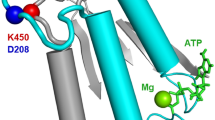
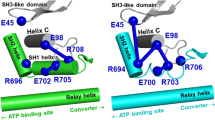
Abstract
Isoforms of the smooth muscle (SM) myosin motor domain differ in the presence or absence of a seven amino acid insert in a flexible surface loop spanning the nucleotide-binding pocket known as Loop 1. The presence of this insert leads to a two-fold increase in actin sliding velocity and ADP release rate between these isoforms, although the effect of Loop 1 on the kinetics of ADP release remains unclear. To further investigate the role of the Loop 1 insert in modulating ADP release in SM myosin we have inserted a single tryptophan residue into Loop 1 of both isoforms as a probe of local structural dynamics. By monitoring the dynamics of Loop 1 in relation to the release of ADP we have observed a unique movement of Loop 1 in the inserted isoform, preceding nucleotide release, which is absent in the non-inserted isoform. This movement is sequence dependent as alanine replacement of the insert residues abolishes the transition and slows ADP release. Thus movement of Loop 1 is a critical factor in increasing the ADP release rate in the inserted faster isoform of SM myosin.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babij P, Kelly C, Periasamy M (1991) Characterization of a mammalian smooth muscle myosin heavy-chain gene: complete nucleotide and protein coding sequence and analysis of the 5′ end of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(23):10676–10680
Bagshaw CR, Trentham DR (1973) The reversibility of adenosine triphosphate cleavage by myosin. Biochem J 133(2):323–328
Bagshaw CR, Trentham DR (1974) The characterization of myosin-product complexes and of product-release steps during the magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase reaction. Biochem J 141(2):331–349
Bagshaw CR, Eccleston JF, Eckstein F, Goody RS, Gutfreund H, Trentham DR (1974) The magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase of myosin. Two-step processes of adenosine triphosphate association and adenosine diphosphate dissociation. Biochem J 141(2):351–364
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brizzard BL, Chubet RG, Vizard DL (1994) Immunoaffinity purification of FLAG epitope-tagged bacterial alkaline phosphatase using a novel monoclonal antibody and peptide elution. Biotechniques 16(4):730–735
Cremo CR, Geeves MA (1998) Interaction of actin and ADP with the head domain of smooth muscle myosin: implications for strain-dependent ADP release in smooth muscle. Biochemistry 37(7):1969–1978. doi:10.1021/bi9722406
Decarreau JA, James NG, Chrin L, Berger CL (2011) Switch I closure simultaneously promotes strong binding to actin and ADP in smooth muscle myosin. JBC. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.219014
De La Cruz EM, Ostap EM (2004) Relating biochemistry and function in the myosin superfamily. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16(1):61–67
De La Cruz EM, Wells AL, Rosenfeld SS, Ostap EM, Sweeney HL (1999) The kinetic mechanism of myosin V. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(24):13726–13731
Eddinger TJ, Meer DP (2001) Single rabbit stomach smooth muscle cell myosin heavy chain SMB expression and shortening velocity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280(2):C309–C316
Greene LE, Sellers JR, Eisenberg E, Adelstein RS (1983) Binding of gizzard smooth muscle myosin subfragment 1 to actin in the presence and absence of adenosine 5′-triphosphate. Biochemistry 22(3):530–535
Hamada Y, Yanagisawa M, Katsuragawa Y, Coleman JR, Nagata S, Matsuda G, Masaki T (1990) Distinct vascular and intestinal smooth muscle myosin heavy chain mRNAs are encoded by a single-copy gene in the chicken. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 170(1):53–58
Johnson KA, Simpson ZB, Blom T (2009a) FitSpace explorer: an algorithm to evaluate multidimensional parameter space in fitting kinetic data. Anal Biochem 387(1):30–41. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2008.12.025
Johnson KA, Simpson ZB, Blom T (2009b) Global kinetic explorer: a new computer program for dynamic simulation and fitting of kinetic data. Anal Biochem 387(1):20–29. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2008.12.024
Jontes JD, Milligan RA, Pollard TD, Ostap EM (1997) Kinetic characterization of brush border myosin-I ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(26):14332–14337
Kelley CA (1997) Characterization of isoform diversity among smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin heavy chains. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 117(1):39–49
Kelley CA, Sellers JR, Goldsmith PK, Adelstein RS (1992) Smooth muscle myosin is composed of homodimeric heavy chains. J Biol Chem 267(4):2127–2130
