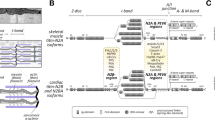
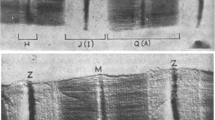
Abstract
The efficient functioning of striated muscle is dependent upon the proper alignment and coordinated activities of several cytoskeletal networks including myofibrils, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. However, the exact molecular mechanisms dictating their cooperation and contributions during muscle differentiation and maintenance remain unknown. Recently, the muscle specific RING finger (MURF) family members have established themselves as excellent candidates for linking myofibril components (including the giant, multi-functional protein, titin/connectin), with microtubules, intermediate filaments, and nuclear factors. MURF-1, the only family member expressed throughout development, has been implicated in several studies as an ubiquitin ligase that is upregulated in response to multiple stimuli during muscle atrophy. Cell culture studies suggest that MURF-1 specifically has a role in maintaining titin M-line integrity and yeast two-hybrid studies point toward its participation in muscle stress response pathways and gene expression. MURF-2 is developmentally down-regulated and is assembled at the M-line region of the sarcomere and with microtubules. Functionally, its expression is critical for maintenance of the sarcomeric M-line region, specific populations of stable microtubules, desmin and vimentin intermediate filaments, as well as for myoblast fusion and differentiation. A recent study also links MURF-2 to a titin kinase-based protein complex that is reportedly activated upon mechanical signaling. Finally, MURF-3 is developmentally upregulated, associates with microtubules, the sarcomeric M-line (this report) and Z-line, and is required for microtubule stability and myogenesis. Here, we focus on the biochemical and functional properties of this intriguing family of muscle proteins, and discuss how they may tie together titin-mediated myofibril signaling pathways (perhaps involving the titin kinase domain), biomechanical signaling, the muscle stress response, and gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antin PB, Forry-Schaudies S, Friedman TM, Tapscott SJ, Holtzer H, (1981) Taxol induces postmitotic myoblasts to assemble interdigitating microtubule-myosin arrays that exclude actin filaments J Cell Biol 90: 300–308
Arya R, Kedar V, Hwang JR, McDonough H, Li H-H,Taylor J, (2004) Muscle ring finger protein-1 inhibits PKCε activation and prevents cardiomyocyte hypertrophyJ Cell Biol 167: 1147–1159
Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach A, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, Witt C, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S, (2001) The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual ∼ ∼700 kDa titin isoform and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking systemCirc Res 89: 1065–1072
Belmadani S, Pous C, Ventura-Clapier R, Fischmeister R, Mery PF, (2002) Post-translational modifications of cardiac tubulin during chronic heart failure in the ratMol Cell Biochem 237: 39–46
Benian GM, Kiff JE, Neckelmann N, Moerman DG, Waterston RH, (1989) Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegansNature 342: 45–50
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK, Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K, Pan ZQ, Valenzuela DM, DeChiara TM, Stitt TN, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ, (2001) Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophyScience 294: 1704–1708
Borden KL, (1998) RING fingers and B-boxes: zinc-binding protein-protein interaction domains Biochem Cell Biol 76: 351–358
Borden KL, (2000) RING domains: master builders of molecular scaffolds? J Mol Biol 295: 1103–1112
Bullard B, Linke WA, Leonard K, (2002) Varieties of elastic protein in invertebrate musclesJ Muscle Res Cell Motil 23: 435–447
Cai D, Frantz JD, Tawa NE, Melendez PA, Oh BC, Lidov HG, hasselgren PO, Frontera WR, Lee J, Glass DJ, Shoelson SE, (2004) IKKbeta/NF-kappaB activation causes severe muscle wasting in miceCell 119: 285–298
Calaghan SC, Le Guennec JY, White E, (2001) Modulation of Ca2+ signaling by microtubule disruption in rat ventricular myocytes and its dependence on the ruptured patch-clamp configuration Circ Res 88: E32–E37
