Abstract
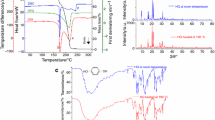
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a chemical compound used widely in industry, having been adopted in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations as a preservative, antimicrobial, and antiseptic agent. In pharmaceutical development, thermal analysis and Infrared Spectrum (FTIR) are widely used on preformulation studies. Thus, in this work we performed the thermal characterization of CPC through DSC and TG/DTA techniques, and evaluated it by FTIR to understand the thermal events that characterize CPC. In addition, its binary combinations with possible adjuvants: sugar alcohols (sorbitol and xylitol) and flavoring agents (menthol and thymol), were evaluated. Statistical analysis using Pearson's correlation allowed us to define clearly the extent of these interactions. The DSC study showed endothermic peaks at 84.09 °C and 233.84 °C for CPC. TG analysis indicated mass loss of 92.91% at a temperature of 239.57 °C. DTA evaluation showed endothermic peaks at 83.68 °C and 240.12 °C. In the FTIR analysis, bands of characteristic spectra for CPC were presented. The evaluation of binary combinations with the components studied allowed for the identification of interactions of CPC with menthol and thymol, with alterations of melting point and eutectic mixtures formation, even at room temperature, with thymol. The spectral constancy of CPC and mixtures with different components were evaluated through linear correlation, with no significant chemical interactions evidenced. This was due to the Pearson's correlation values being greater than 0.8, which represents an absence of chemical interactions between the components tested.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trandafirescu C, Ledeţi I, Şoica C, Ledeţi A, Vlase G, Borcan F, et al. Albendazole-cyclodextrins binary systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138:3039–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08326-1.
Teixeira FV, Alves GL, Ferreira MH, Taveira SF, da Cunha-Filho MSS, Marreto RN. Preformulation studies to guide the development of raloxifene lipid-based delivery systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:365–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-6964-x.
Henríquez LC, Redondo GM, Zúñiga RV, Berrocal GC. Combined use of DSC, TGA, XDR and NIR in the compatibility study of preformulation mixtures for the development of 10 mg tablets of Rupatadine Fumarate. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2018;8(3):42–54.
Alarcon RT, Holanda BBC, Oliveira AR, Magdalena AG, Bannach G. Production and characterization of the new thermoplastic polymer by linseed oil and glycerol following green chemistry principles. Rev Virtual Quim. 2017;9(1):163–75. https://doi.org/10.21577/1984-6835.20170013.
Matos APS, Costa JS, Boniatti J, Seiceira RC, Pitaluga A Jr, Oliveira DL, et al. Compatibility study between diazepam and tablet excipients: infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis in accelerated stability conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127(2):1675–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5350-9.
Liu J, Ling JQ, Wu CD. Cetylpyridinium chloride suppresses gene expression associated with halitosis. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;2013(58):1686–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2013.08.014.
Osso D, Kanani N. Antiseptic mouth rinses: an update on comparative effectiveness, risks and recommendations. J Dent Hyg. 2013;87(1):10–8.
Park JB, Kang JH, Song KB. Antibacterial activities of a cinnamon essential oil with cetylpyridinium chloride emulsion against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium in basil leaves. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2018;27(1):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0241-9.
Mao X, Aue DL, Buchalla W, Hiller K-A, Maisch T, Hellwig E, et al. Cetylpyridinium chloride: mechanism of action, antimicrobial efficacy in biofilms, and potential risks of resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64(8):102. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00576-20.
Husain A. Effects of Cetylpyridinium Chloride-Based Chewing Gum Plus Tooth Brushing on Plaque Formation and Gingivitis: A Randomized Triple- Blind, Crossover, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Gastron ecuatoriana y Tur local. Published online 2020.
Rajendiran M, Trivedi HM, Chen D, Gajendrareddy P, Chen L. Recent development of active ingredients in mouthwashes and toothpastes for periodontal diseases. Molecules. 2021;26(7):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072001.
Grembecka M. Sugar alcohols—their role in the modern world of sweeteners: a review. Eur Food Res Technol. 2015;241(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-015-2437-7.
Sachdev R. Sugar substitutes and dental health. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2018;7(9):1667. https://doi.org/10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20183472.
Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Quinn ME. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 6th ed. Washington: Pharmaceutical Press and American Pharmacists Association; 2009.
