Abstract
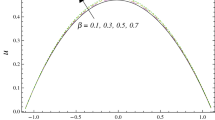
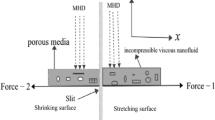
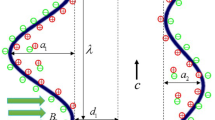
The aim of this study is to explore the effects of radiative-induced magneto-Prandtl nanofluid on peristaltic waves, in conjunction with viscous dissipation and double-diffusivity convection caused by slip boundaries over an asymmetric channel, using the long wavelength and low but finite Reynold number approximation. The application of thermal radiation and double diffusion is significant in medical research, particularly for treating skin-related ailments through the use of infrared radiation technique. Additionally, infrared radiation can be utilized for medical treatment to restore thermal regulation homeostasis. This study integrates peristaltic motion theory, heat flux using linear approximation, and thermal radiation to analyze the flow problem which incorporates the situation with small temperature difference. The mathematical framework is based on partial differential equations that are further calculated through Numerical Solutions. The numerical solution is calculated using built-in command in the software Mathematica 11 and MATLAB. The impact of various physical parameters on the temperature profile, pressure rise, velocity profile, solute (species) concentration of thermal radiation is illustrated graphically. The significant finding of the study is that the heat radiation effect on blood circulation enhances the temperature which may help to destroy the cancer tissues in drug distribution.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu QY, Zhuang YJ, Yu HZ. Entropy generation due to three-dimensional double-diffusive convection of power-law fluids in heterogeneous porous media. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;106:61–82.
Eid MR, Mabood F, Mahny KL. On 3D Prandtl nanofluid flow with higher-order chemical reaction. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci. 2021;235:3962–74.
Elmaboud YA, Abdelsalam SI. DC/AC magnetohydrodynamic-micropump of a generalized Burger’s fluid in an annulus. Phys Scr. 2019;94:115209.
Khan MI, Qayyum S, Hayat T, Alsaedi A. Investigation of Sisko fluid through entropy generation. J Mol Liq. 2018;257:155–63.
Amanulla CH, Saleem S, Wakif A, Al Qarni MM. MHD Prandtl fluid flow past an isothermal permeable sphere with slip effects. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2019;14:100447.
Eid MR, Mahny KL, Al-Hossainy AF. Homogeneous-heterogeneous catalysis on electromagnetic radiative Prandtl fluid flow: Darcy-Forchheimer substance scheme. Surf Interfaces. 2021;24:101119.
Ullah Z, Zaman G, Ishak A. Magnetohydrodynamic tangent hyperbolic fluid flow past a stretching sheet. Chin J Phys. 2020;66:258–68.
Latham TW. Fluid Motions in a peristaltic pump, M.Sc. Thesis, MIT, Cambridge;1966.
Shapiro AH, Jaffrin MY, Weinberg SL. Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number. Cambridge Uni Press. 1969;37:799–825.
Jaffrin MY, Shapiro AH. Peristaltic pumping. Annu Rev Fluid Mech. 1971;3:13–36.
Vajravelu K, Sreenadh S, Devaki P, Prasad KV. Mathematical model for a Herschel-Bulkley fluid flow in an elastic tube. Cent Eur J Phys. 2011;9:1357–65.
Akbar NS, Nadeem S, Lee C. Peristaltic flow of a Prandtl fluid model in an asymmetric channel. Int J Phys Sci. 2012;7:687–95.
Mishra M, Rao AR. Peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in an asymmetric channel. Z Angew Math Phys. 2003;54:532–50.
Haroun MH. Non-linear peristaltic transport flow of a fourth grade fluid in an inclined asymmetric channel. Comput Mater Sci. 2007;39:324–33.
Elmaboud YA, Abdelsalam SI, Mekheimer KS. Couple stress fluid flow in a rotating channel with peristalsis. J Hydrodyn. 2018;30:307–16.
Eytan O, David E. Analysis of intra-uterine fluid motion induced by uterine contractions. Bull Math Biol. 1999;61:221–38.
Ellahi R, Bhatti MM, Riaz A. Effects of magnetohydrodynamics on peristaltic flow of Jeffrey fluid in a rectangular duct through a porous medium. J Porous Media. 2014;17:143–57.
Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R. Simultaneous effects of coagulation and variable magnetic field on peristaltically induced motion of Jeffrey nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganism. Microvasc Res. 2017;110:32–42.
Haider S, Ijaz N, Zeeshan A, Li Y-Z. Magneto-hydrodynamics of a solid-liquid two-phase fluid in rotating channel due to peristaltic wavy movement. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2019;30:2501–16.
Shit GC, Roy M, Ng EYK. Effect of induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of a micropolar fluid in an asymmetric channel. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng. 2010;26:1380–403.
Khan AA, Saleem I, Ellahi R, Sait SM, Vafai K. On magnetohydrodynamics Powell-Eyring fluid with Cattaneo-Christov heat flux over a curved surface. Int J Mod Phys B. 2023;37:2350190.
Riaz A, Zeeshan A, Ahmad S, Razaq A, Zubair M. Effects of external magnetic field on Non-newtonian two phase fluid in an annulus with peristaltic pumping. J Magn. 2019;24:1–8.
Mekheimer KS. Effect of the induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of a couple stress fluid. Phys Lett A. 2008;372:4271–8.
Kothandapani M, Prakash J. Effects of thermal radiation parameter and magnetic field on the peristaltic motion of Williamson nanofluids in a tapered asymmetric channel. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;81:234–45.
Hayat T, Nisar Z, Yasmin H, Alsaedi A. Peristaltic transport of nanofluid in a compliant wall channel with convective conditions and thermal radiation. J Mol Liq. 2016;220:448–53.
Hayat T, Ahmed B, Abbasi FM, Alsaedi A. Numerical investigation for peristaltic flow of Carreau-Yasuda magneto-nanofluid with modified Darcy and radiation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137:1359–67.
Ayub S, Hayat T, Asghar S, Ahmad B. Thermal radiation impact in mixed convective peristaltic flow of third grade nanofluid. Results Phys. 2017;7:3687–95.
Hussain Q, Latif T, Alvi N, Asghar S. Nonlinear radiative peristaltic flow of hydromagnetic fluid through porous medium. Results Phys. 2018;9:121–34.
Rosseland S. Astrophysik und atom-theoretische Grundlagen. Berlin: Springer; 1931. p. 41–4.
Beard DW, Walters K. Elastico-viscous boundary-layer flows: I: Two-dimensional flow near a stagnation point. Math Proc Camb Philos Soc. 1964;60:667–74.
Navier LM. Memoire sur les lois du mouvement des fluids. Mémoires L’académie R Sci L’institut Fr. 1816;6:389–440.
Turkyilmazoglu M. Velocity slip and entropy generation phenomena in thermal transport through metallic porous channel. J Non Equil Thermody. 2020;45:247–56.
Riaz A, Nadeem S, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A. Exact solution for peristaltic flow of Jeffrey fluid model in a three-dimensional rectangular duct having slip at the walls. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2014;11:81–90.
Bhatti MM, Abbas MA, Rashidi MM. Combine effects of Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) and partial slip on peristaltic blood flow of Ree-Eyring fluid with wall properties. Eng Sci Technol Int J Eng Sci Technol. 2016;19:1497–502.
Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A, Ijaz N. Slip effects and endoscopy analysis on blood flow of particle-fluid suspension induced by peristaltic wave. J Mol Liq. 2016;218:240–5.
Turkyilmazoglu M. Exact multiple solutions for the slip flow and heat transfer in a converging channel. J Heat Trans-T ASME. 2015;137:101301.
Choi SUS, Eastman JA. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Int Mech Eng Congress Expo. 1995;66:99–105.
Buongiorno J. Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J Heat Transf. 2006;128:240–50.
Daungthongsuk W, Wongwises S. A critical review of convective heat transfer nanofluids. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 2007;11:797–817.
Kakaç S, Pramuanjaroenkij A. Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52:3187–96.
Jamshed W, Nasir NAAM, Isa SSPM, Safdar R, Shahzad F, Nisar KS, Eid MR, Abdel-Aty AH, Yahia IS. Thermal growth in solar water pump using Prandtl-Eyring hybrid nanofluid: a solar energy application. Sci Rep. 2021;11:18704.
Shaheen S, Maqbool K, Ellahi R, Sait SM. Heat transfer analysis of tangent hyperbolic nanofluid in a ciliated tube with entropy generation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;144:2337–46.