Centner T, Yano J, Kimura E, McElhinny AS, Pelin K, Witt CC, Bang ML, Trombitas K, Granzier H, Gregorio CC, Sorimachi H, Labeit S, (2001) Identification of muscle specific ring finger proteins as potential regulators of the titin kinase domainJ Mol Biol 306: 717–726
Chang W, Webster DR, Salam AA, Gruber D, Prasad A, Eiserich JP, Bulinski JC, (2002) Alteration of the C-terminal amino acid of tubulin specifically inhibits myogenic differentiationJ Biol Chem 277: 30690–30698
Dai KS, Liew CC, (2001) A novel human striated muscle RING zinc finger protein, SMRZ, interacts with SMT3b via its RING domainJ Biol Chem 276: 23992–23999
Dehoux MJ, van Beneden RP, Fernandez-Celemin L, Lause PL, Thissen JP, (2003) Induction of MafBx and Murf ubiquitin ligase mRNAs in rat skeletal muscle after LPS injectionFEBS Lett 544: 214–217
Flaherty DB, Gernert KM, Shmeleva N, Tang X, Mercer KB, Borodovsky M, Benian GM, (2002) Titins in C. elegans with unusual features: coiled-coil domains, novel regulation of kinase activity and two new possible elastic regionsJ Mol Biol 323: 533–549
Franch HA, Price SR, (2005) Molecular signaling pathways regulating muscle proteolysis during atrophyCurr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 8:271–275
Freemont PS, (2000) RING for destruction?Curr Biol 10: R84–R87
Gill G, (2004) SUMO and ubiquitin in the nucleus: different functions, similar mechanisms?Genes Dev 18: 2046–2059
Gomez AM, Kerfant BG, Vassort G, (2000) Microtubule disruption modulates Ca(2+) signaling in rat cardiac myocytesCirc Res 86: 30–36
Gotthardt M, Hammer RE, Hubner N, Monti J, Witt CC, McNabb M, Richardson JA, Granzier H, Labeit S, Herz J, (2003) Conditional expression of mutant M-line titins results in cardiomyopathy with altered sarcomere structureJ Biol Chem 278: 6059–6065
Granzier H, Labeit S, (2002) Cardiac titin: an adjustable multi-functional springJ Physiol 541: 335–342
Granzier HL, Labeit S, (2004) The giant protein titin: a major player in myocardial mechanics, signaling, and diseaseCirc Res 94: 284–295
Gregorio CC, Fowler VM, (1995) Mechanisms of thin filament assembly in embryonic chick cardiac myocytes: Tropomodulin requires tropomyosin for assemblyJ Cell Biol 129: 683–695
Gregorio CC, Trombitas K, Centner T, Komerer B, Stier G, Kunke K, Suzuki K, Obermayr F, Hermann B, Granzier H, Sorimachi H, Labeit S, (1998) The NH2 terminus of titin spans the Z-disc: its interaction with a novel 19-kDa ligand (T-cap) is required for sarcomeric integrityJ Cell Biol 143: 1013–1027
Gundersen GG, Khawaja S, Bulinski JC, (1989) Generation of a stable, posttranslationally modified microtubule array is an early event in myogenic differentiationJ Cell Biol 109: 2275–2288
Gurland G, Gundersen GG, (1995) Stable, detyrosinated microtubules function to localize vimentin intermediate filaments in fibroblastsJ Cell Biol 131: 1275–1290
Gustafson TA, Bahl JJ, Markham BE, Roeske WR, Morkin E, (1987) Hormonal regulation of myosin heavy chain and alpha-actin gene expression in cultured fetal rat heart myocytesJ Biol Chem 262: 13316–13322
Gyoeva FK, Gelfand VI, (1991) Coalignment of vimentin intermediate filaments with microtubules depends on kinesinNature 353: 445–448
Ikeda K, Emoto N, Matsuo M, Yokoyama M, (2003) Molecular identification and characterization of a novel nuclear protein whose expression is up-regulated in insulin-resistant animalsJ Biol Chem 278: 3514–3520
Jeyaseelan R, Poizat C, Baker RK, Abdishoo S, Isterabadi LB, Lyons GE, Kedes L, (1997) A novel cardiac-restricted target for doxorubicin. CARP, a nuclear modulator of gene expression in cardiac progenitor cells and cardiomyocytesJ Biol Chem 272: 22800–22808
Kano Y, Fujimaki N, Ishikawa H, (1991) The distribution and arrangement of microtubules in mammalian skeletal muscle fibersCell Struct Funct 16: 251–261
Kedar V, McDonough H, Arya R, Li H-H, Rockman HA, Patterson C, (2004) Muscle-specific RING finger 1 is a bona fide ubiquitin ligase that degrades cardiac troponin IPNAS 101:18135–18140
Kemp TJ, Sadusky TJ, Saltisi F, Carey N, Moss J, Yang SY, (2000) Identification of Ankrd2, a novel skeletal muscle gene coding for a stretch-responsive ankyrin-repeat proteinGenomics 66: 229–241
