Abstract
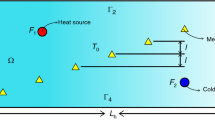
In this paper, the inverse heat transfer problem is studied in a two-dimensional cross-section of a horizontal pipe to estimate the unknown time-varying fluid temperature close to the inner wall of the pipe. The uneven mixing of fluids at different temperatures leads to temperature fluctuations in the inner wall of the pipeline, which could result in wall stress changes and structural thermal fatigue. An inversion algorithm based on the ant lion optimizer-salp swarm algorithm (ALO-SSA) is proposed. The temperature data are utilized as input data for the inverse heat transfer problem (IHCP). The fluid temperature fluctuations are most dramatic near the inner wall at 0° and 30°. ALO-SSA algorithm exhibits significantly lower average error compared to the other two contrasting algorithms, with an estimated average error of 0.0395 at 0° and 0.0413 at 30° for temperature estimation. Experimental analysis showed that the algorithm has good speed and accuracy for solving similar inverse heat transfer problems.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T :
-
Temperature
- r :
-
Radius
- θ :
-
Angle
- τ :
-
Time
- ∆τ :
-
Time step
- ρ :
-
Density
- c :
-
Specific heat capacity
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity
- n :
-
Normal vector
- h f,in :
-
Inner convection heat transfer coefficient
- h f,out :
-
Outer convection heat transfer coefficient
- T f,in :
-
Fluid temperature
- T f,out :
-
Ambient temperature
- T w :
-
Wall temperature
- T 0 :
-
Initial temperature of the pipe
- J :
-
Wall temperature
- T Est,m,n :
-
Estimated temperature
- T Exp,m,n :
-
Experimental temperature
- N :
-
Population size
- D :
-
Dimension
- X :
-
Population position of ant
- Fitness (x):
-
Fitness function
- t :
-
Current number of iterations
- i :
-
The ith individual
- I :
-
Proportion of traps
- X_AL:
-
Population position of ant lion
- X best :
-
Optimal individual
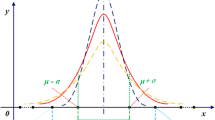
- μ :
-
Chaos parameter
- ub:
-
Upper bound
- lb:
-
Lower bound
- I_real:
-
Real iteration
- I_current:
-
Current iteration
- I_factor:
-
Iteration factor
- I_MAX:
-
Max iteration
- F j :
-
Optimal position
- c 1 c 2 c 3 :
-
Random numbers
- j :
-
jth individual
- IHCP:
-
Inverse heat conduction problem
- DHCP:
-
Direct heat conduction problem
- ALO:
-
Ant lion optimizer
- SSA:
-
Salp swarm algorithm
References
Jo B, Erkan N, Takahashi S, Song D, Sagawa W, Okamoto K. Thermal stratification in a scaled-down suppression pool of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants. Nucl Eng Des. 2016;305:39–50.
Kim JH, Roidt RM, Deardorff AF. Thermal stratification and reactor piping integrity. Nucl Eng Des. 1993;139(1):83–95.
Ali MY, Wu G, Liu S, Jin M, Zhao Z, Wu Y. CFD Analysis of thermal stratification under PLOFA transient in CLEAR-S. Prog Nucl Energy. 2019;115:21–9.
Boros I, Aszodi A. Analysis of thermal stratification in the primary circuit of a VVER-440 reactor with the CFX code. Nucl Eng Des. 2008;238(3):453–9.
Wang S, Ni R. Solving of two-dimensional unsteady-state heat-transfer inverse problem using finite difference method and model prediction control method. Complexity. 2019;2019(7):1–12.
Lu T, Liu B, Jiang PX. A two-dimensional inverse heat conduction problem in estimating the fluid temperature in a pipeline. Appl Therm Eng. 2010;30(13):1574–9.
Lu T, Liu B, Jiang PX. Inverse estimation of the inner wall temperature fluctuations in a pipe elbow. Appl Therm Eng. 2011;31(11–12):1976–82.
