Abstract
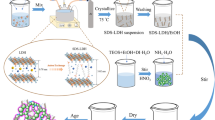
Hollow silica microsphere (h-SiO2) has been widely applied in the field of thermal insulation, catalyst supports and drug storage/delivery containers. In this research, h-SiO2 has been innovatively used as synergistic agent to enhance the flame retardancy of intumescent flame-retardant polystyrene. The synergistic effects of h-SiO2 on intumescent flame-retardant polystyrene have been studied by limiting oxygen index (LOI), UL-94 test and cone calorimeter test (CCT). When 0.5 mass% h-SiO2 was substituted for the intumescent flame-retardant additive, the LOI of polystyrene composite (PS/IFR/Si0.5) increased by 5 units and the composite preserved the V-0 rating. Manipulation of parameters from CCT indicated that the peak heat release rate was reduced by 27% for the PS/IFR/Si0.5 composite, whereas the total heat release decreased by 14.5% and the ratio of residue increased by 85.6% (from 13.2 to 24.5%) compared to those of the composite without h-SiO2. The synergistic effects of h-SiO2 on intumescent flame-retardant polystyrene are attributed to physical and chemical processes in the condensed phase. The morphologies of charred layer after CCT proved that h-SiO2 induced compact charred layer with enhanced thermal and gas barrier effect, which in turn protected the inner matrix from combustion and decreased specific extinction area by 24.2%.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kerekes Z, Restás Á, Lublóy É. The effects causing the burning of plastic coatings of fire-resisitant cables and its consequences. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(2):775–87.
Vuluga Z, Panaitescu DM, Sanporena CG, Radovici C, Gabor R, Nicolae CA, Corobea MC, Iorga M, Florea D. The effect of polystyrene blocks content and of type of elastomer blocks on the properties of block copolymer/layered silicate nanocomposites. J Alloys Comp. 2014;616:569–76.
Wang Y, Jiang H, Ni J, Chen J, Zhou H, Wang X, Xin F. Study on the effect of polyFR and its FR system on the flame retardancy and foaming behavior of polystyrene. RSC Adv. 2019;9:192–205.
Wang Y, Zhao J. Comparative study on flame retardancy of silica fume-based geopolymer activated by different activators. J Alloys Comp. 2018;743:108–14.
Attia NF, Saleh BK. Nover synthesis of renewable and green flame-retardant, antibacterial and reinforcement materials for styrene-butadiene rubber nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(3):1817–27.
Xu Y, Lv C, Shen R, Wang Z, Wang Q. Experimental investigation of thermal properties and fire behavior of carbon/epoxy laminate and its foam core sandwich composite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136(3):1237–47.
Morris S, Allchin CR, Zegers BN, Haftka JJH, Boon JP, Belpaire C. Distribution and fate of HBCD and TBBPA brominated flame retardants in north sea estuaries and aquatic food webs. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38:5497–504.
Poma G, Roscioli C, Guzzella L. PBDE, HBCD and novel brominated flame retardant contamination in sediments from Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy). Environ Monit Assess. 2014;186:7683–92.
Zhang H, Kuo YY, Gerecke AC, Wang J. Co-release of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) and nano- and microparticles from thermal cutting of polystyrene foams. Environ Sci Technol. 2012;46:10990–6.
Beach MW, Rondan NG, Froese RD, Gerhart BB, Green JG, Stobby BG. Studies of degradation enhancement of polystyrene by flame retardant additives. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2008;93:1664–73.
Law RJ, Kohler M, Heeb NV, Gerecke AC, Schmid P, Voorspoels S, Covaci A, Becher G, Janák K, Thomsen C. Hexabromocyclododecane challenges scientists and regulators. Environ Sci Technol. 2005;39:281A–7A.
Schütz MR, Kalo H, Lunkenbein T, Breu J, Wilkie CA. Intumescent-like behavior of polystyrene synthetic clay nanocomposites. Polymer. 2011;52:3288–94.