Kerfant BG, Vassort G, Gomez AM, (2001) Microtubule disruption by colchicine reversibly enhances calcium signaling in intact rat cardiac myocytesCirc Res 88: E59–E65
Klein I, (1983) Colchicine stimulates the rate of contraction of heart cells in cultureCardiovasc Res 17: 459–465
Labeit S, Kolmerer B, (1995) Titins, giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticityScience 270: 293–296
Labeit S, Gautel M, Lakey A, Trinick J, (1992) Towards a molecular understanding of titin EMBO J 11: 1711–1716
Lange S, Xiang F, et al. (2005) The kinase domain of titin controls muscle gene expression and protein turnover. Science: ScienceExpress
Latres E, Amini AR, Amini AA, Griffiths J, Martin FJ, Wei Y, Lin HC, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ, (2005) IGF-1 inversely regulates atrophy-induced genes via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (P13K/Akt/TOR) pathwayJ Biol Chem 280: 2737–2744
Lecker SH, (2003) Ubiquitin-protein ligases in muscle wasting: multiple parallel pathways?Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 6: 271–275
Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Gilbert A, Gomes M, Baracos V, Bailey J, Price SR, Mitch WE, Goldberg AL, (2004) Multiple types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of changes in gene expressionFASEB J 18: 39–51
Linke WA, Granzier H, (1998) A spring tale: new facts on titin elasticityBiophys J 75: 2613–2614
Maruyama K, Matsubara R, Natori Y, Nonomura S, Kimura S, (1977) Connectin, an elastic protein of muscleJ Biochem 82: 317–337
McElhinny AS, Kakinuma K, Sorimachi H, Labeit S, Gregorio CC, (2002) Muscle-specific RING finger-1 interacts with titin to regulate sarcomeric M-line and thick filament structure and may have nuclear functions via its interaction with glucocorticoid modulatory element binding protein-1J Cell Biol 157: 125–136
McElhinny AS, Perry CN, Witt C, Labeit S, Gregorio CC, (2004) Muscle specific RING finger-2 (MURF-2) has multiple subcellular localizations and is required for microtubule, intermediate filament, and sarcomeric M-line maintenance in striated muscleJ Cell Sci 117: 3175–3188
Melchior F, (2000) SUMO–nonclassical ubiquitinAnnu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16: 591–626
Melchior F, Schergaut M, Pichler A, (2003) SUMO: ligases, isopeptidases and nuclear pores Trends Biochem Sci 28: 612–618
Miller M, Bang ML, Witt CC, Labeit D, Trombitas C, Watanabe K, Granzier H, McElhinny AS, Gregorio CC, Labeit S, (2003) The muscle ankyrin repeat proteins: CARP/ankrd2/DARP as a family of titin filament based stress response moleculesJ Mol Biol 333: 951–964
Miller MK, Granzier H, Ehler E, Gregorio CC, (2004) The sensitive giant: the role of titin-based stretch sensing complexes in the heartTrends Cell Biol 14: 119–126
Mues A, van der Ven PF, Young P, Furst DO, Gautel M, (1998) Two immunoglobulin-like domains of the Z-disc portion of titin interact in a conformation-dependent way with telethoninFEBS Lett 428: 111–114
Nikawa T, Ishidoh K, Hirasaka K, Ishihara I, Ikemoto M, Kano M, Kominami E, Nonaka I, Ogawa T, Adams GR, Baldwin KM, Yasui N, Kishi K, Takeda S, (2004) Skeletal muscle gene expression in space-flown ratsFASEB J 18: 522–524
Obermann WM, Gautel M, Weber K, Fürst DO, (1997) Molecular structure of the sarcomeric M band: mapping of titin and myosin binding domains in myomesin and the identification of a potential regulatory phosphorylation site in myomesinEMBO J 16: 211–220
Olson NJ, Pearson RB, Needleman DS, Hurwitz MY, Kemp BE, Means AR, (1990) Regulatory and structural motifs of chicken gizzard myosin light chain kinaseProc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 2284–2288
Perhonen M, Sharp WW, Russell B, (1998) Microtubules are needed for dispersal of alpha-myosin heavy chain mRNA in rat neonatal cardiac myocytesJ Mol Cell Cardiol 30: 1713–1722
Pizon V, Iakovenko A, van Der Ven PF, Kelly R, Fatu C, Furst DO, Karsenti E, Gautel M, (2002) Transient association of titin and myosin with microtubules in nascent myofibrils directed by the MURF2 RING-finger proteinJ Cell Sci 115: 4469–4482
