Abstract
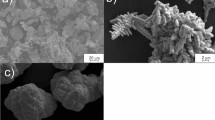
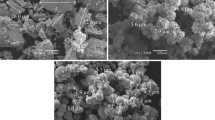
Due to their high hardness, excellent redox ability, good corrosion resistance and catalytic abilities, the materials with high content of crystalline Ni3P phase are promising candidates for application in various fields. In this work, amorphous and amorphous/nanocrystalline Ni–P powder alloys-precursors were prepared by chemical reduction, and further subjected to crystallization process to obtain Ni3P-rich alloys. Two different Ni–P alloys-precursors (“1” and “2”) were prepared using different reactant ratios. Applying DTA and XRD techniques, the range of thermal stability and thermally induced microstructural transformations of individual Ni–P alloys (precursors of Ni3P-rich alloys) were studied. SEM analysis allowed evaluation of particle size distribution for individual Ni–P samples. Microstructure of the as-prepared and thermally treated samples and mechanism of thermally induced transformations, including the phase composition of completely crystallized material, exhibited significant dependence on the reactant ratio used in the synthesis. Kinetic triplets of individual crystallization steps were deduced by processing the DTA curves, including deconvolution of complex crystallization peaks. Although exhibiting somewhat higher Ni3P crystallization Ea than the Ni–P alloy 1, the Ni–P alloy 2, obtained by use of larger amount of the reducing agent, gave greater content of the Ni3P phase in the crystallized material, around 90% (mass).
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diegle RB, Sorensen NR, Clayton CR, Helfand MA, Yu YC. An XPS investigation into the passivity of an amorphous Ni-20P alloy. J Electrochem Soc. 1988;135:1085–92.
Shozib IA, Ahmad A, Abdul-Rani AM, Beheshti M, Aliyu AA. A review on the corrosion resistance of electroless Ni-P based composite coatings and electrochemical corrosion testing methods. Corros Rev. 2022;40:1–37.
Jeong DH, Erb U, Aust KT, Palumbo G. The relationship between hardness and abrasive wear resistance of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Ni–P coatings. Scr Mater. 2003;48:1067–72.
Bakonyi I, Burgstaller A, Socher W, Voitländer J, Tóth-Kádár E, Lovas A, Ebert H, Wachtel E, Willmann N, Liebermann HH. Magnetic properties of electrodeposited, melt-quenched, and liquid Ni-P alloys. Phys Rev B. 1993;47:14961–76.
Shibli SMA, Anupama VR, Arun PS, Jineesh P, Suji L. Synthesis and development of nano WO3 catalyst incorporated Ni-P coating for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2016;41:10090–102.
Tian M, Jian Z, Hai R, Chang F. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of amorphous electroless nickel-phosphorus alloy plating. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2023;148:1959–70.
Agarwala RC, Agarwala V. Electroless alloy/composite coatings: a review. Sadhana. 2003;28:475–93.
Naderi J, Sarhan AAD. Measure and evaluate the hardness of the electrodeposited nickel-phosphorous (Ni-P) thin film coating on carbon steel alloy for automotive applications. Measurement. 2019;139:490–7.
Gao S, Wu C, Yang X, Cheng J, Kang R. Study on adhesion properties and process parameters of electroless deposited Ni-P alloy for PEEK and its modified materials. Coatings. 2023;13:388.
Samanta S, Singh C, Banerjee A, Mondal K, Dutta M, Singh SB. Development of amorphous Ni-P coating over API X70 steel for hydrogen barrier application. Surf Coat Technol. 2020;403:126356.
Deng J, Yang J, Sheng S, Chen H, Xiong G. The study of ultrafine Ni-B and Ni-P amorphous alloy powders as catalysts. J Catal. 1994;150:434–8.
Suryanarayana C, Inoue A. Iron-based bulk metallic glasses. Int Mater Rev. 2013;58:131–66.
Zhang H, Yan ZC, Chen Q, Feng Y, Qi ZG, Liu HZ, Li XY, Wang WM. Hardness, magnetism and passivation of Fe-Si-B-Nb glasses. J Non Cryst Solids. 2021;564:120830.
Wu Y, Zhang Z, Xu K, Dai X, Zhu H, Ni T, Liu Y. Amorphous Ni-P coating modified by laser remelting: the effect of remelted crystallization layer on microhardness and wear resistance. Tribol Int. 2022;176:107884.
Lee SP, Chen YW. Nitrobenzene hydrogenation on Ni–P, Ni–B and Ni–P–B ultrafine materials. J Mol Catal A Chem. 2000;152:213–23.
