Abstract
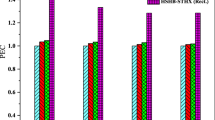
An increase in the thermal performance of heat exchangers leaves a dramatic influence on the energy consumption of industries, addressing why such studies are of interest. The current numerical work, therefore, aims to increase heat transfer in a shell-and-tube heat exchanger by innovative, novel topological changes, using Cassini cross-sectional tubes and proposed segmental curved baffles. Cassini oval and triple Cassini cross sections in horizontal, vertical, and oblique tube arrangements are applied, not investigated yet. Further, the heat transfer is augmented by adding carbon nanotubes to the pure water. The inlet Reynolds number is chosen between 10,000 and 30,000 and the nanotube volume fraction falls in the range of 0 and 2%. The friction factor, Nusselt number, performance evaluation criteria as well as the second law of thermodynamics analysis, including thermal and frictional entropy generation, are monitored. The Witte–Shamsunder efficiency is also detected to consider both the first and second low. Using the water as the working fluid and irrespective of the baffle geometry, the case with the triple Cassini cross-section tube has the highest value of the Nusselt number up to 100, while the circular tube case sets in the lowest rank, with the value near 50. Additionally, the circular tubes show the worst PEC value, while triple Cassini tubes pretend as the most valuable case, with values of 40–50% higher than those of circular tubes, highlighted more at the lower Reynolds numbers. The cases with curved baffles make the PEC increment in all cases up to 15% compared to those with simple baffles. The entropy generation reduces by using the curved baffles up to 20%.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotube
- EEC:
-
Efficiency evaluation criteria
- PEC:
-
Performance evaluation criteria
- RNG:
-
Renormalization group
- T.K.E.:
-
Turbulent kinetic energy
- in:
-
Inlet
- Lm:
-
Logarithmic mean temperature difference
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- W-S:
-
Witte–Shamsunder
- A:
-
Area, m2
- A o :
-
Total heat transfer area, m2
- C p :
-
Specific heat, j kg−1 K−1
- d:
-
Diameter, m
- d h :
-
Hydraulic diameter, m
- Exloss :
-
Exergy loss
- f :
-
Friction factor
- h :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient, w m−2 K−1
- k :
-
Turbulent kinetic energy, m2 s−2
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow, kg/s
- N g :
-
Dimensionless volumetric entropy generation
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Pressure, Pa
- P k :
-
Turbulent generation, m2 s−3
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- Q:
-
Thermal energy, j
- r:
-
Radius, m
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- \({\dot{\mathrm{S}}}_{\mathrm{g}}^{\mathrm{^{\prime}}\mathrm{^{\prime}}}\) :
-
Entropy generation rate, W K−1 m−3
- T:
-
Temperature, K
- T o :
-
Ambient temperature, K
- u :
-
Velocity component, m s−1
- x :
-
Coordinate component, m
- ε :
-
Shape factor, m−1
- ε ijk :
-
Turbulent dissipation rate, m2 s−3
- λ :
-
Levi-Civitia symbol
- φ :
-
Conduction heat transfer coefficient, w m−1 K−1
- β :
-
Nanofluid volume friction
- ρ :
-
Density, kg m−3
- μ:
-
Dynamic viscosity, kg m−1 s−1
- \({\upsilon }_{\mathrm{t}}\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity, m2 s−1
- τw :
-
Wall shear stress, Pa
- ξ:
-
Vorticity, s−1
- bf:
-
Base flow
- eff:
-
Effective
- i, j, k:
-
Dummy indexes
- lm:
-
Logarithmic mean temperature difference
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- t:
-
Turbulent
- o:
-
Base state
- out:
-
Outlet
- p:
-
Particle
- Δp:
-
Frictional
- Δt:
-
Thermal
References
Ajeel RK, Salim WSIW, Hasnan K. Design characteristics of symmetrical semicircle-corrugated channel on heat transfer enhancement with nanofluid. Int J Mech Sci. 2019;151:236–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.11.022.
