Abstract
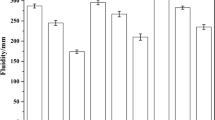
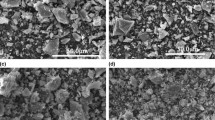
Effects of Na2SO4 on rheological performance and hydration kinetics of lithium slag (LS) binder were investigated. Results showed that Na2SO4 impaired the viscosity property of LS-cement binder. Increased dosage of Na2SO4 led to increased consistency coefficient (K) and declined flow behavior index (n), indicating enhanced viscosity and reduced flow behavior of LS-cement binder in the function of Na2SO4. A high amount of Na2SO4 led to a relatively high hydration degree during the transformation process of NG to I and the transformation process of I to D. Increased dosage of Na2SO4 led to the raised value of KA–B, higher hydration peak ((dQ/dt)C), and decreased value of n, referring to enhanced nucleation rate of C–S–H, increased total nuclei number at the early acceleration stage. Na2SO4 advanced the hydration of LS-cement binder, shortened introduction period, advanced acceleration period, and accelerated hydration process with enhanced formation of C–S–H and AFt, which contributed to compacter matrix with denser microstructure and higher mechanical strength.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong P, Ahmad MR, Chen B, MunirKazami MJSMA. Preparation and study of magnesium ammonium phosphate cement from waste lithium slag. J Clean Prod. 2021;316:128371.
Zhang T, Ma BG, Tan HB, Liu XH, Chen P, Luo ZT. Effect of TIPA on mechanical properties and hydration properties of cement-lithium slag system. J Environ Manag. 2020;276:111274.
Tan HB, Li XG, He C, Ma BG, BaiLuo YZT. Utilization of lithium slag as an admixture in blended cements: physico-mechanical and hydration characteristics. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed. 2015;30(1):129–33.
Tan HB, Li MG, He XY, Su Y, Zhang JJ, Pan H, Yang J, Wang YB. Preparation for micro-lithium slag via wet grinding and its application as accelerator in Portland cement. J Clean Prod. 2020;250:119528.
Li BL, Cao RL, You NQ, Chen C, Zhang YM. Products and properties of steam cured cement mortar containing lithium slag under partial immersion in sulfate solution. Constr Build Mater. 2019;220:596–606.
He Y, Liu SH, Hooton RD, ZhangHe XS. Effects of TEA on rheological property and hydration performance of lithium slag-cement composite binder. Constr Build Mater. 2022;318:125757.
Wang JX, Han L, Liu Z, Wang DM. Setting controlling of lithium slag-based geopolymer by activator and sodium tetraborate as a retarder and its effects on mortar properties. Cem Concr Compos. 2020;110:103598.
Wang JX, Jiang QK, Cheng GD, Li L, Kang YX, Wang DM. A green route to sustainable alkali-activated materials by heat and chemical activation of lithium slag. J Clean Prod. 2019;225:1184–93.
Zhai M, Zhao J, Wang D, Wang Y, Wang Q. Hydration properties and kinetic characteristics of blended cement containing lithium slag powder. J Build Eng. 2021;39:102287.
He Y, Zhang QL, Chen QS, Bian JW, Qi CC, Kang Q, Feng Y. Mechanical and environmental characteristics of cemented paste backfill containing lithium slag-blended binder. Constr Build Mater. 2021;271:121567.
Wang WC. Effects of fly ash and lithium compounds on the water-soluble alkali and lithium content of cement specimens. Constr Build Mater. 2014;50:727–35.
Lu JH, Yu ZX, Zhu YZ, Huang SW, Luo Q, Zhang SY. Effect of lithium-slag in the performance of slag cement mortar based on least-squares support vector machine prediction. Materials. 2019;12(10):1652.
He Y, Chen QS, Qi CC, Zhang QL, Xiao CC. Lithium slag and fly ash-based binder for cemented fine tailings backfill. J Environ Manag. 2019;248:109282.
Li JZ, Lian PH, Huang SW, Huang L. Recycling of lithium slag extracted from lithium mica by preparing white Portland cement. J Environ Manag. 2020;265:110551.
Zhang L, Lv SZ, Liu Y. Influence of lithium slag on cement properties. J Wuhan Univ Technol. 2015;37(3):23–7.
Liu Z, Wang JX, Li L, Wang DM. Characteristics of alkali-activated lithium slag at early reaction age. J Mater Civ Eng. 2019;31(12):04019312.