Liebermann HH. Sample preparation: methods and process characterization. In: Luborsky FE, editor. Amorphous metallic alloys. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1983. p. 26–41.
Liu Y, Niu S, Li F, Zhu Y, He Y. Preparation of amorphous Fe-based magnetic powder by water atomization. Powder Technol. 2011;213:36–40.
Ji SJ, Sun JC, Yu ZW, Hei ZK, Yan L. On the preparation of amorphous Mg–Ni alloys by mechanical alloying. Int J Hydrog Energy. 1999;24:59–63.
Russew K, Stojanova L. Most important methods for production of amorphous metallic alloys. In: Glassy metals. Berlin: Springer; 2016. p. 9–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-47882-0_2.
Chen Y. Chemical preparation and characterization of metal-metalloid ultrafine amorphous alloy particles. Catal Today. 1998;44:3–16.
Minić DG, Blagojević VA, Mihajlović LE, Ćosović VR, Minić DM. Kinetics and mechanism of structural transformations of Fe75Ni2Si8B13C2 amorphous alloy induced by thermal treatment. Thermochim Acta. 2011;519:83–9.
Gleiter H. Nanocrystalline materials. Prog Mater Sci. 1989;33:223–315.
Du SW, Ramanujan RV. Crystallization and magnetic properties of Fe40Ni38B18Mo4 amorphous alloy. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2005;351:3105–13.
Keong KG, Sha W. Crystallisation and phase transformation behavior of electroless nickel-phosphorus deposits and their engineering properties. Surf Eng. 2002;18:329–43.
Kumar PS, Nair PK. Studies on crystallization of electroless Ni–P deposits. J Mater Process Tech. 1996;56:511–20.
Staia MH, Puchi ES, Castro G, Ramirez FO, Lewis DB. Effect of thermal history on the microhardness of electroless Ni–P. Thin Solid Films. 1999;355–6:472–9.
Hur KH, Jeong JH, Lee DN. Microstructures and crystallization of electroless Ni–P deposits. J Mater Sci. 1990;25:2573–84.
Zhao X, Chen X, Wang Y, Song P, Zhang Y. High-efficiency Ni–P catalysts in amorphous and crystalline states for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Sustain Energy Fuels. 2020;4:4733–42.
Osaka T, Usuda M, Koiwa I, Sawai H. Effect of phosphorus content on the magnetic and electric properties of electroless Ni–P film after heat treatment. Jpn J Appl Phys. 1988;27:1885–9.
Hamada AS, Sahu P, Porter DA. Indentation property and corrosion resistance of electroless nickel-phosphorus coatings deposited on austenitic high-Mn TWIP steel. Appl Surf Sci. 2015;356:1–8.
Wang SL. Studies of electroless plating of Ni–Fe–P alloys and the influences of some deposition parameters on the properties of the deposits. Surf Coat Technol. 2004;186:372–6.
Czagány M, Baumli P, Kaptay G. The influence of the phosphorous content and heat treatment on the nano-micro-structure, thickness and micro-hardness of electroless Ni–P coatings on steel. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;423:160–9.
Šušić MV, Uskoković DP. Crystallization kinetics of amorphous Ni78P22 powders and hydrogen adsorption on both amorphous and crystal alloy powders. J Mater Sci. 1988;23:4076–80.
Keong KG, Sha W, Malinov S. Crystallization and phase transformation behaviour of electroless nickel-phosphorus deposits with low and medium phosphorus contents under continuous heating. J Mater Sci. 2002;37:4445–50.
Krasteva N, Fotty V, Armyanov S. Thermal stability of Ni–P and Ni–Cu–P amorphous alloys. J Electrochem Soc. 1994;141:2864–7.
Sun P, Qiu M, Huang J, Zhao J, Chen L, Fu Y, Cui G, Tong Y. Scalable three-dimensional Ni3P-based composite networks for flexible asymmertric supercapacitors. Chem Eng J. 2020;380:122621.
Kamboj N, Dey RS. Electrochemically grown highly crystalline single-phase Ni3P superstructure accelerating ionic diffusion in rechargeable Ni–Zn battery. J Power Sour. 2021;512:230527.
Laursen AB, Wexler RB, Whitaker MJ, Izett EJ, Calvinho KUD, Hwang S, Rucker R, Wang H, Li J, Garfunkel E, Greenblatt M, Rappe AM, Dismukes GC. Climbing the volcano of electrocatalytic activity while avoiding catalyst corrosion: Ni3P, a hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst stable in both acid and alkali. ACS Catal. 2018;8:4408–19.