Khan AA, Arshad A, Ellahi R, Sait SM. Heat transmission in Darcy-Forchheimer flow of Sutterby nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms. Int J Numer Method H. 2023;33:135–52.
Zeeshan A, Ahmad M, Ellahi R, Sait SM, Shehzad N. Hydromagnetic flow of two immiscible nanofluids under the combined effects of Ohmic and viscous dissipation between two parallel moving plates. J Magn Magn Mater. 2023;575:170741.
Turkyilmazoglu M. Algebraic solutions of flow and heat for some nanofluids over deformable and permeable surfaces. Int J Numer Method H. 2017;27:2259–67.
Jamshed W, Safdar R, Brahmia A, Alanazi AK, Abo-Dief HM, Eid MR. Numerical simulations of environmental energy features in solar pump application by using hybrid nanofluid flow: Prandtl-Eyring case. Energy Environ. 2023;34:780–807.
Akbar NS, Nadeem S. Endoscopic effects on peristaltic flow of a nanofluid. Commun Theor Phys. 2011;56:761–8.
Alqarni AJ, Abo-Elkhair RE, Elsaid EM, Abdel-Aty AH, Abdel-wahed MS. Effect of magnetic force and moderate Reynolds number on MHD Jeffrey hybrid nanofluid through peristaltic channel: application of cancer treatment. Eur Phys J Plus. 2023;138:137.
Riaz A, Ellahi R, Sait SM. Role of hybrid nanoparticles in thermal performance of peristaltic flow of Eyring-Powell fluid model. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;143:1021–35.
Mekheimer K, Hasona W, Abo-Elkhair R, Zaher A. Peristaltic blood flow with gold nanoparticles as a third grade nanofluid in catheter: Application of cancer therapy. Phys Lett A. 2018;382:85–93.
Hayat T, Tanveer A, Alsaedi A. Numerical analysis of partial slip on peristalsis of MHD Jeffery nanofluid in curved channel with porous space. J Mol Liq. 2016;224:944–53.
Hussain F, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Vafai K. Modelling study on heated couple stress fluid peristaltically conveying gold nanoparticle through coaxial tube: a remedy for gland tumor and arthritis. J Mol Liq. 2018;268:149–55.
Prakash J, Tripathi D, Tiwari AK, Sait SM, Ellahi R. Peristaltic pumping of nanofluids through a tapered channel in a porous environment: applications in blood flow. Symmetry. 2019;11:868.
Prakash J, Siva EP, Tripathi D, Beg OA. Thermal slip and radiative heat transfer effects on electroosmotic magneto nanoliquid peristaltic propulsion through a microchannel. Heat Transf Asian Res. 2019;48:2882–908.
Garimella SV, Simpson JE. Effect of thermo solutal convection on directional solidification. Sadhana. 2001;26:121–36.
Bég OA, Tripathi D. Mathematica simulation of peristaltic pumping with double-diffusive convection in nanofluids a bio-nanoengineering model. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part N J Nanoeng Nanosyst. 2012;225:99–114.
Alolaiyan H, Riaz A, Razaq A, Saleem N, Zeeshan A, Bhatti MM. Effects of double diffusion convection on Third grade nanofluid through a curved compliant peristaltic channel. Coatings. 2020;10:154.
Sharma A, Tripathi D, Sharma RK, Tiwari AK. Analysis of double diffusive convection in electroosmosis regulated peristaltic transport of nanofluids. Phys A. 2019;535:122148.
Asha SK, Sunitha G. Thermal radiation and hall effects on peristaltic blood flow with double diffusion in the presence of nanoparticles. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2020;17:100560.
Akram S, Athar M, Saeed K, Umair MY. Nanomaterials effects on induced magnetic field and double-diffusivity convection on peristaltic transport of Prandtl nanofluids in inclined asymmetric channel. Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/18479804211048630.
Acknowledgement
The authors extend their appreciation to the Ministry of Education in KSA for funding this research work through the project number KKU-IFP2-DA-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akram, S., Athar, M., Saeed, K. et al. Role of thermal radiation and double-diffusivity convection on peristaltic flow of induced magneto-Prandtl nanofluid with viscous dissipation and slip boundaries. J Therm Anal Calorim 149, 761–776 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12643-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12643-x