Abstract
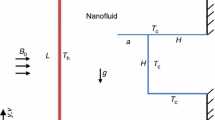
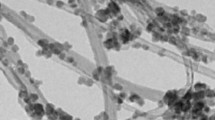
Evaluation of the natural convection heat transfer in different systems is widely used to increase the performance of the energy applications systems. In this paper, the internal natural heat transfer of Fe3O4-water nanofluid, MWCNT-water nanofluid and Fe3O4/MWCN-water hybrid nanofluid at two concentrations of 0.1 and 0.3% under constant and periodic magnetic field is experimentally studied to evaluate the effects of different nanoparticles and magnetic fields on increase in the natural convectional of the system. Fe3O4 nanoparticles are used to consider the impact of ferrohydrodynamic. One of the vertical walls is under high temperature, the opposite is under low temperature, and the other sides are fully insulated. The different nanoparticle volume fractions, hot wall temperature and angle of the enclosure in the conditions of the various magnetic fields have been used to find the highest rate of natural convection. The magnetic field is considered in the direction of the buoyancy force. The cost of natural convection heat transfer, exergoeconomic and environmental parameters was studied. The results showed that the optimum angle of square enclosure in the various magnetic fields was about 30°. Also, CO2 mitigation of the cavity with a periodic magnetic field was improved by 25.5% higher than the cavity without a magnetic field. Also, the cost of natural convection heat transfer of the cavity using periodic and constant magnetic fields was about 0.155 and 0.169 $ kW-1, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(E\,_{{{\text{in}}}}\) :
-
Embodied energy/kWh
- \(E_{{{\text{ex}}}}\) :
-
Annual exergy/kWh year-1
- \({E}_{\mathrm{en}}\) :
-
Annual energy/kWh year-1
- H :
-
Height of hot surface/m
- h :
-
Natural convection heat transfer coefficient/W m-2 K-1
- i :
-
Interest rate/%
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity/W m-1 K-1
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- q :
-
Heat transfer/W
- n :
-
Life time/years
- R :
-
Exergoeconomic/kWh $-1
- S :
-
Salvage value/$
- T :
-
Temperature/K
- \(Z_{{{\text{co}}_{2} }}\) :
-
Enviroeconomic parameter/$
- W :
-
Width of the hot surface/m
- \(\beta\) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient/K-1
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density/kg m-3
- \(\vartheta\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity/m2 s-1
- \(\varphi_{{{\text{co}}_{2} }}\) :
-
Environmental parameter/ton \({\mathrm{CO}}_{2}\)
- 1, 2, 3:
-
Number of thermocouple
- c :
-
Cold side
- corr:
-
Corrected parameter
- en:
-
Energy
- ex:
-
Exergy
- h :
-
Hot side
- nf:
-
Nanofluid, nanofluid properties at mean temperature
- nf,h:
-
Nanofluid properties at hot temperature
- pr:
-
Product
- AMC:
-
Annual maintenance price/$ year-1
- CHT:
-
The cost of natural convection heat transfer/$ kW-1
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- CRF:
-
Capital recovery factor
- FAC:
-
First annual price/$ year-1
- FESEM:
-
Field emission scanning electron microscope
- FHD:
-
Ferrohydrodynamic
- Gr:
-
Grashof number
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- MHD:
-
Magnetohydrodynamic
- MWCN:
-
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number
- UAC:
-
Uniform annual cost/$ year-1
References
Shoeibi S, Ali Agha Mirjalily S, Kargarsharifabad H, Panchal H, Dhivagar R. Comparative study of double-slope solar still, hemispherical solar still, and tubular solar still using Al2O3/water film cooling: a numerical study and CO2 mitigation analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(43):65353–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20437-1.
Rahbar N, Esfahani JA. Productivity estimation of a single-slope solar still: theoretical and numerical analysis. Energy. 2013;49:289–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.10.023.
Kargarsharifabad H. Optimization of arrangement of conducting fins and insulated obstacles inside a cavity: the couple of numerical solutions and genetic algorithm methods. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147(1):421–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10276-y.
Hussain S, Shoeibi S, Armaghani T. Impact of magnetic field and entropy generation of Casson fluid on double diffusive natural convection in staggered cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;127:105520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105520.
