Abstract
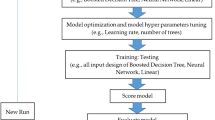
Prediction of solar energy data is very crucial for the effective utilization of freely available renewable energy abundantly in nature. Solar energy data are widely available which must be carefully prepared and arranged for modelling. In this work, typical meteorological year (TMY) data made available by the Korea institute of energy research (KIER) and the National renewable energy laboratory (NREL) are used for modelling in different phases. TMY data at single-point location and multiple locations from KIER are initially used for training of machine learning (ML) algorithms. Later, the TMY data from NREL and KIER are combined and then modelled using radius nearest neighbour (RNN), decision tree regressor (DTR), random forest regressor (RFR), and X-gradient boosting (XGB) algorithms. The solar energy parameters modelled in this work are dew point temperature (DPT), dry bulb temperature (DBT), relative humidity (RH), surface pressure (SP), windspeed (WS), and solar insolation of horizontal plane (IHP). Quantitative analysis of the algorithms is also performed in each stage of the work. The modelling indicates that the DBT, DPT, RH, and SP are able to be predicted with a minimum accuracy of over 90% in each stage. The WS and IHP data when modelled from a single-source TMY data provide superior accuracy than when they are combined. RFR and XGB have outperformed overall as they provide good accuracy for WS and IHP data as well. RNN and DTR achieved 100% accuracy in training, while RFR and XGB showed slightly lower training accuracy due to their avoidance of overfitting. There are errors in testing for RNN/DTR. Using RNN/DTR, the training errors are 0% in all cases, while in some cases like DTP the error by RFR/XGB up to 3%, whereas RNN/DTR testing errors go up to 5% and in case of RFR/XGB they are up to 7.5%. For RH modelling RFR/XGB, training errors are max 6%. RNN/DTR testing errors go up to 11%, while for RFR/XGB up to 7.5% which indicates their robustness. It is observed that many solar parameters, when combined with different source data, can be predicted easily with good accuracy, while WS and IHP become a little bit challenging to model.




































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malik P, Gehlot A, Singh R, Gupta LR, Thakur AK. A review on ANN based model for solar radiation and wind speed prediction with real-time data. Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2022;29:3183–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09687-3.
Sudharshan K, Naveen C, Vishnuram P, KrishnaRao Kasagani DVS, Nastasi B. Systematic review on impact of different irradiance forecasting techniques for solar energy prediction. Energies. 2022;15:6267. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176267.
Prema V, Bhaskar MS, Almakhles D, Gowtham N, Rao KU. Critical review of data, models and performance metrics for wind and solar power forecast. IEEE Access. 2022;10:667–88. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3137419.
Soleimani B, Keshavarz A. Heat transfer enhancement of an internal subcooled flow boiling over a hot spot. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;99:206–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.12.043.
Garud KS, Jayaraj S, Lee MY. A review on modeling of solar photovoltaic systems using artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, genetic algorithm and hybrid models. Int J Energy Res. 2021;45:6–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5608.
Bayrakçı HC, Demircan C, Keçebaş A. The development of empirical models for estimating global solar radiation on horizontal surface: a case study. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;81:2771–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.082.
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Wang D, Wang Y, Zhu Y. Comparison of support vector machine and copula-based nonlinear quantile regression for estimating the daily diffuse solar radiation: a case study in China. Renew Energy. 2020;146:1101–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.07.053.
Fan J, Wang X, Wu L, Zhang F, Bai H, Lu X, Xiang Y. New combined models for estimating daily global solar radiation based on sunshine duration in humid regions: a case study in South China. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;156:618–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.11.085.
Koo C, Li W, Cha SH, Zhang S. A novel estimation approach for the solar radiation potential with its complex spatial pattern via machine-learning techniques. Renew Energy. 2019;133:575–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.10.066.
Mccandless TC, Haupt SE, Young GS. A regime-dependent arti fi cial neural network technique for short-range solar irradiance forecasting. Renew Energy. 2016;89:351–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.12.030.
Olatomiwa L, Mekhilef S, Shamshirband S, Petković D. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy approach for solar radiation prediction in Nigeria. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;51:1784–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.05.068.
Quej VH, Almorox J, Arnaldo JA, Saito L. ANFIS, SVM and ANN soft-computing techniques to estimate daily global solar radiation in a warm sub-humid environment. J Atmos Solar Terr Phys. 2017;155:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2017.02.002.
Marzo A, Trigo M, Alonso-Montesinos J, Martínez-Durbán M, López G, Ferrada P, Fuentealba E, Cortés M, Batlles FJ. Daily global solar radiation estimation in desert areas using daily extreme temperatures and extraterrestrial radiation. Renew Energy. 2017;113:303–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.01.061.