Öktemer T, Muluk NB, Cingi C. A pastille combining myrrh tincture, peppermint oil and menthol to treat the upper airway. ENT Updat. 2015;5(3):128–31. https://doi.org/10.2399/jmu.2015003011.
Dai J, Hu W, Yang H, Li C, Cui H, Li X, et al. Controlled release and antibacterial properties of PEO/casein nanofibers loaded with Thymol/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in beef preservation. Food Chem. 2022;382(December 2021):132369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132369.
Escobar A, Pérez M, Romanelli G, Blustein G. Thymol bioactivity: a review focusing on practical applications. Arab J Chem. 2020;13(12):9243–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.11.009.
Zhao Y, Du L-D, Du G-H. Menthol. In: Du G-H, editor. Natural small molecule drugs from plants. Singapore: Springer; 2018. p. 289–94.
Santos MG. Desenvolvimento e caracterização de microcápsulas de xilitol e mentol por coacervação complexa e sua aplicação em gomas de mascar. Published online 2014.
Zanin MHA, Santos VA, Oliveira AM, Cerize NNP, Borsatti MMA. Electrospun nanofibers for Sustained Delivery of Cetylpyridinium Chloride for Buccal Topical Application. Biotech, Biomater Biomed TechConnect Br. Published online 2015 pp. 9–12.
Santos WM, Nóbrega FP, Andrade JC, Almeida LF, Conceição MM, Medeiros ACD, et al. Pharmaceutical compatibility of dexamethasone with excipients commonly used in solid oral dosage forms. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;145(2):361–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09753-1.
Kulkarni P, Rawtani D, Barot T. Design, development and in-vitro/in-vivo evaluation of intranasally delivered Rivastigmine and N-Acetyl Cysteine loaded bifunctional niosomes for applications in combinative treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;2021(163):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.02.015.
Daniel JSP, Cruz JC, Catelani TA, Garcia JS, Trevisan MG. Erythromycin-excipients compatibility studies using the thermal analysis and dynamic thermal infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;143(4):3127–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09691-y.
Silva EP. Estudo de compatibilidade entre atorvastatina e excipientes por técnicas térmicas (TG, DSC) e FTIR utilizando correlação de Pearson. Published online 2016.
USP 32-NF 27. Melting range or temperature in USP General chapter. Rockville: Convention, Inc.; 2009. p. 294.
de Miranda TM, Oliveira AR, Pereira JR, Silva JG, Lula IS, Nascimento CS Jr, et al. Inclusion vs micellization in the cethylpyridine chloride/β-cyclodextrin system: a structural and thermodynamic approach. J Mol Struct. 2019;1184:289–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.02.033.
Dubovoy V, Nawrocki S, Verma G, Wojtas L, Desai P, Al-Tameemi H, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and investigation of the antimicrobial activity of cetylpyridinium tetrachlorozincate. ACS Omega. 2020;5(18):10359–65. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00131.
Dezena RMB, Malta Junior JS. Preformulation comparative study between two samples of sorbitol used as excipient in the direct compression process. Braz J Anal Chem. 2017;4(15):19–26.
Fan C, Yuan G, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z. Thermal storage performance of eutectic sugar alcohols applied to buildings and enhancement of crystallization. Sol Energy. 2021;2022(234):231–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2022.01.069.
Birta N, Doca N, Vlase G, Vlase T. Kinetic of sorbitol decomposition under non-isothermal conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92(2):635–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-7938-6.
Hasan A, Ramadan AE, Elghany MA, Sabry S. Design and characterization of intra-oral fast dissolving tablets containing diacerein-solid dispersion. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2020;10(6):44–53. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2020.10607.
Santana APR, Andrade DF, Mora-Vargas JA, Amaral CDB, Oliveira A, Gonzalez MH. Natural deep eutectic solvents for sample preparation prior to elemental analysis by plasma-based techniques. Talanta. 2019;2019(199):361–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.02.083.
Corvis Y, Négrier P, Massip S, Leger JM, Espeau P. Insights into the crystal structure, polymorphism and thermal behavior of menthol optical isomers and racemates. CrystEngComm. 2012;14(20):7055–64. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce26025e.
Maruchenko R, Espeau P. Revised phase diagrams based on racemic ibuprofen with thymol and l-menthol. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;145(6):3087–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10119-w.