Allahverdi A, Maleki A, Mahinroosta M. Chemical activation of slag-blended Portland cement. J Build Eng. 2018;18:76–83.
Islam M, Patel R. Thermal activation of basic oxygen furnace slag and evaluation of its fluoride removal efficiency. Chem Eng J. 2011;169(1–3):68–77.
Rieger D, Kovarik T, Riha J, Medlin R, Novotny P, Belsky P, Kadlec J, Holba P. Effect of thermal treatment on reactivity and mechanical properties of alkali activated shale-slag binder. Constr Build Mater. 2015;83:26–33.
Joseph S, Snellings R, Cizer O. Activation of Portland cement blended with high volume of fly ash using Na2SO4. Cem Concr Compos. 2019;104:103417.
Tan HB, Zhang X, He XY, Guo YL, Deng XF, Su Y, Yang J, Wang YB. Utilization of lithium slag by wet-grinding process to improve the early strength of sulphoaluminate cement paste. J Clean Prod. 2018;205:536–51.
Tan HB, Li MG, He XY, Su Y, Yang J, Zhao H. Effect of wet grinded lithium slag on compressive strength and hydration of sulphoaluminate cement system. Constr Build Mater. 2021;267:120465.
Abdel-Gawwad HA, Khalil KA. Application of thermal treatment on cement kiln dust and feldspar to create one-part geopolymer cement. Constr Build Mater. 2018;187:231–7.
Long JF, Yang K, Wang SF, Xu LL, Yang ZH, Ye CF, Luo JJ, Wu K, Zhang LH. New insights into the contribution of quartz powder byproduct from manufactured sand to the performance of cementitious materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2023;148:4105–17.
Cavusoglu I, Yilmaz E, Yilmaz AO. Additivity effect on fresh and hardened properties of cemented coal fly ash backfill containing water-reducing admixtures. Constr Build Mater. 2021;267:121021.
Cavusoglu I, Yilmaz E, Yilmaz AO. Sodium silicate effect on setting properties, strength behavior andmicrostructure of cemented coal fly ash backfill. Powder Technol. 2021;384:17–28.
Brykov AS, Danilov VV, Korneev VI, Larichkov AV. Effect of hydrated sodium silicates on cement paste hardening. Russ J Appl Chem. 2002;75(10):1577–9.
Brykov AS, Danilov BV, Larichkov AV. Specific features of Portland cement hydration in the presence of sodium hydrosilicates. Russ J Appl Chem. 2006;79(4):521–4.
Santana-Carrillo JL, Ortega-Zavala DE, Burciaga-Diaz O, Escalante-Garcia JI. Modified blended limestone-Portland cement binders: Evaluation of 4 different sodium silicates. Cem Concr Compos. 2021;118:103935.
Cristelo N, Garcia-Lodeiro I, Rivera JF, Miranda T, Palomo A, Coelho J, Fernandez-Jimenez A. One-part hybrid cements from fly ash and electric arc furnace slag activated by sodium sulphate or sodium chloride. J Build Eng. 2021;44:103298.
Cristelo N, Miranda T, Oliveira DV, Rosa I, Soares E, Coelho P, Fernandes L. Assessing the production of jet mix columns using alkali activated waste based on mechanical and financial performance and CO2 (eq) emissions. J Clean Prod. 2015;102:447–60.
Habert G, de Lacaillerie JBD, Roussel N. An environmental evaluation of geopolymer based concrete production: reviewing current research trends. J Clean Prod. 2011;19(11):1229–38.
Zhu ZY, Wang ZP, Zhou Y, Chen YT, Li PZ, Shan QJ, Wu K. Synthesis and characterization of pregelatinized starch modified C–S–H: inspired by the historic binders. Constr Build Mater. 2022;354:129114.
Zhu Z, Wang Z, Xu L, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Wu K, Schutter GD. Synthesis and characterization of an intermediate for C–S–H structure tailoring. Cem Concr Res. 2022;160:106923.
Fu JY, Jones AM, Bligh MW, Holt C, Keyte LM, Moghaddam F, Foster SJ, Waite TD. Mechanisms of enhancement in early hydration by sodium sulfate in a slag-cement blend: insights from pore solution chemistry. Cem Concr Res. 2020;135:106110.
Neto JDA, De la Torre AG, Kirchheim AP. Effects of sulfates on the hydration of Portland cement: a review. Constr Build Mater. 2021;279:122428.