Haq RU, Shah SS, Algehyne EA, Tlili I. Heat transfer analysis of water based SWCNTs through parallel fins enclosed by square cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2020;119:104797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104797.
Zhang X, Lorente S, Wemhoff AP. Modeling the thermal energy storage capability of a phase change material confined in a rectangular cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;126:105367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105367.
Moria H. Natural convection in an L-shape cavity equipped with heating blocks and porous layers. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;126:105375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105375.
Barman P, Rao PS. Effect of aspect ratio on natural convection in a wavy porous cavity submitted to a partial heat source. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;126:105453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105453.
Massoudi MD, Ben Hamida MB, Almeshaal MA, Hajlaoui K. The influence of multiple fins arrangement cases on heat sink efficiency of MHD MWCNT-water nanofluid within tilted T-shaped cavity packed with trapezoidal fins considering thermal emission impact. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;126:105468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105468.
Selimefendigil F, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection in superposed nanofluid and porous layers in square enclosure with inner rotating cylinder. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;124–125:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.03.007.
Giwa SO, Sharifpur M, Ahmadi MH, Meyer JP. A review of magnetic field influence on natural convection heat transfer performance of nanofluids in square cavities. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;145(5):2581–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09832-3.
Buschmann MH. Critical review of heat transfer experiments in ferrohydrodynamic pipe flow utilising ferronanofluids. Int J Therm Sci. 2020;157:106426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106426.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Alizadeh A. An experimental study of Cu–water nanofluid flow inside serpentine tubes with variable straight-section lengths. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2015;61:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2014.09.014.
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Davoudi S, Dibaei MH. Performance of agitated-vessel U tube heat exchanger using spiky twisted tapes and water based metallic nanofluids. Chem Eng Res Des. 2018;133:26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.02.030.
Ahmadi MH, Ahmadi MA, Nazari MA, Mahian O, Ghasempour R. A proposed model to predict thermal conductivity ratio of Al2O3/EG nanofluid by applying least squares support vector machine (LSSVM) and genetic algorithm as a connectionist approach. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(1):271–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7035-z.
Ramezanizadeh M, Alhuyi Nazari M, Ahmadi MH, Lorenzini G, Pop I. A review on the applications of intelligence methods in predicting thermal conductivity of nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138(1):827–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08154-3.
Pordanjani AH, Aghakhani S, Afrand M, Sharifpur M, Meyer JP, Xu H, et al. Nanofluids: physical phenomena, applications in thermal systems and the environment effects- a critical review. J Clean Product. 2021;320:128573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128573.
Mehryan SAM, Kashkooli FM, Ghalambaz M, Chamkha AJ. Free convection of hybrid Al2O3-Cu water nanofluid in a differentially heated porous cavity. Adv Powder Technol. 2017;28(9):2295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.06.011.
Hatami M, Zhou J, Geng J, Song D, Jing D. Optimization of a lid-driven T-shaped porous cavity to improve the nanofluids mixed convection heat transfer. J Mol Liq. 2017;231:620–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.02.048.
Sharifpur M, Giwa SO, Lee K-Y, Ghodsinezhad H, Meyer JP. Experimental investigation into natural convection of zinc oxide/water nanofluids in a square cavity. Heat Transfer Eng. 2021;42(19–20):1675–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/01457632.2020.1818384.
Armaghani T, Kasaeipoor A, Alavi N, Rashidi MM. Numerical investigation of water-alumina nanofluid natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation in a baffled L-shaped cavity. J Mol Liq. 2016;223:243–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.07.103.
Ahmed SE, Rashed ZZ. MHD natural convection in a heat generating porous medium-filled wavy enclosures using Buongiorno’s nanofluid model. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2019;14:100430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2019.100430.
Mliki B, Abbassi MA, Guedri K, Omri A. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in an L-shaped enclosure in the presence of nanofluid. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2015;18(3):503–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2015.04.008.
Mansour MA, Bakeir MA, Chamkha A. Natural convection inside a C-shaped nanofluid-filled enclosure with localized heat sources. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2014;24(8):1954–78. https://doi.org/10.1108/hff-06-2013-0198.