Zhu J, Cao L, Li C, Zhao G, Zhu T, Hu W, Sun W, Lu Y. Nanoporous Ni3P evolutionarily structured onto a Ni foam for highly selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:37635–43.
Yu Z, Wang Y, Sun Z, Li X, Wang A, Camaioni DM, Lercher JA. Ni3P as a high-performance catalytic phase for hydrodeoxygenation of phenolic compounds. Green Chem. 2018;20:609–19.
Minić DM, Šušić MV. Thermal behaviour of 82Ni-18P amorphous powder alloy in hydrogen atmosphere. Mater Chem Phys. 1995;40:281–4.
ICSD Inorganic Crystals Structure Database, Release 2014/2, FIZ Karlsruhe, Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen, Germany.
Lutterotti L. Total pattern fitting for the combined size-strainstress-texture determination in thin film diffraction. Nucl Instrum Meth B. 2010;268:334–40.
Scherrer P. Bestimmung der grösse und der inneren struktur von kolloidteilchen mittels röntgenstrahlen. Göttinger Nachrichten Math Phys. 1918;2:98–100.
Ortega A. A simple and precise linear integral method for isoconversional data. Thermochim Acta. 2008;474:81–6.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38:1881–6.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. Polym Lett. 1966;4:323–8.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29:1702–6.
Akahira T, Sunose T. Trans. joint convention of four electrical Institutes, paper no. 246, 1969 research report, Chiba Institute of Technology. J Sci Educ Technol. 1971;16:22–31.
Kaloshkin SD, Tomilin IA. The crystallization kinetics of amorphous alloys. Thermochim Acta. 1996;280(281):303–17.
Málek J. Kinetic analysis of crystallization processes in amorphous materials. Thermochim Acta. 2000;355:239–53.
Johnson WA, Mehl KF. Reaction kinetics in processes of nucleation and growth. Trans Am Inst Min (Metall) Eng. 1939;135:416–42.
Avrami M. Granulation, phase change, and microstructure—kinetics of phase change III. J Chem Phys. 1941;7:177–84.
Kolmogorov AN. On the statistical theory of the crystallization of metals. Bull Acad Sci USSR. 1937;1:355–9.
Vasić M, Minić DM, Blagojević VA, Minić DM. Mechanism of thermal stabilization of Fe89.8Ni1.5Si5.2B3C0.5 amorphous alloy. Thermochim Acta. 2013;562:35–41.
Vasić MM, Žák T, Minić DM. Kinetics and influence of thermally induced crystallization of Fe, Ni-containing phases on thermomagnetic properties of Fe40Ni40B12Si8 amorphous alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147:3543–51.
Vasić MM, Surla R, Minić DM, Radović LJ, Mitrović N, Maričić A, Minić DM. Thermally induced microstructural transformations of Fe72Si15B8V4Cu1 alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2017;48:4393–402.
Šesták J, Berggren G. Study of the kinetics of the mechanism of solid-state reactions at increasing temperatures. Thermochim Acta. 1971;3:1–12.
Vasić MM, Blagojević VA, Begović NN, Žák T, Pavlović VB, Minić DM. Thermally induced crystallization of amorphous Fe40Ni40P14B6 alloy. Thermochim Acta. 2015;614:129–36.
Criado JM, Malek J, Ortega A. Applicability of the master plots in kinetic analysis of non-isothermal data. Thermochim Acta. 1989;147:377–85.
Perez-Maqueda LA, Criado JM, Gotor FJ, Malék J. Advantages of combined kinetic analysis of experimental data obtained under any heating profile. J Phys Chem A. 2002;106:2862–8.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, Pérez-Maqueda LA, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC kinetics committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia (contract No. 451-03-47/2023-01/200146). The authors would like to sincerely thank Prof. Dr. Slavko Mentus (Faculty of Physical Chemistry, University of Belgrade, Serbia) for recording the DTA curves, Prof. Nemanja Gavrilov (Faculty of Physical Chemistry, University of Belgrade, Serbia) for performing SEM-EDS measurements, and Ing. Pavla Roupcová, PhD (Institute of Physics of Materials CAS, Brno, Czech Republic) for help with the XRD measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. M. Vasić: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing, Visualization. D. M. Minić: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vasić, M.M., Minić, D.M. Kinetics of crystallization of Ni3P phase from amorphous Ni–P powder alloy precursors for preparation of Ni3P-rich alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13242-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13242-0