Ajeel RK, Sopian K, Zulkifli R. A novel curved-corrugated channel model: thermal-hydraulic performance and design parameters with nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2021;120:105037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.105037.
Ajeel RK, Salim WSI, Sopian K, Yusoff MZ, Hasnan K, Ibrahim A, et al. Turbulent convective heat transfer of silica oxide nanofluid through corrugated channels: an experimental and numerical study. Int J Heat Mass Transfer. 2019;145:118806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118806.
Ajeel RK, Salim WSIW, Hasnan K. Experimental and numerical investigations of convection heat transfer in corrugated channels using alumina nanofluid under a turbulent flow regime. Chem Eng Res Des. 2019;148:202–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.06.003.
Abbasian Arani AA, Moradi R. Shell and tube heat exchanger optimization using new baffle and tube configuration. Appl Therm Eng. 2019;157:113736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.113736.
Cao X, Chen D, Du T, Liu Z, Ji S. Numerical investigation and experimental validation of thermo-hydraulic and thermodynamic performances of helical baffle heat exchangers with different baffle configurations. Int J Heat Mass Transfer. 2020;160:120181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120181.
Gu X, Chen W, Fang Y, Song S, Wang C, Wang Y. Analysis of flow dead zone in shell side of a heat exchanger with torsional flow in shell side. Appl Therm Eng. 2020;180:115792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115792.
Vivekanandan M, Venkatesh R, Periyasamy R, Mohankumar S, Devakumar L. Experimental and CFD investigation of helical coil heat exchanger with flower baffle. Mater Today: Proc. 2021;37:2174–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.642.
Ghalambaz M, Aljaghtham M, Chamkha AJ, Fteiti M, Abdullah A. Latent heat thermal energy storage in a shell-tube: A wavy partial layer of metal foam over tubes. J Energy Storage. 2023;59:106493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.106493.
Aghaei A. Thermal-hydraulic analysis of Syltherm 800 thermal oil / γ-AlOOH nanofluid in a baffled shell and tube heat exchanger equipped with corrugated helical tube with two-phase approach. Eng Anal Boundary Elem. 2023;146:668–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2022.11.005.
Abbasian Arani AA, Uosofvand H. Different tube bundles effect on the shell-and-tube heat exchanger performance. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow. 2021;ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). doi:https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-10-2020-0646.
Wang D, Wang H, Xing J, Wang Y. Investigation of the thermal-hydraulic characteristics in the shell side of heat exchanger with quatrefoil perforated plate. Int J Therm Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106580.
El-Said EMS, Elsheikh AH, El-Tahan HR. Effect of curved segmental baffle on a shell and tube heat exchanger thermohydraulic performance: Numerical investigation. Int J Therm Sci. 2021;165:106922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.106922.
Thondiyil D, Kizhakke KS. Optimization of a shell and tube heat exchanger with staggered baffles using Taguchi method. Mater Today: Proc. 2021;46:9983–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.04.092.
Liu Y, Wen J, Wang S, Tu J. Numerical investigation on the shell and tube heat exchanger with baffle leakage zones blocked. Int J Therm Sci. 2021;165:106959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.106959.
Saffarian MR, Fazelpour F, Sham M. Numerical study of shell and tube heat exchanger with different cross-section tubes and combined tubes. Int J Energy Environ Eng. 2019;10(1):33–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-019-0297-9.
Ajeel RK, Saiful-Islam W, Sopian K, Yusoff MZ. Analysis of thermal-hydraulic performance and flow structures of nanofluids across various corrugated channels: an experimental and numerical study. Therm Sci Eng Progr. 2019;19:100604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2020.100604.
Naqvi SMA, Elfeky KE, Cao Y, Wang Q. Numerical analysis on performances of shell side in segmental baffles, helical baffles and novel clamping anti-vibration baffles with square twisted tubes shell and tube heat exchangers. Energy Proc. 2019;158:5770–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.553.