Zhao YL, Qiu JP, Xing J, Sun XG. Chemical activation of binary slag cement with low carbon footprint. J Clean Prod. 2020;267:121455.
Zou FB, Hu CL, Wang FZ, Ruan YX, Hu SG. Enhancement of early-age strength of the high content fly ash blended cement paste by sodium sulfate and C–S–H seeds towards a greener binder. J Clean Prod. 2020;244:118566.
Criado M, Jimenez AF, Palomo A. Effect of sodium sulfate on the alkali activation of fly ash. Cem Concr Compos. 2010;32(8):589–94.
Velandia DF, Lynsdale CJ, Provis JL, Ramirez F, Gomez AC. Evaluation of activated high volume fly ash systems using Na2SO4, lime and quicklime in mortars with high loss on ignition fly ashes. Constr Build Mater. 2016;128:248–55.
Onuaguluchi O, Ratu R, Banthia N. Effect of sodium sulfate activation on the early-age matrix strength and steel fiber bond in high volume fly ash (HVFA) cement mortar. Constr Build Mater. 2022;341:127808.
Li C, Zhu HB, Wu MX, Wu KF, Jiang ZW. Pozzolanic reaction of fly ash modified by fluidized bed reactor-vapor deposition. Cem Concr Res. 2017;92:98–109.
Velandia DF, Lynsdale CJ, Provis JL, Ramirez F. Effect of mix design inputs, curing and compressive strength on the durability of Na2SO4-activated high volume fly ash concretes. Cem Concr Compos. 2018;91:11–20.
Aydin S, Baradan B. Sulfate resistance of alkali-activated slag and Portland cement based reactive powder concrete. J Build Eng. 2021;43:103205.
Guo S, Zhang Y, Wang K, Bu Y, Wand C, Ma C. Delaying the hydration of Portland cement by sodium silicate: setting time and retarding mechanism. Constr Build Mater. 2019;205:543–8.
Rakhimova NR, Rakhimov RZ, Morozov VP, Potapova LI, Osin YN. Mechanism of solidification of simulated borate liquid wastes with sodium silicate activated slag cements. J Clean Prod. 2017;149:60–9.
Roy S, Chanda S, Bandopadhyay SK, Ghosh SN. Investigation of Portland slag cement activated by waterglass. Cem Concr Res. 1998;28(7):1049–56.
Nguyen HA, Chang TP, Thymotie A. Enhancement of early engineering characteristics of modified slag cement paste with alkali silicate and sulfate. Constr Build Mater. 2020;230:117013.
Myers RJ, Bernal SA, Provis JL. A thermodynamic model for C–(N–)A–S–H gel: CNASH_ss. Derivation and validation. Cem Concr Res. 2014;66:27–47.
Zhang JJ, Tan HB, Bao M, Liu XH, Luo ZT, Wang PG. Low carbon cementitious materials: Sodium sulfate activated ultrafine slag/fly ash blends at ambient temperature. J Clean Prod. 2021;280:124363.
He Y, Zhang X, Hooton RD. Effects of organosilane-modified polycarboxylate superplasticizer on the fluidity and hydration properties of cement paste. Constr Build Mater. 2017;132:112–23.
Liu M, Tan HB, He XY. Effects of nano-SiO2 on early strength and microstructure of steam-cured high volume fly ash cement system. Constr Build Mater. 2019;194:350–9.
He Y, Zhang X, Liu SH, Hooton RD, Ji T, Kong YN. Impacts of sulphates on rheological property and hydration performance of cement paste in the function of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr Build Mater. 2020;256:119428.
Li HX, Xue Z, Liang GW, Wu K, Dong BQ, Wang WS. Effect of C–S–Hs–PCE and sodium sulfate on the hydration kinetics and mechanical properties of cement paste. Constr Build Mater. 2021;266:121096.
Xu C, Li HX, Yang XJ, Dong BQ, Wang WS. Action of the combined presence of C–S–Hs-PCE and triethanolamine on the performances of cement paste/mortar. Constr Build Mater. 2021;269:121345.
He Y, Zhang X, Hooton RD, Wang Y, Kong Y, Wang X, Wang H. Influence of PCE on rheological and hydration performances of cement paste. J Mater Civ Eng. 2020;32(3):04020002.