Kelley CA, Takahashi M, Yu JH, Adelstein RS (1993) An insert of seven amino acids confers functional differences between smooth muscle myosins from the intestines and vasculature. J Biol Chem 268(17):12848–12854
Lauzon AM, Tyska MJ, Rovner AS, Freyzon Y, Warshaw DM, Trybus KM (1998) A 7-amino-acid insert in the heavy chain nucleotide binding loop alters the kinetics of smooth muscle myosin in the laser trap. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 19(8):825–837
Nagai R, Kuro-o M, Babij P, Periasamy M (1989) Identification of two types of smooth muscle myosin heavy chain isoforms by cDNA cloning and immunoblot analysis. J Biol Chem 264(17):9734–9737
Pardee JD, Spudich JA (1982) Purification of muscle actin. Methods Enzymol 85(Pt B):164–181
Parker CA, Reese WT (1960) Correction of fluorescence spectra and measurement of fluorescence quantum efficiency. Analyst 85:587–600
Ritchie MD, Geeves MA, Woodward SK, Manstein DJ (1993) Kinetic characterization of a cytoplasmic myosin motor domain expressed in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(18):8619–8623
Robertson CI, Gaffney DP 2nd, Chrin LR, Berger CL (2005) Structural rearrangements in the active site of smooth-muscle myosin. Biophys J 89(3):1882–1892
Rosenfeld SS (2000) Kinetic and spectroscopic evidence for three actomyosin: ADP states in smooth muscle. J Biol Chem 275(33):25418–25426. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002685200
Rovner AS (2002) The carboxyl-terminal isoforms of smooth muscle myosin heavy chain determine thick filament assembly properties. J Cell Biol 156(1):113–124. doi:10.1083/jcb.200107131
Rovner AS, Murphy RA, Owens GK (1986) Expression of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin heavy chains in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 261(31):14740–14745
Rovner AS, Freyzon Y, Trybus KM (1997) An insert in the motor domain determines the functional properties of expressed smooth muscle myosin isoforms. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 18(1):103–110
Siemankowski RF (1985) ADP dissociation from actomyosin subfragment 1 is sufficiently slow to limit the unloaded shortening velocity in vertebrate muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci 82(3):658–662. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.3.658
Sweeney HL, Rosenfeld SS, Brown F, Faust L, Smith J, Xing J, Stein LA, Sellers JR (1998) Kinetic tuning of myosin via a flexible loop adjacent to the nucleotide binding pocket. J Biol Chem 273(11):6262–6270
Trybus KM (1994) Regulation of expressed truncated smooth muscle myosins. Role of the essential light chain and tail length. J Biol Chem 269(33):20819–20822
Veigel C, Molloy JE, Schmitz S, Kendrick-Jones J (2003) Load-dependent kinetics of force production by smooth muscle myosin measured with optical tweezers. Nat Cell Biol 5(11):980–986. doi:10.1038/ncb1060
Volkmann N, Hanein D, Ouyang G, Trybus KM, DeRosier DJ, Lowey S (2000) Evidence for cleft closure in actomyosin upon ADP release. Nat Struct Biol 7(12):1147–1155. doi:10.1038/82008
White HD (1982) Special instrumentation and techniques for kinetic studies of contractile systems. Methods Enzymol 85(Pt B):698–708
White S, Martin AF, Periasamy M (1993) Identification of a novel smooth muscle myosin heavy chain cDNA: isoform diversity in the S1 head region. Am J Physiol 264(5 Pt 1):C1252–C1258
Yengo CM, Fagnant PM, Chrin L, Rovner AS, Berger CL (1998) Smooth muscle myosin mutants containing a single tryptophan reveal molecular interactions at the actin-binding interface. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(22):12944–12949
Yengo CM, De La Cruz EM, Chrin LR, Gaffney DP, Berger CL (2002) Actin-induced closure of the actin-binding cleft of smooth muscle myosin. J Biol Chem 277(27):24114–24119. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111253200
Acknowledgments
We thank Derrick McVicker and Dr. Andrew Thompson for their technical and intellectual contributions to this project. Also we would like to thank Alan Howard for his assistance with preparation of the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant to C.L.B. from the NIH/NHLBI (HL-63798).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10974_2011_9251_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplemental Fig. 1 Resultant rate constants observed upon the release of mADP (10 µM) from F215W (1 µM), initial concentrations, at two different excitation wavelengths, 295 and 360 nm. (DOC 1034 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Decarreau, J.A., Chrin, L.R. & Berger, C.L. Loop 1 dynamics in smooth muscle myosin: isoform specific differences modulate ADP release. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 32, 49–61 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-011-9251-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-011-9251-z