Mehdizadeh S, Behmanesh J, Khalili K. Comparison of artificial intelligence methods and empirical equations to estimate daily solar radiation. J Atmos Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2016;146:215–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2016.06.006.
Azimi R, Ghayekhloo M, Ghofrani M. A hybrid method based on a new clustering technique and multilayer perceptron neural networks for hourly solar radiation forecasting. ENERGY Convers Manag. 2016;118:331–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.04.009.
Anwar I, Khatib T. A novel hybrid model for hourly global solar radiation prediction using random forests technique and firefly algorithm. Energy Convers Manag. 2017;138:413–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.02.006.
Jiang H. A novel approach for forecasting global horizontal irradiance based on sparse quadratic RBF neural network. Energy Convers Manag. 2017;152:266–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.09.043.
Heng SY, Ridwan WM, Kumar P, Ahmed AN, Fai CM, Birima AH, El-Shafie A. Artificial neural network model with different backpropagation algorithms and meteorological data for solar radiation prediction. Sci Rep. 2022;12:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13532-3.
Geetha A, Santhakumar J, Sundaram KM, Usha S. ScienceDirect prediction of hourly solar radiation in Tamil Nadu using ANN Model with different learning algorithms. Energy Rep. 2022;8:664–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.11.190.
Ghazvinian H, Mousavi S, Karami H, Farzin S, Ehteram M, Hossain S, Fai CM, Bin HH, Singh P, Ros FC, et al. Integrated support vector regression and an improved particle swarm optimization-based model for solar radiation prediction. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0217634.
Hussain S, AlAlili A. A hybrid solar radiation modeling approach using wavelet multiresolution analysis and artificial neural networks. Appl Energy. 2017;208:540–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.100.
Rao DVSKK, Premalatha M, Naveen C. Analysis of different combinations of meteorological parameters in predicting the horizontal global solar radiation with ANN approach: a case study. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;91:248–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.096.
Xiong G, Li L, Mohamed AW, Yuan X, Zhang J. A new method for parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic models using gaining-sharing knowledge based algorithm. Energy Rep. 2021;7:3286–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.05.030.
Gao X, Cui Y, Hu J, Xu G, Wang Z, Qu J, Wang H. Parameter extraction of solar cell models using improved shuffled complex evolution algorithm. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;157:460–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.12.033.
Bendiek P, Taha A, Abbasi QH, Barakat B. Solar irradiance forecasting using a data-driven algorithm and contextual optimisation. Appl Sci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010134.
Khosravi A, Koury RNN, Machado L, Pabon JJG. Prediction of hourly solar radiation in abu musa island using machine learning algorithms. J Clean Prod. 2018;176:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.065.
Ağbulut Ü, Gürel AE, Biçen Y. Prediction of daily global solar radiation using different machine learning algorithms: evaluation and comparison. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110114.
Patel D, Patel S, Patel P, Shah M. Solar radiation and solar energy estimation using ANN and Fuzzy logic concept: A comprehensive and systematic study. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(22):32428–42.
Meenal R, Selvakumar AI. Assessment of SVM, empirical and ANN based solar radiation prediction models with most influencing input parameters. Renew Energy. 2018;121:324–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.12.005.
Wang Z, Li Y, Li D, Zhu Z, Du W. Entropy and gravitation based dynamic radius nearest neighbor classification for imbalanced problem. Knowl Based Syst. 2020;193: 105474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105474.
Jin Z, Shang J, Zhu Q, Ling C, Xie W, Qiang B. RFRSF: employee turnover prediction based on random forests and survival analysis. Lect Notes Comput Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62008-0_35.
Santhanam R, Uzir N, Raman S, Banerjee S. Experimenting XGBoost algorithm for prediction and classi Fi cation of different datasets. Int J Control Theory Appl. 2017;9:651–62.
Gouda SG, Hussein Z, Luo S, Yuan Q. Model selection for accurate daily global solar radiation prediction in China. J Clean Prod. 2019;221:132–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.211.
Zang H, Cheng L, Ding T, Cheung KW, Wang M, Wei Z, Sun G. Application of functional deep belief network for estimating daily global solar radiation: a case study in China. Energy. 2020;191: 116502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116502.
Sharma P, Said Z, Kumar A, Nizetic S, Pandey A, Hoang AT, Huang Z, Afzal A, Li C, Le AT, Nguyen XP. Recent advances in machine learning research for nanofluid-based heat transfer in renewable energy system. Energy Fuels. 2022;36(13):6626–58.
Farooq S, Rativa D, Said Z, de Araujo RE. High performance blended nanofluid based on gold nanorods chain for harvesting solar radiation. Appl Therm Eng. 2023;5(218): 119212.
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF- 2021R1C1C1008791).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Afzal, A., Buradi, A., Alwetaishi, M. et al. Single- and combined-source typical metrological year solar energy data modelling. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 12501–12523 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12604-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12604-4