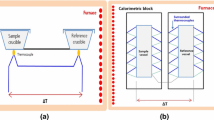
Abstract
Precise determination of the metallic rubidium (Rb) inside a Rb bulb is critical to the life of on-board RAFS. Calorimetric mass estimation is an accurate and non-destructive method to validate the Rb content, without deforming the glass bulb under test. We present a faithful and precise calorimetric method using an indigenous cold-point-formation apparatus (CPA), which efficiently collects the metallic Rb in the glass bulb for a precise calorimetric estimation (\(\pm 20 \mu g\)). We have also performed repeated mass estimations with our calorimetric method revealing a maximum estimation difference only of about \(10\,\mu\)g. Further, with the ongoing life test of five Rb bulbs, we report a preliminary estimate of Rb consumption rate inside our bulbs as 0.64 \(\mu g/\sqrt{h}r\), which is in good agreement with the previously reported results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camparo J. The rubidium atomic clock and basic research. Phys Today. 2007;60(11):33–9.
Riley W. A History of the Rubidium Frequency Standard. IEEE UFFC-Hist. 2019; 2.
Jaduszliwer B, Camparo J. Past, present and future of atomic clocks for GNSS. GPS Sol. 2021;25(1):1–13.
Batori E, Almat N, Affolderbach C, Mileti G. GNSS-grade space atomic frequency standards: current status and ongoing developments. Adv Space Res. 2021;68(12):4723–33.
Venkatraman V, Shea H, Petremand Y, de Rooij N, Affolderbach C, Mileti G. Low-Power chip-scale rubidium plasma light source for miniature atomic clocks. In: 2011 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control and the European Frequency and Time Forum (FCS) Proceedings 2011; pp. 1-4).
Almat N, Gharavipour M, Moreno W, Affolderbach C, Mileti G. Long-Term Stability Analysis towards \(<10^{-14}\) Level for Compact POP Rb Cell Atomic Clock. In: 2019 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and European Frequency and Time Forum (EFTF/IFC) 2019, pp. 1–2.
Bell WE, Bloom AL, Lynch J. Alkali metal vapor spectral lamps. Rev Sci Instr. 1961;32(6):688–92.
Huang M, Bazurto R, Camparo J. Fluorescence quenching and the ringmode to red-mode transition in alkali inductively coupled plasmas. J Appl Phys. 2018;123:043303.
Encalada NL, Jaduszliwer B, Lybarger WE, Camparo J. Noble-gas loss in alkali rf-duscharge lamps and its possible dependance on electron temperature. IEEE Trans Instr Meas. 2014;63(11):2642–50.
Gozzelino M, Micalizio S, Calosso CE, Godone A, Levi F. Kr-based buffer gas for Rb vapor-cell clocks. IEEE Trans Ultra, Ferr Freq Cont. 2020;68(4):1442–7.
Camparo J, Sesia I, Formichella V, Signorile G, Galleani L, Tavella P. Rubidium clock lamplight variations and long-term frequency instability: first analyses of multiyear GPS data. In: Proceedings of the 47th Annual Precise Time and Time Interval Systems and Applications Meeting 2016, pp. 150-156.
Volk CH, Frueholz RP, English TC, Lynch TJ, Riley W. Lifetime and Reliability of Rubidium Discharge Lamps for Use in Atomic Frequency Standards. Aerosp. Corp. El Segundo CA Chem. & Phys. Lab. 1984; 0084A:5404-30-1.
Frueholz RP, Wun-Fogle M, Eckert HU, Volk CH, Jones PF. Lamp reliability studies for improved satellite rubidium frequency standard. In: Proceedings of the 13th Annual Precise Time and Time Interval Systems and Applications Meeting 1981 pp. 767-790.
Klimcak CM, Huang M, Camparo J. Alkali metal consumption by discharge lamps fabricated from GE-180 aluminosilicate glass. In: 2015 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium & the European Frequency and Time Forum 2015 Apr 12 (pp. 180-187). IEEE.
Hohne G, Hemminger WF, Flammershiem HJ. Differential Scanning calorimetry. Spr. Sci. & Bus. Med. 2013.
Fundell KA, Klimcak CM, Camapro JC. Measurements of the Hg Fill Level in Low-Pressure Hg Discharge Lamps via Macrophotography. In: 2021 Joint Conference of the European Frequency and Time Forum and IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium 2021 Jul 7 (pp. 1-4).
Camparo J, Hagerman JO, McClelland TA. Long-term behavior of rubidium clocks in space. 2012 Eur. Freq. & Time Forum IEEE. 2012; 501-508.
Wunderlich B. Thermal Analysis. United States: Academic Press; 1990.
Steck DA. Rubidium 87 D line data. 2001.
Schawe J. Evaluation and interpretation of peak temperatures of dsc curves. 2016;1:6–9.
Dupuis RT, Lynch TJ, Vaccaro JR. Rubidium frequency standard for the GPS IIF program and modifications for the RAFSMOD program. In: Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Int. Freq. Cont. Symp. 2008; 655–660.
Mei G, Zhong D, An S, Zhao F, Qi F, Wang F, Ming G, Li W, Wang P. Main features of space rubidium atomic frequency standard for BeiDou satellites. 2016 Eur. Freq. & Time Forum IEEE. 2016; 1-4.
Cook RA, Frueholz RP. An improved rubidium consumption model for discharge lamps used in rubidium frequency standards. In: Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Frequency Control Symposium, IEEE. 1988. pp. 525-531.
Camparo J, Fathi G. Discharge lamps for Rb atomic clocks : The role of rf-power. In: 2009 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium Joint with the 22nd European Frequency and Time forum 2009 pp. 994-997. IEEE.
Huang M, Stapleton A, Camparo J. Lamplight stabilization for GPS Rb atomic clocks via RF-power control. IEEE Trans Ultr, Ferr Freq Cont. 2018;65(10):1804–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to NM Desai (Director SAC) for constant support and encouragement. In addition, we acknowledge the support from Niranjan Reddy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma Kesarkar, R., Attri, D., Saiyed, M.A.R. et al. Precise calorimetric rubidium mass estimation and its application to the rubidium atomic frequency standard (RAFS). J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 10049–10056 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11276-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11276-w