Kim H, Park JW, Lee JH, Jang SW, Kim HJ, Choi Y. Clay-organic intumescent hybrid system for the synergetic flammability of polymer nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:2009–14.
Lu H, Wilkie CA. Study on intumescent flame retarded polystyrene composites with improved flame retardancy. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2010;95:2388–95.
Ahmed L, Zhang B, Shen RQ, Agnew RJ, Park H, Cheng ZD, Mannan MS. Fire reaction properties of polystyrene-based nanocomposites using nanosilic and nanoclay as additives in cone calorimeter test. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:1853–65.
Zhou KQ, Gui Z, Hu Y. The influence of graphene based smoke suppression agents on reduced fire hazards of polystyrene composites. Compos Part A Appl S. 2016;80:217–27.
Durkin DP, Gallagher MJ, Frank BP, Knowlton ED, Trulove PC, Fairbrother DH, Fox DM. Phosphorus-functionalized multi-wall carbon nanotubes as flame-retardant additives for polystyrene and poly (methyl methacrylate). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;130:735–53.
Liu L, Xu XX. Polystyrene nanocomposites with improved combustion properties by using TMA-POSS and organic clay. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;214:743–9.
Gilman JW, Jackson CL, Borgan AB, Harris R. Flammability properties of polymer-layered-silicate nanocomposites. Polypropylene and polystyrene nanocomposites. Chem Mater. 2000;12:1866–73.
Chen YJ, Zhan J, Zhang P, Nie SB, Lu HD, Song L, Hu YA. Preparation of intumescent flame retardant poly(butylene succinate) using fumed silica as synergistic agent. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2010;49:8200–8.
Gong J, Tian NN, Wen X, Chen XC, Liu J, Jiang ZW. Synergistic effect of fumed silica with Ni2O3 on improving flame retardancy of poly(lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stabil. 2014;104:18–27.
Shen RQ, Hatanaka LC, Ahmed L, Agnew RJ, Mannan MS, Wang QS. Cone calorimeter analysis of flame retardant poly(methyl methacrylate)-silica nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128(3):1443–51.
Chigwada G, Kandare E, Wang D, Majoni S, Mlambo D, Wilkie CA. Thermal stability and degradation kinetics of polystyrene/organically-modified montmorillonite nanocomposites. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2008;8:1927–36.
Kashiwagi T, Shields JR, Harris RH, Davis RD. Flame-retardant mechanism of silica: effects of resin molecular weight. J Appl Polym Sci. 2003;87:1541–53.
Ye L, Wu QH, Qu BJ. Synergistic effects of fumed silica on intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene. J Appl Polym Sci. 2000;115:3508–15.
Jia Z, Wang Z, Hwang D, Wang LF. Prediction of the effective thermal conductivity of hollow sphere foams. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2018;1:1146–57.
Umegaki T, Katori H, Otake K, Yamamoto R, Kojima Y. Fabrication of copper supported on hollow silica-alumina composite spheres for catalytic decomposition of nitrous oxide. J Sol Gel Sci Technol. 2019;92:715–22.
Rahman ZU, Wei N, Li ZX, Sun WX, Wang DA. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres: controllable template synthesis and their application in drug delivery. New J Chem. 2017;41:14122–9.
Schartel B, Hull TR. Development of fire retardant materials-interpretation of cone calorimeter data. Fire Mater. 2007;31:27–54.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (YQ2019E030) and Foundation for Universities of Heilongjiang Province (LGYC2018JC032).
Funding
This study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (YQ2019E030) and Foundation for Universities of Heilongjiang Province (LGYC2018JC032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. ZH finished the experimental design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by XM, HS and CW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YW and XM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Meng, X., Wang, C. et al. Fire reaction properties of polystyrene-based composites using hollow silica as synergistic agent. J Therm Anal Calorim 146, 1679–1686 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10165-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10165-4