Navickaitė K, Mocerino A, Cattani L, Bozzoli F, Bahl C, Liltrop K, et al. Enhanced heat transfer in tubes based on vascular heat exchangers in fish: experimental investigation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;137:192–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.03.067.
Khaledabadi FM, Fattahi A. Thermo-hydrodynamic analysis of a nanofluid flow over diamond-shaped tubes array of a heat exchanger. Energy Sourc, Part: Recov, Utilization, Environ Effects. 2020;2020:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1825566.
Alnakeeb MA, Saad MA, Hassab MA. Numerical investigation of thermal and hydraulic performance of fin and flat tube heat exchanger with various aspect ratios. Alex Eng J. 2021;60(5):4255–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.03.036.
Abbasian Arani AA, Uosofvand H. Double-pass shell-and-tube heat exchanger performance enhancement with new combined baffle and elliptical tube bundle arrangement. Int J Therm Sci. 2021;167:106999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.106999.
Ben Slimene M, Poncet S, Bessrour J, Kallel F. Numerical investigation of the flow dynamics and heat transfer in a rectangular shell-and-tube heat exchanger. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2022;32:101873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.101873.
Zaboli M, Ajarostaghi SSM, Noorbakhsh M, Delavar MA. Effects of geometrical and operational parameters on heat transfer and fluid flow of three various water based nanofluids in a shell and coil tube heat exchanger. SN Appl Sci. 2019;1(11):1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1431-2.
Singh SK, Sarkar J. Improving hydrothermal performance of hybrid nanofluid in double tube heat exchanger using tapered wire coil turbulator. Adv Powder Technol. 2020;31(5):2092–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.03.002.
Singh Rajput N, Dilipbhai Shukla D, Ishan L, Seshu MK. Enhancement of Nusselt number by using CNT and CuO nanofluids in heat exchangers. Mater Today: Proc. 2021;47:6508–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.190.
Bashtani I, Esfahani JA, Kim KC. Effects of water-aluminum oxide nanofluid on double pipe heat exchanger with gear disc turbulators: a numerical investigation. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2021;124:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.05.001.
Bahiraei M, Naseri M, Monavari A. Irreversibility features of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger fitted with novel trapezoidal oblique baffles: Application of a nanofluid with different particle shapes. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2021;126:105352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105352.
Kaushik S, Singh S, Panwar K. Comparative analysis of thermal and fluid flow behaviour of diverse nano fluid using Al2O3, ZnO, CuO nano materials in concentric spiral tube heat exchanger. Mater Today: Proc. 2021;46:6625–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.04.100.
Naik B, Hosmani AK, Kerur SM, Jadhav CC, Benni S, Annigeri S, et al. Numerical analysis of two tube helical heat exchanger using various nano-fluids. Mater Today: Proc. 2021;47:3137–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.187.
Tian M-W, Abidi A, Yan S-R, Toghraie D, Degani M. Economic cost and efficiency analysis of the employment of inserting rods with helical fins in a shell and tube heat exchanger under magnetic field and filled with nanofluid. Ain Shams Eng J. 2022;13(4):101651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2021.11.020.
Çolak AB, Akgul D, Mercan H, Dalkılıç AS, Wongwises S. Estimation of leading heat transfer parameters of shell-helical coiled tube heat exchangers by machine learning. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2023;2023:102713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2023.102713.
Wu Y, Rong J, Wang D, Zhao X, Meng L, Arıcı M, et al. Synergistic enhancement of heat transfer and thermal storage characteristics of shell and tube heat exchanger with hybrid nanoparticles for solar energy utilization. J Clean Prod. 2023;2023:135882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.135882.
Soltani H, Soltani M, Nathwani J. Optimization of thermal energy storage: Evaluation of natural convection and melting-solidification time of eccentricity for a rotational shell-and-tube unit. J Energy Storage. 2023;58:106423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.106423.