He Y, Zhang X, Shui L, Wang Y, Gu M. Effects of PCEs with various carboxylic densities and functional groups on the fluidity and hydration performances of cement paste. Constr Build Mater. 2019;202:656–68.
He Y, Zhang X, Kong YN, Wang XF, Shui LL, Wang HR. Influence of polycarboxylate superplasticizer on rheological behavior in cement paste. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed. 2018;33(4):932–7.
He Y, Zhang X, Ji T, Shui LL. Effect of carboxylic density on sulfate sensitivity of polycarboxylate superplasticizers. KSCE J Civ Eng. 2019;23(12):5163–72.
He Y, Zhang X, Guan J. Effect and mechanism of sulfates on dispersity of polycarboxylate-type superplasticizers. KSCE J Civ Eng. 2016;10:1–7.
Wu K, Hu Y, Zhang LT, Xu LL, Yang ZH. Promoting the sustainable fabrication of bricks from municipal sewage sludge through modifying calcination: microstructure and performance characterization. Constr Build Materi. 2022;324:126401.
Xu LL, Yang K, Tang CY, Yang XJ, Wu K, Lothenbach B. Lead retardation on cement hydration: inhibition and re-acceleration of clinker dissolution. Cem Concr Compos. 2023;138:104986.
Li HX, Xu C, Dong BQ, Chen Q, Gu LN, Yang XJ. Enhanced performances of cement and powder silane based waterproof mortar modified by nucleation C–S–H seed. Constr Build Mater. 2020;246:104986.
GB/T17671-2021, Test methods of cement mortar strength (ISO method).
Zhang Y, Kong X. Correlations of the dispersing capability of NSF and PCE types of superplasticizer and their impacts on cement hydration with the adsorption in fresh cement pastes. Cem Concr Res. 2015;69:1–9.
Han FH, Wang Q, Liu MT, Mei YJ. Early hydration properties of composite binder containing limestone powder with different finenesses. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123(2):1141–51.
Han FH, Zhang ZQ, Wang DM, Yan PY. Hydration kinetics of composite binder containing slag at different temperatures. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121(2):815–27.
Zhou LF, Gou MF, Guan XM. Hydration kinetics of cement-calcined activated bauxite tailings composite binder. Constr Build Mater. 2021;301:124296.
Zhang XW, Lu CX, Shen JY. Influence of tartaric acid on early hydration and mortar performance of Portland cement-calcium aluminate cement-anhydrite binder. Constr Build Mater. 2016;112:877–84.
Zhang YJ, Yu P, Pan F, He Y. The synergistic effect of AFt enhancement and expansion in Portland cement-aluminate cement-FGD gypsum composite cementitious system. Constr Build Mater. 2018;190:985–94.
Zhang RX, Bassim N, Panesar DK. Characterization of Mg components in reactive MgO: Portland cement blends during hydration and carbonation. J Co2 Util. 2018;27:518–27.
Zhang YR, Kong XM, Lu ZB, Lu ZC, Hou SS. Effects of the charge characteristics of polycarboxylate superplasticizers on the adsorption and the retardation in cement pastes. Cem Concr Res. 2015;67:184–96.
Lyu XJ, Yao G, Wang ZM, Wang Q, Li L. Hydration kinetics and properties of cement blended with mechanically activated gold mine tailings. Thermochim Acta. 2020;683:178457.
Han FH, Zhang ZQ, LiuYan JHPY. Hydration kinetics of composite binder containing fly ash at different temperatures. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124(3):1691–703.
Nocun-Wczelik W. Differential calorimetry as a tool in the studies of cement hydration kinetics with sulphate and nitrate solutions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130(1):249–59.
Han FH, Zhang ZQ, LiuYan JHPY. Effect of water-to-binder ratio on the hydration kinetics of composite binder containing slag or fly ash. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128(2):855–65.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51808369, 51890911), CRSRI Open Research Program (CKWV20221020/KY), Jiangsu graduate Innovation Project (SJCX22_1577, SJCX23_1722).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YH was contributed to formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft. CY was contributed to writing—review, software, Methodology. MJ was contributed to supervision, methodology, conceptualization. SL was contributed to conceptualization, supervision, methodology. JS was contributed to resources, supervision. RDH was contributed to resources.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., You, C., Jiang, M. et al. Rheological performance and hydration kinetics of lithium slag-cement binder in the function of sodium sulfate. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 11653–11668 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12531-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12531-4