Sacheck JM, Ohtsuka A, McLary SC, Goldberg AL, (2004) IGF-1 stimulates muscle growth by suppressing protein breakdown and expression of atrophy-related ubiquitin ligases, atrogin-1 and MURF1Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287: E591–E601
Saitoh O, Arai T, Obinata T, (1988) Distribution of microtubules and other cytoskeletal filaments during myotube elongation as revealed by fluorescence microscopyCell Tissue Res 252: 263–273
Saitoh H, Hinchey J, (2000) Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3J Biol Chem 275: 6252–6258
Sanger JW, Sanger JM, (2001) Fishing out proteins that bind to titinJ Cell Biol 154: 21–24
Sorimachi H, Kinbara K, Kimura S, Takahashi M, Ishiura S, Sasagawa N, Sorimachi N, Shimada H, Tagawa K, Maruyama K, (1995) Muscle-specific calpain responsible for limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, associates with connectin through IS2, a p94-specific sequenceJ Biol Chem 270: 31158–31162
Southgate A, Vigoreaux J, Benian G, Pardue ML, (1991) Drosophila has a twitchin/titin-related gene that appears to encode projectinProc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 7973–7977
Spencer JA, Eliazer S, Ilaria RL, Jr Richardson JA, Olson EN, (2000) Regulation of microtubule dynamics and myogenic differentiation by MURF, a striated muscle RING-finger protein J Cell Biol 150: 771–784
Stitt TN, Drujan D, Clarke BA, Panaro F, Timofeyva Y, Kline WO, Gonzalez M, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ, (2004) The IGF-1/P13K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription factorsMol Cell 14: 395–403
Takahashi M, Tsutsui H, Tagawa H, Igarashi-Saito K, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Takeshita A, (1998) Microtubules are involved in early hypertrophic responses of myocardium during pressure overloadAm J Physiol 275: H341–H348
Toyama Y, Forry-Schaudies S, Hoffman B, Holtzer H, (1982) Effects of taxol and Colcemid on myofibrillogenesisProc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 6556–6560
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J, (2003) Titin: properties and family relationshipsNat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 679–689
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J, (2004) Properties of titin immunoglobulin and fibronectin-3 domains J Biol Chem 279: 46351–46354
Tsutsui H, Ishihara K, Cooper GT, (1993) Cytoskeletal role in the contractile dysfunction of hypertrophied myocardiumScience 260: 682–687
Wang K., McClure J, Tu A, (1979) Titin: major myofibrillar components of striated muscle Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 76:3698–3702
Webster DR, (1997) Regulation of post-translationally modified microtubule populations during neonatal cardiac developmentJ Mol Cell Cardiol 29: 1747–1761
Wu SH, Granzier H, Witt CC, Labeit S, (2005) MURF-1 and MURF-2 target a specific subset of myofibrillar proteins redundantly: towards understanding MURF-dependent muscle ubiquitinationJ Mol Biol 350: 713–722
Young P, Ehler E, Gautel M, (2001) Obscurin, a giant sarcomeric Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor protein involved in sarcomere assemblyJ Cell Biol 154: 123–136
Zou Y, Evans S, Chen J, Kuo HC, Harvey RP, Chien KR, (1997) CARP, a cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, is downstream in the Nkx2–5 homeobox gene pathwayDevelopment 124: 793–804
Acknowledgments
This article was written in memory of Dr. Koscak Maruyama. The authors would like to thank Siegfried Labeit for providing MURF-3 cDNA and for insightful editorial comments, and Sarah Mount-Patrick and Catherine Schwach for assistance in preparing the figures. This study was funded by grants from the NIH (HL63926) and (HL57461) to C.C.G., the American Heart Association (0435316N) to A.S.M., and a HHMI grant (71195-521304) to the University of Arizona for undergraduate biology research funding to C.N.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregorio, C.C., Perry, C.N. & McElhinny, A.S. Functional properties of the titin/connectin-associated proteins, the muscle-specific RING finger proteins (MURFs), in striated muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26, 389–400 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9021-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9021-x