Abstract
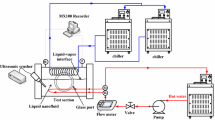
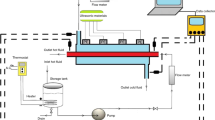
In this research, the pool boiling heat transfer of the Fe3O4/deionized water nanofluid was studied experimentally under applying mechanical vibration. The results obtained from studying concentration also showed that the boiling heat transfer increases by increasing concentration at low values, while it decreases by increasing concentration at high values. Therefore, for the nanofluid, the optimum value of the boiling heat transfer coefficient was evaluated at a concentration of 0.1 vol%. Besides, the study of the effect of mechanical vibration on the boiling process showed that the mechanical vibration applied at all vibrational frequencies leads to improving the boiling heat transfer. In the current research, by applying mechanical vibration at the optimum concentration and a vibrational frequency of 33 Hz, the maximum increase in the boiling heat transfer coefficient was reported to be equal to 87.26%.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peng Y, et al. Analysis of the effect of roughness and concentration of Fe3O4/water nanofluid on the boiling heat transfer using the artificial neural network: an experimental and numerical study. Int J Therm Sci. 2021;163: 106863.
Tian Z, et al. Experimental study of the effect of various surfactants on surface sediment and pool boiling heat transfer coefficient of silica/DI water nano-fluid. Powder Technol. 2019;356:391–402.
Salimpour MR, et al. Providing a model for Csf according to pool boiling convection heat transfer of water/ferrous oxide nanofluid using sensitivity analysis. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2019;30(6):2867–81.
Bergles AE. Enhancement of pool boiling. Int J Refrig. 1997;20(8):545–51.
Sathyabhama A, Dinesh A. Augmentation of heat transfer coefficient in pool boiling using compound enhancement techniques. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;119:176–88.
Abadi SNR, Ahmadpour A, Meyer J. Effects of vibration on pool boiling heat transfer from a vertically aligned array of heated tubes. Int J Multiph Flow. 2019;118:97–112.
Chang T-B, Wang Z-L. Experimental investigation into effects of ultrasonic vibration on pool boiling heat transfer performance of horizontal low-finned U-tube in TiO2/R141b nanofluid. Heat Mass Transf. 2016;52(11):2381–90.
You S, Simon TW, Bar-Cohen A. A technique for enhancing boiling heat transfer with application to cooling of electronic equipment. In: [1992 Proceedings] intersociety conference on thermal phenomena in electronic systems. 1992; IEEE.
Alangar S. Effect of boiling surface vibration on heat transfer. Heat Mass Transf. 2017;53(1):73–9.
Bakhtiari R, et al. Preparation of stable TiO2-Graphene/Water hybrid nanofluids and development of a new correlation for thermal conductivity. Powder Technol. 2021;385:466–77.
Kumar N, et al. Experimental study on pool boiling and Critical Heat Flux enhancement of metal oxides based nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2018;96:37–42.
Neto AR, Oliveira J, Passos J. Heat transfer coefficient and critical heat flux during nucleate pool boiling of water in the presence of nanoparticles of alumina, maghemite and CNTs. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;111:1493–506.
Kwon YC, et al. Experimental study on CHF enhancement in pool boiling using ultrasonic field. J Ind Eng Chem. 2005;11(5):631–7.
Ali HM, et al. Experimental investigation of nucleate pool boiling heat transfer enhancement of TiO2-water based nanofluids. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;113:1146–51.
Fang X, et al. Heat transfer and critical heat flux of nanofluid boiling: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2016;62:924–40.
Ciloglu D, Bolukbasi A. A comprehensive review on pool boiling of nanofluids. Appl Therm Eng. 2015;84:45–63.
Raveshi MR, et al. Experimental investigation of pool boiling heat transfer enhancement of alumina–water–ethylene glycol nanofluids. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci. 2013;44:805–14.
Prisnyakov V, Prisnyakov K. Action of vibrations on heat and mass transfer in boiling. J Eng Phys Thermophys. 2001;74(4):1015–23.