Han WW, Chen HB, Lu T. Estimation of the time-dependent convective boundary condition in a horizontal pipe with thermal stratification based on inverse heat conduction problem. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;132:723–30.
Wikström P, Blasiak W, Berntsson F. Estimation of the transient surface temperature and heat flux of a steel slab using an inverse method. Appl Therm Eng. 2007;27(14–15):2463–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2007.02.005.
Lu T, Han WW, Jiang PX, Zhu YH, Wu J, Liu CL. A two-dimensional inverse heat conduction problem for simultaneous estimation of heat convection coefficient, fluid temperature and wall temperature on the inner wall of a pipeline. Prog Nucl Energy. 2015;81(may):161–8.
Xie T, He Y-L, Tong Z-X, Yan W-X, Xie X-Q. An inverse analysis to estimate the endothermic reaction parameters and physical properties of aerogel insulating material. Appl Therm Eng. 2015;87:214–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.05.008.
Cebula A, Taler J. Determination of transient temperature and heat flux on the surface of a reactor control rod based on temperature measurements at the interior points. Appl Therm Eng. 2014;63(1):158–69.
Qi H, Ruan LM, Zhang HC, Wang YM, Tan HP. Inverse radiation analysis of a one-dimensional participating slab by stochastic particle swarm optimizer algorithm. Int J Therm Sci. 2007;46(7):649–61.
Czel B, Grof G. Inverse identification of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity via genetic algorithm with cost function-based rearrangement of genes. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55(15–16):4254–63.
Yang YC, Chen WL. A nonlinear inverse problem in estimating the heat flux of the disc in a disc brake system. Appl Therm Eng. 2011;31(14–15):2439–48.
Liu FB. Particle Swarm Optimization-based algorithms for solving inverse heat conduction problems of estimating surface heat flux. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55(7–8):2062–8.
Yang Z, Liu M, Luo X. First-optimize-then-discretize strategy for the parabolic PDE constrained optimization problem with application to the reheating furnace. IEEE Access. 2021;9:90283–94.
Han W, Lu T, Chen H. Sensitivity analysis about transient three-dimensional IHCP with multi-parameters in an elbow pipe with thermal stratification. IEEE Access. 2019;7:146791–800.
Cui M, Duan W, Gao X. A new inverse analysis method based on a relaxation factor optimization technique for solving transient nonlinear inverse heat conduction problems. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;90:491–8.
Cui M, Yang K, Xu X-l, Shengdong W, Gao X. A modified Levenberg Marquardt algorithm for simultaneous estimation of multi-parameters of boundary heat flux by solving transient nonlinear inverse heat conduction problems. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;97:908–16.
Wang S, Deng Y, Sun X. Solving of two-dimensional unsteady inverse heat conduction problems based on boundary element method and sequential function specification method. Complexity. 2018;2018:1–11.
Wang S, Zhang L, Sun X, Jia H. Solution to two-dimensional steady inverse heat transfer problems with interior heat source based on the conjugate gradient method. Math Probl Eng. 2017;2017:1–9.
Wan S, Wang K, Xu P, Huang Y. Numerical and experimental verification of the single neural adaptive PID real-time inverse method for solving inverse heat conduction problems. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2022;189:122657.
Oommen V, Srinivasan B. Solving inverse heat transfer problems without surrogate models: a fast, data-sparse, physics informed neural network approach. J Comput Inf Sci Eng. 2022;4:22.
Oliveira AVS, Avrit A, Gradeck M. Thermocouple response time estimation and temperature signal correction for an accurate heat flux calculation in inverse heat conduction problems. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2022;185:122398.
Sajedi R, Faraji J, Kowsary F. A new damping strategy of Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm with a fuzzy method for inverse heat transfer problem parameter estimation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;126(2):105433.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Song, J., Peng, G. et al. A novel ant lion optimizer-salp swarm algorithm for inverse heat conduction problem in pipeline fluid temperature recognition. J Therm Anal Calorim 149, 173–185 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12743-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12743-8