Ribeiro BD, Florindo C, Iff LC, Coelho MAZ, Marrucho IM. Menthol-based eutectic mixtures: hydrophobic low viscosity solvents. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2015;3(10):2469–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00532.
Pochivalov KV, Basko AV, Lebedeva TN, Antina LA, Golovanov LY, Artemov VV, et al. Low-density polyethylene-thymol: thermal behavior and phase diagram. Thermochim Acta. 2017;2018(659):113–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2017.11.012.
Bezerra GSN, Pereira MAV, Ostrosky EA, Barbosa EG, Moura MFV, Ferrari M, et al. Compatibility study between ferulic acid and excipients used in cosmetic formulations by TG/DTG, DSC and FTIR. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;127:1683–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5654-9.
Mendonça CMS, Lima IPB, Aragão CFS, Gomes APB. Thermal compatibility between hydroquinone and retinoic acid in pharmaceutical formulations. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:2277–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-2941-6.
Fahelelbom KM, Saleh A, Al-Tabakha MMA, Ashames AA. Recent applications of quantitative analytical FTIR spectroscopy in pharmaceutical, biomedical, and clinical fields: a brief review. Rev Anal Chem. 2022;41(1):21–33. https://doi.org/10.1515/revac-2022-0030.
Segall AI. Preformulation: the use of FTIR in compatibility studies. J Innov Appl Pharm Sci. 2019;4(3):1–6.
ArockiaSelvi J, Kamaraj P, Arthanareeswari M, PushpaMalini T, Mohanapriya S, Subasree N. Effect of cetylpyridinium chloride on corrosion inhibition of mild steel in chloride environment. Mater Today Proc. 2019;14:264–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.04.146.
Banjare RK, Banjare MK, Panda S. Effect of acetonitrile on the colloidal behavior of conventional cationic surfactants: a combined conductivity, surface tension, fluorescence and FTIR study. J Solut Chem. 2020;49(1):34–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-019-00937-4.
Liu L, Ge Y, Liu X, Ruan J, Cao J, Wei C, et al. One-pot ball-milling preparation of cetylpyridinium chloride/α-zirconium phosphate composite for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid and dopamine. J Alloys Compd. 2021;860:157927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157927.
Cao L, Liu W, Wang L. Developing a green and edible film from Cassia gum: the effects of glycerol and sorbitol. J Clean Prod. 2018;175:276–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.064.
Lee SH, Shin SR, Lee DS. Sorbitol as a chain extender of polyurethane prepolymers to prepare self-healable and robust polyhydroxyurethane elastomers. Molecules. 2018;23(10):2515. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102515.
Ali HH, Ghareeb MM, Al-Remawi M, Al-Akayleh FT. New insight into single phase formation of capric acid/menthol eutectic mixtures by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Trop J Pharm Res. 2020;19(2):361–9. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v19i2.19.
Shahriarinour M, Divsar F, Eskandari Z. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of thymol loaded SBA-15 mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem. 2019;49(6):182–9.
Macasoi C, Pincu E, Meltzer V, Bogdan J. Increasing the bromazepam solubility by forming eutectic mixture with citric acid. Thermochim Acta. 2021;702:178954. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TCA.2021.178954.
Martins MAR, Pinho SP, Coutinho JAP. Insights into the nature of eutectic and deep eutectic mixtures. J Solut Chem. 2019;48:962–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-018-0793-1.
Roda A, Matias AA, Paiva A, Duarte ARC. Polymer science and engineering using deep eutectic solvents. Polymers (Basel). 2019;11(5):1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050912.
Ünlü AE, Arikaya A, Takaç S. Use of deep eutectic solvents as catalyst: a mini-review. Green Process Synth. 2019;8:355–72.
Murador DC, Mesquita LMS, Vannuchi N, Braga ARC, de Rosso VV. Bioavailability and biological effects of bioactive compounds extracted with natural deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids: advantages over conventional organic solvents. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2019;26:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2019.03.002.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank to Núcleo de Pesquisa em Alimentos e Medicamentos (NUPLAM) from Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte for the availability of structure, support team and additional financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Aquino, D.A.O., Oliveira, A.S., Amorim, M.V.P. et al. Thermal behavior of cetylpyridinium hydrochloride and its association with sugar alcohols and flavoring agents: a preformulation study. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 9477–9488 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12320-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12320-z