A. Gómez-Sal J.M. Rey-Benayas A. López-Pintor S. Rebollo (1999) ArticleTitleRole of disturbance in maintaining a savanna-like pattern in Mediterranean Retama sphaerocarpa shrubland J. Veget. Sci. 10 365–370
A. Guisan N.E. Zimmermann (2000) ArticleTitlePredictive habitat distribution models in ecology Ecol. Model. 135 147–186 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00354-9
C.M. Hurvich C.L. Tsay (1991) ArticleTitleRegression and time series model selection in small samples Biometrika 76 297–307
InstitutionalAuthorNameInstituto de Cartografía de Andalucía (1999) Mapa Digital de Andalucía 1:100,000 Junta de Andalucía SevillaSpain
A.R. Ives E.D. Klopfer (1997) ArticleTitleSpatial variation in abundance created by stochastic temporal variation Ecology 78 1907–1913
D.H. Johnson (1980) ArticleTitleThe comparison of usage and availability measurements for evaluating resource preference Ecology 61 65–71
H.K. Keitt O.N. Bjørnstand P.M. Dixon S. Citron-Pousty (2002) ArticleTitleAccounting for spatial pattern when modeling organism-environment interactions Ecography 25 616–625 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0587.2002.250509.x
N.B. Kotliar (2000) ArticleTitleApplication of the new keystone-species concept to prairie dogs: how well does it work? Conserv. Biol. 14 1715–1721 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-1739.2000.98384.x
N.B. Kotliar J.A. Wiens (1990) ArticleTitleMultiple scales of patchiness and patch structure: a hierarchical framework for the study of heterogeneity Oikos 59 253–260
J. Letty S. Marchandeau J. Clobert J. Aubineau (2000) ArticleTitleImproving translocation success: an experimental study of anti-stress treatment and release method for wild rabbits Animal Conserv. 3 211–219 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S1367943000000925
J.W. Lichstein T.R. Simons K.E. Franzreb (2002) ArticleTitleLandscape effects on breeding songbird abundance in managed forests Ecol. Appl. 12 836–857
L. Lombardi N. Fernández S. Moreno R. Villafuerte (2003) ArticleTitleHabitat-related differences in rabbit abundancedistribution and activity J. Mammal. 84 26–36 Occurrence Handle10.1644/1545-1542(2003)084<0026:HRDIRO>2.0.CO;2
S. Manel H.C. Williams S.J. Ormerod (2001) ArticleTitleEvaluating presence-absence models in ecology: the need to account for prevalence J. Appl. Ecol. 38 921–931 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2664.2001.00647.x
M.J. Mazerolle M.-A. Villard (1999) ArticleTitlePatch characteristics and landscape context as predictors of species presence and abundance: a review Ecoscience 6 117–124
P. McCullagh J.A. Nelder (1989) Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed Chapman and Hall London, UK
T. Micol C.P. Doncaster L.A. Mackinlay (1994) ArticleTitleCorrelates of local variation in the abundance of hedgehogs Erinaceus europaeus J. Animal Ecol. 63 851–860
C. Montes F. Borja M.A. Bravo J.M. Moreira (Eds) (1998) Reconocimiento biofísico de Espacios Naturales Protegidos. Doñana: una aproximación ecosistémica Junta de AndalucíaConsejería de Medio Ambiente Madrid
J.M. Moreira A. Fernández-Palacios (1995) Usos y coberturas del suelo en Andalucía: seguimiento a través de imágenes de satélite Agencia de Medio AmbienteJunta de Andalucía SevillaSpain
S. Moreno R. Villafuerte (1995) ArticleTitleTraditional management of scrubland for the conservation of rabbits Oryctolagus cuniculus and their predators in Doñana National Park, Spain Biol. Conserv. 73 81–85 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-3207(95)90069-1
J.L. Orrock J.F. Pagels W.J. McShea E.K. Harper (2000) ArticleTitlePredicting presence and abundance of a small mammal species: the effect of scale and resolution Ecol. Appl. 10 1356–1366
R.T. Paine (1992) ArticleTitleFood-web analysis through field measurement of per capita interaction strength Nature 355 73–75 Occurrence Handle10.1038/355073a0
F. Palomares (2001a) ArticleTitleComparison of 3 methods to estimate rabbit abundance in a Mediterranean environment Wildlife Soc. Bull. 29 578–585
F. Palomares (2001b) ArticleTitleVegetation structure and prey abundance requirements of the Iberian lynx: implications for the design of reserves and corridors J. Appl. Ecol. 38 9–18 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2664.2001.00565.x
F. Palomares (2003) ArticleTitleThe negative impact of heavy rains on the abundance of a Mediterranean population of European rabbits Mammal. Biol. 68 224–234