Nwaokocha C, Momin M, Giwa S, Sharifpur M, Murshed SMS, Meyer JP. Experimental investigation of thermo-convection behaviour of aqueous binary nanofluids of MgO-ZnO in a square cavity. Therm Sci Eng Prog. 2021;28:101057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2021.101057.
Giwa SO, Sharifpur M, Meyer JP. Experimental study of thermo-convection performance of hybrid nanofluids of Al2O3-MWCNT/water in a differentially heated square cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2020;148:119072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.119072.
Mehryan SAM, Izadpanahi E, Ghalambaz M, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection flow caused by an oscillating cylinder in a square cavity filled with Cu–Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137(3):965–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08012-2.
Ismael MA, Armaghani T, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection and entropy generation in a lid-driven cavity filled with a hybrid nanofluid and heated by a triangular solid. Heat Transf Res. 2018;49(17):1645–65. https://doi.org/10.1615/HeatTransRes.2018020222.
Karimdoost Yasuri A, Izadi M, Hatami H. Numerical study of natural convection in a square enclosure filled by nanofluid with a baffle in the presence of magnetic field. Iran J Chem Chem Eng. 2019;38(5):209–20. https://doi.org/10.30492/ijcce.2019.32165.
Matt CFT, Quaresma JNN, Cotta RM. Analysis of magnetohydrodynamic natural convection in closed cavities through integral transforms. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;113:502–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.05.043.
Hasanuzzaman M, Öztop HF, Rahman MM, Rahim NA, Saidur R, Varol Y. Magnetohydrodynamic natural convection in trapezoidal cavities. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2012;39(9):1384–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2012.08.009.
Gireesha BJ, Shankaralingappa BM, Prasannakumar BC, Nagaraja B. MHD flow and melting heat transfer of dusty Casson fluid over a stretching sheet with Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model. Int J Ambient Energy. 2020;43:2931–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2020.1785938.
Eid MR, Mabood F. Entropy analysis of a hydromagnetic micropolar dusty carbon NTs-kerosene nanofluid with heat generation: Darcy-Forchheimer scheme. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;143(3):2419–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09928-w.
Zhang J-K, Li B-W, Chen Y-Y, Li H-L, Tian X-Y. Critical parameter research on natural convection of radiation-magnetohydrodynamics in a square cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;68:114–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.08.022.
Al-Farhany K, Al-Chlaihawi KK, Al-dawody MF, Biswas N, Chamkha AJ. Effects of fins on magnetohydrodynamic conjugate natural convection in a nanofluid-saturated porous inclined enclosure. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2021;126:105413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105413.
Shaker H, Abbasalizadeh M, Khalilarya S, Motlagh SY. Two-phase modeling of the effect of non-uniform magnetic field on mixed convection of magnetic nanofluid inside an open cavity. Int J Mech Sci. 2021;207:106666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106666.
Sáchica D, Treviño C, Martínez-Suástegui L. Numerical study of magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection and entropy generation of Al2O3-water nanofluid in a channel with two facing cavities with discrete heating. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2020;86:108713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2020.108713.
Ghalambaz M, Sabour M, Sazgara S, Pop I, Trâmbiţaş R. Insight into the dynamics of ferrohydrodynamic (FHD) and magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) nanofluids inside a hexagonal cavity in the presence of a non-uniform magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater. 2020;497:166024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166024.
Rahman MM, Parvin S, Saidur R, Rahim NA. Magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection in a horizontal channel with an open cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;38(2):184–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2010.12.005.
Aminossadati SM, Ghasemi B, Kargar A. Computational analysis of magnetohydrodynamic natural convection in a square cavity with a thin fin. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2014;46:154–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2014.03.002.
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD. Numerical modeling of magnetohydrodynamic CuO—water transportation inside a porous cavity considering shape factor effect. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2017;529:705–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.06.046.
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD. Ferrohydrodynamic and magnetohydrodynamic effects on ferrofluid flow and convective heat transfer. Energy. 2014;75:400–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.07.089.
Giwa SO, Sharifpur M, Meyer JP. Experimental investigation into heat transfer performance of water-based magnetic hybrid nanofluids in a rectangular cavity exposed to magnetic excitation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2020;116:104698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104698.
Teamah MA, El-Maghlany WM. Augmentation of natural convective heat transfer in square cavity by utilizing nanofluids in the presence of magnetic field and uniform heat generation/absorption. Int J Therm Sci. 2012;58:130–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2012.02.029.