Ajeel RK, Zulkifli R, Sopian K, Fayyadh SN, Fazlizan A, Ibrahim A. Numerical investigation of binary hybrid nanofluid in new configurations for curved-corrugated channel by thermal-hydraulic performance method. Powder Technol. 2021;385:144–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2021.02.055.
Ajeel RK, Sopian K, Zulkifli R. Thermal-hydraulic performance and design parameters in a curved-corrugated channel with L-shaped baffles and nanofluid. J Energy Storage. 2021;34:101996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101996.
Hamad AJ, Ajeel RK. Combined effect of oblique ribs and a nanofluid on the thermal-hydraulic performance of a corrugated channel: numerical study. J Eng Phys Thermophys. 2022;95(4):970–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-022-02552-5.
Irshad K, Islam N, Zahir MH, Pasha AA, AbdelGawad AF. Thermal performance investigation of Therminol55/MWCNT+CuO nanofluid flow in a heat exchanger from an exergy and entropy approach. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2022;34:102010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.102010.
Bartsch H-J. 6 - Differential geometry. In: Bartsch H-J, editor. Handbook of mathematical formulas. Academic Press; 1974. p. 303–29.
Ajeel RK, Salim WSIW, Hasnan K. Thermal performance comparison of various corrugated channels using nanofluid: numerical study. Alex Eng J. 2019;58(1):75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2018.12.009.
Ajeel RK, Salim WSIW, Hasnan K. Influences of geometrical parameters on the heat transfer characteristics through symmetry trapezoidal-corrugated channel using SiO2-water nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2019;101:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2018.12.016.
Ajeel RK, Sopian K, Zulkifli R, Fayyadh SN, Kareem HA. Assessment and analysis of binary hybrid nanofluid impact on new configurations for curved-corrugated channel. Adv Powder Technol. 2021;32(10):3869–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.08.041.
Ajeel RK, Salim WSIW, Hasnan K. Numerical investigations of heat transfer enhancement in a house shaped-corrugated channel: combination of nanofluid and geometrical parameters. Therm Sci Eng Progr. 2020;17:100376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2019.100376.
Shi X, Wang Y, Huai X, Cheng K. Influence of geometrical parameters on thermal-hydraulic performance and entropy generation in cross-wavy channels with variable air properties. Appl Therm Eng. 2019;157:113714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.113714.
Witte L, Shamsundar N. A thermodynamic efficiency concept for heat exchange devices. 1983.
Dalkilic AS, Küçükyıldırım BO, Akdogan Eker A, Çebi A, Tapan S, Jumpholkul C, et al. Experimental investigation on the viscosity of water-CNT and antifreeze-CNT nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2017;80:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.11.011.
Sinnot R, Towler G. Chemical engineering design. Elsevier; 2009.
Kraus AD, Aziz A, Welty J, Sekulic DP. Reviewer. Extended Surface Heat Transfer. Appl Mech Rev. 2001;54(5):B92. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1399680.
Colebrook C. Turbulent flow in pipes, with particular reference to the transition region between the smooth and rough pipe laws. J Inst Civ Eng. 1939;1939(11):133–56.
Petukhov BS. Heat transfer and friction in turbulent pipe flow with variable physical properties. In: Hartnett JP, Irvine TF, editors. Advances in heat transfer. Elsevier; 1970. p. 503–64.
Mellal M, Benzeguir R, Sahel D, Ameur H. Hydro-thermal shell-side performance evaluation of a shell and tube heat exchanger under different baffle arrangement and orientation. Int J Therm Sci. 2017;121:138–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.07.011.
Luo C, Song K. Thermal performance enhancement of a double-tube heat exchanger with novel twisted annulus formed by counter-twisted oval tubes. Int J Therm Sci. 2021;164:106892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2021.106892.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mazdak, S., Sheikhzadeh, G.A. & Fattahi, A. Numerical analysis of a heat exchanger with curved segmental baffle and Cassini oval cross-section tubes in various bundle arrangements. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 8459–8476 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12062-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12062-y