F. Palomares M. Delibes E. Revilla J. Calzada J.M. Fedriani (2001) ArticleTitleSpatial ecology of Iberian lynx and abundance of European rabbits in southwestern Spain Wildlife Monogr. 148 1–36
F. Palomares P. Gaona P. Ferreras M. Delibes (1995) ArticleTitlePositive effects on game species of top predators by controlling smaller predator populations: an example with lynx, mongooses, and rabbits Conserv. Biol. 9 295–305 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-1739.1995.9020295.x
E. Paradis S. Baillie W.J. Sutherland R.D. Gregory (2002) ArticleTitleExploring density–dependent relationships in demographic parameters in populations of birds at large spatial scale Oikos 97 293–307 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0706.2002.970215.x
J. Pearce S. Ferrier (2001) ArticleTitleThe practical value of modelling relative abundance of species for regional conservation planning: a case study Biol. Conserv. 98 33–43 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-3207(00)00139-7
R.P. Pech A.R.E. Sinclair A.E. Newsome P.C. Catling (1992) ArticleTitleLimits to predator regulation of rabbits in Australia: evidence from predator-removal experiments Oecologia 89 102–112 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00319021
A. Rodríguez M. Delibes (1992) ArticleTitleCurrent range and status of the Iberian lynx Felis pardina Temminck 1824 in Spain Biol. Conserv. 61 189–196 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-3207(92)91115-9
P.M. Rogers K. Myers (1979) ArticleTitleEcology of the European wild rabbitOryctolagus cuniculus (L.), in Mediterranean habitats J. Appl. Ecol. 16 691–703
S.P. Rushton D. Hill S.P. Carter (1994) ArticleTitleThe abundance of river corridor birds in relation to their habitats: a modelling approach J. Appl. Ecol. 31 313–328
V. Saab (1999) ArticleTitleImportance of spatial scale to habitat use by breeding birds in riparian forests: a hierarchical analysis Ecol. Appl. 9 135–151
E.W. Schweiger J.E. Diffendorfer R. Pierotti R.D. Holt (1999) The relative importance of small-scale and landscape-level heterogeneity in structuring small mammal distributions G.W. Barret J.D. Peles (Eds) Landscape Ecology of Small Mammals Springer-Verlag Athens, GAUSA 175–207
R.C. Soriguer (1986) ArticleTitleThe rabbit as a plant seed disperser Mammal Rev. 16 197–200
A. Sousa P. García-Murillo (2001) ArticleTitleCan place names be used as indicators of landscape changes? Application to the Doñana Natural Park (Spain) Landscape Ecol. 16 391–406 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1017585101389
J.N. Thompson (1996) ArticleTitleEvolutionary ecology and the conservation of biodiversity Trends Ecol. Evol. 11 300–303 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0169-5347(96)20048-5
Thompson H.V. and King C.M. 1994. The European Rabbit. The History and Biology of a Successful Colonizer. Oxford University Press.
A. Travaini M. Delibes P. Ferreras F. Palomares (1997) ArticleTitleDiversity, abundance or rare species as a target for the conservation of mammalian carnivores: a case study in Southern Spain Biodiv. Conserv. 6 529–535 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1018329127772
W.N. Venables B.D. Ripley (1997) Modern Applied Statistics with S-Plus Springer New York, USA
R. Villafuerte C. Calvete J.C. Blanco J. Lucientes (1995) ArticleTitleIncidence of viral hemorrhagic disease in wild rabbit populations in Spain Mammalia 59 651–659
R. Villafuerte C. Calvete C. Gortázar S. Moreno (1994) ArticleTitleFirst epizootic of rabbit hemorrhagic disease in free living populations of Oryctolagus cuniculus at Doñana National Park, Spain J. Wildlife Dis. 30 176–179
R. Villafuerte A. Lazo S. Moreno (1997) ArticleTitleInfluence of food abundance and quality on rabbit fluctuations: conservation and management implications in Doñana National Park (SW Spain) La Terre et la Vie 52 345–355
J.F. Weltzin S. Archer R.K. Heitschmidt (1997) ArticleTitleSmall-mammal regulation of vegetation structure in a temperate Savanna Ecology 78 751–763
G.C. White R.E. Bennetts (1996) ArticleTitleAnalysis of frequency count data using the negative binomial distribution Ecology 77 2549–2557
J.A. Wiens J.T. Rotenberry B. Van Horne (1987) ArticleTitleHabitat occupancy patterns of North American shrubsteppe birds: the effects of spatial scale Oikos 48 132–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, N. Spatial Patterns in European Rabbit Abundance After a Population Collapse. Landscape Ecol 20, 897–910 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-004-3976-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-004-3976-7