Wen D, Ding Y. Experimental investigation into the pool boiling heat transfer of aqueous based γ-alumina nanofluids. J Nanopart Res. 2005;7(2):265–74.
Tu J, Dinh N, Theofanous T. An experimental study of nanofluid boiling heat transfer. In: Proceedings of 6th international symposium on heat transfer, Beijing, China; 2004.
Salari E, et al. Boiling thermal performance of TiO2 aqueous nanofluids as a coolant on a disc copper block. Periodica Polytech Chem Eng. 2016;60(2):106–22.
Salari E, et al. Thermal behavior of aqueous iron oxide nano-fluid as a coolant on a flat disc heater under the pool boiling condition. Heat Mass Transf. 2017;53(1):265–75.
Kathiravan R, et al. Pool boiling characteristics of multiwalled carbon nanotube (CNT) based nanofluids over a flat plate heater. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54(5–6):1289–96.
Sarafraz M, Hormozi F. Nucleate pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of dilute Al2O3–ethyleneglycol nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;58:96–104.
Shi M, et al. Study on pool boiling heat transfer of nano-particle suspensions on plate surface. J Enhanc Heat Transf. 2007;14(3):223–31.
Chopkar M, et al. Pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of ZrO2–water nanofluids from a flat surface in a pool. Heat Mass Transf. 2008;44(8):999–1004.
Liu Z-H, Liao L. Sorption and agglutination phenomenon of nanofluids on a plain heating surface during pool boiling. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2008;51(9–10):2593–602.
You S, Kim J, Kim K. Effect of nanoparticles on critical heat flux of water in pool boiling heat transfer. Appl Phys Lett. 2003;83(16):3374–6.
Park K-A, Bergles A. Ultrasonic enhancement of saturated and subcooled pool boiling. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1988;31(3):664–7.
Iida Y, Tsutsui K. Effects of ultrasonic waves on natural convection, nucleate boiling, and film boiling heat transfer from a wire to a saturated liquid. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci. 1992;5(1):108–15.
Vinko Z, Naim A. Boiling heat transfer from oscillating surface. J Enhanc Heat Transf. 1994;1(2):191–6.
Prisniakov V, et al. Heat exchange of the vibrating heat source within the liquid capacity. Space Technol Sci. 1990;1:871–7.
Navruzov YV, Mamontov P, Stoychev A. Subcooled liquid pool boiling heat transfer on a vibrating heating surface. Heat Transf Res. 1992;24(6):771–6.
Markov I. The effect of vibration on the effect of long puzyreobrazuyuschee: boiling and condensation [Inter-university collection of scientific papers]. Riga: EPI; 1980. p. 33–9.
Moffat RJ. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci. 1988;1(1):3–17.
Abareshi M, et al. Fabrication, characterization and measurement of thermal conductivity of Fe3O4 nanofluids. J Magn Magn Mater. 2010;322(24):3895–901.
Rohsenow WM. A method of correlating heat transfer data for surface boiling of liquids. Cambridge: MIT Division of Industrial Cooporation; 1951.
Shahmoradi Z, Etesami N, Esfahany MN. Pool boiling characteristics of nanofluid on flat plate based on heater surface analysis. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2013;47:113–20.
Soltani S, Etemad SG, Thibault J. Pool boiling heat transfer performance of Newtonian nanofluids. Heat Mass Transf. 2009;45(12):1555–60.
Junhong L, et al. Experiments and mechanism analysis of pool boiling heat transfer enhancement with water-based magnetic fluid. Heat Mass Transf. 2004;41(2):170–5.
Prisnyakov V, et al. Characteristics of heat emission from a vibrating heat source in a vessel with liquid. High Temp. 1992;30(1):90–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Boroumand Ghahnaviyeh, M., Abdollahi, A. Experimental study of the effect of mechanical vibration on pool boiling heat transfer coefficient of Fe3O4/deionized water nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 14343–14357 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11591-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11591-2