Kargarsharifabad H. Experimental and numerical study of natural convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a cubic enclosure under constant and alternating magnetic fields. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2020;119:104957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104957.
Giwa SO, Sharifpur M, Meyer JP. Effects of uniform magnetic induction on heat transfer performance of aqueous hybrid ferrofluid in a rectangular cavity. Appl Therm Eng. 2020;170:115004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115004.
Brusly Solomon A, van Rooyen J, Rencken M, Sharifpur M, Meyer JP. Experimental study on the influence of the aspect ratio of square cavity on natural convection heat transfer with Al2O3/Water nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2017;88:254–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2017.09.007.
Joubert JC, Sharifpur M, Solomon AB, Meyer JP. Enhancement in heat transfer of a ferrofluid in a differentially heated square cavity through the use of permanent magnets. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;443:149–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.07.062.
Metergroup. Thermal properties analyzer KD2 pro instrument. In: metergroup, editor.
Ho CJ, Liu WK, Chang YS, Lin CC. Natural convection heat transfer of alumina-water nanofluid in vertical square enclosures: an experimental study. Int J Therm Sci. 2010;49(8):1345–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2010.02.013.
Fath HES, El-Samanoudy M, Fahmy K, Hassabou A. Thermal-economic analysis and comparison between pyramid-shaped and single-slope solar still configurations. Desalination. 2003;159(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(03)90046-4.
Shoeibi S, Rahbar N, Abedini Esfahlani A, Kargarsharifabad H. Energy matrices, economic and environmental analysis of thermoelectric solar desalination using cooling fan. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147(17):9645–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11217-7.
Saini V, Sahota L, Jain VK, Tiwari GN. Performance and cost analysis of a modified built-in-passive condenser and semitransparent photovoltaic module integrated passive solar distillation system. J Energy Storage. 2019;24:100809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2019.100809.
Kabeel AE, Hamed AM, El-Agouz SA. Cost analysis of different solar still configurations. Energy. 2010;35(7):2901–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2010.03.021.
Yousef MS, Hassan H, Sekiguchi H. Energy, exergy, economic and enviroeconomic (4E) analyses of solar distillation system using different absorbing materials. Appl Therm Eng. 2019;150:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.01.005.
Joshi P, Tiwari GN. Energy matrices, exergo-economic and enviro-economic analysis of an active single slope solar still integrated with a heat exchanger: a comparative study. Desalination. 2018;443:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.05.012.
Shoeibi S, Kargarsharifabad H, Rahbar N, Ahmadi G, Safaei MR. Performance evaluation of a solar still using hybrid nanofluid glass cooling-CFD simulation and environmental analysis. Sustain Energy Technol Assess. 2022;49:101728.
Shoeibi S, Rahbar N, Abedini Esfahlani A, Kargarsharifabad H. Improving the thermoelectric solar still performance by using nanofluids—experimental study, thermodynamic modeling and energy matrices analysis. Sustain Energy Technol Assess. 2021;47:101339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101339.
Parsa SM, Rahbar A, Javadi YD, Koleini MH, Afrand M, Amidpour M. Energy-matrices, exergy, economic, environmental, exergoeconomic, enviroeconomic, and heat transfer (6E/HT) analysis of two passive/active solar still water desalination nearly 4000m: altitude concept. J Clean Prod. 2020;261:121243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121243.
Beckwith TG, Marangoni RD, Lienhard JH. Mechanical measurements. Pearson Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ; 2007.
Acknowledgements
Hadi Kargarsharifabad would like to express gratitude to Semnan Branch, Islamic Azad University, for their close cooperation regarding this research that was supported by the Office of the Vice-Chancellor for Research, Islamic Azad University, Semnan Branch, with Grant No. 17751-19/11/1395.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization, and writing—review and editing. HK contributed to methodology, conceptualization, supervision, validation, project administration, formal analysis and writing—review and editing. MS contributed to methodology, conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization, and writing—review and editing. JPM contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shoeibi, S., Kargarsharifabad, H., Sharifpur, M. et al. Hybrid nanofluid natural convection in the square enclosure with periodic magnetic field: experimental investigation and economic evaluation. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 2527–2545 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11924-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11924-1