Abstract
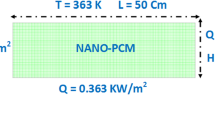
The low thermal conductivity of phase change materials has resulted in prolonged melting and freezing processes (charge and discharge) in these materials. This problem has limited the application of these materials in the field of thermal energy storage. In the present study, the effects of adding Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles at various concentrations as well as applying the magnetic field on the melting process of paraffin as phase change material have been experimentally studied. Thereupon, a cubic chamber in which the left wall applied a constant heat flux was used. At the optimum concentration of nanoparticles (1 mass%), the constant magnetic field with the intensities of 0.01 T and 0.02 T was applied and compared with the case of without field. It was inferred that using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles, due to the increment of thermal conductivity, leads to a decrease in the temperature gradient in the horizontal direction and thus a decrease in melting time. Moreover, applying the magnetic field, due to the formation of high conductive clusters of nanoparticles, reduced the melting time and improved the heat transfer in paraffin. By using an optimum concentration of nanoparticles (1 mass%), in the absence and presence of the magnetic field, melting time is reduced by 8% and 12%, approximately.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C:
-
Centigrade
- f :
-
Frequency
- g:
-
Gram
- Hz:
-
Hertz
- h :
-
Conductive coefficient
- J:
-
Joule
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity coefficient
- T:
-
Tesla
- t :
-
Time
- W:
-
Watt
- Wt.:
-
By mass
- °:
-
Degree
- µ :
-
Viscosity
- ρ :
-
Density
References
Ahmadi MH, Mohammadi O, Sadeghzadeh M, Pourfayaz F, Kumar R, Lorenzini G. Exergy and economic analysis of solar chimney in Iran climate: Tehran, Semnan, and Bandar Abbas exergy and economic analysis of solar chimney in Iran climate: Tehran, Semnan, and Bandar Abbas.
Babapoor MA, Karimi G. Thermal management of a Li-ion battery using carbon fiber-PCM composites. Appl Therm Eng. 2015;82:281–90.
Li D, Zheng Y, Liu C, Wu G. Numerical analysis on thermal performance of roof contained PCM of a single residential building. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;100:147–56.
Farzanehnia A, Khatibi M, Sardarabadi M, Passandideh-Fard M. Experimental investigation of multiwall carbon nanotube/paraffin based heat sink for electronic device thermal management. Energy Convers Manag. 2019;179:314–25.
Rahdar MH, Emamzadeh A, Ataei A. A comparative study on PCM and ice thermal energy storage tank for air-conditioning systems in office buildings. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;96:391–9.
Chaiyat N. Energy and economic analysis of a building air-conditioner with a phase change material (PCM). Energy Convers Manag. 2015;94:150–8.
Li Y, Huang G. Design optimization of the PCM storage tank for heating an Open-air swimming pool. Procedia Eng. 2017;205:842–8.
Bondareva NS, Buonomo B, Manca O, Sheremet MA. Heat transfer inside cooling system based on phase change material with alumina nanoparticles. Appl Therm Eng. 2018;144:972–81.
Ghoghaei MS, et al. A review on the applications of micro-/nano-encapsulated phase change material slurry in heat transfer and thermal storage systems. J Therm Anal Calorim 2020;1–24.
Mehryan S, Ghalambaz M, Gargari LS, Hajjar A, Sheremet M. Natural convection flow of a suspension containing nano-encapsulated phase change particles in an eccentric annulus. J Energy Storage. 2020;28:101236.
Castell A, Solé C, Medrano M, Roca J, Cabeza LF, García D. Natural convection heat transfer coefficients in phase change material (PCM) modules with external vertical fins. Appl Therm Eng. 2008;28(13):1676–86.
Lafdi K, Mesalhy O, Shaikh S. Experimental study on the influence of foam porosity and pore size on the melting of phase change materials. J Appl Phys. 2007;102(8):083549.
Motahar S, Khodabandeh R. Experimental study on the melting and solidification of a phase change material enhanced by heat pipe. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;73:1–6.
Bondareva NS, Buonomo B, Manca O, Sheremet MA. Heat transfer performance of the finned nano-enhanced phase change material system under the inclination influence. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;135:1063–72.
Ghazvini M, Maddah H, Peymanfar R, Ahmadi MH, Kumar R. Experimental evaluation and artificial neural network modeling of thermal conductivity of water based nanofluid containing magnetic copper nanoparticles. Phys A Stat Mech Appl. 2020:124127.
Ahmadi MH, Sadeghzadeh M, Maddah H, Solouk A, Kumar R, Chau K-W. Precise smart model for estimating dynamic viscosity of SiO2/ethylene glycol–water nanofluid. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech. 2019;13(1):1095–105.
Jeyaseelan TR, Azhagesan N, Pethurajan V. Thermal characterization of NaNO 3/KNO3 with different concentrations of Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136(1):235–42.
Kazemi M, Kianifar A, Niazmand H. Nanoparticle loading effect on the performance of the paraffin thermal energy storage material for building applications. J Therm Anal Calorim 2019;1–7.
Mehryan S, Vaezi M, Sheremet M, Ghalambaz M. Melting heat transfer of power-law non-Newtonian phase change nano-enhanced n-octadecane-mesoporous silica (MPSiO2). Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2020;151:119385.
Ebadi S, Tasnim SH, Aliabadi AA, Mahmud S. Melting of nano-PCM inside a cylindrical thermal energy storage system: numerical study with experimental verification. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;166:241–59.
Pramothraj M, Santosh R, Swaminathan M, Kumaresan G. Study of effect of Al and Cu microparticles dispersed in D-Mannitol PCM for effective solar thermal energy storage. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139:1–10.
Singh RP, Kaushik S, Rakshit D. Melting phenomenon in a finned thermal storage system with graphene nano-plates for medium temperature applications. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;163:86–99.
Ho CJ, Gao J. Preparation and thermophysical properties of nanoparticle-in-paraffin emulsion as phase change material. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2009;36(5):467–70.
Chamkha A, Doostanidezfuli A, Izadpanahi E, Ghalambaz M. Phase-change heat transfer of single/hybrid nanoparticles-enhanced phase-change materials over a heated horizontal cylinder confined in a square cavity. Adv Powder Technol. 2017;28(2):385–97.
Ghalambaz M, Doostani A, Izadpanahi E, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate natural convection flow of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid in a square cavity. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(3):2321–36.
Mehryan S, Izadpanahi E, Ghalambaz M, Chamkha A. Mixed convection flow caused by an oscillating cylinder in a square cavity filled with Cu–Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137(3):965–82.
Ghalambaz M, Mehryan S, Izadpanahi E, Chamkha A, Wen D. MHD natural convection of Cu–Al2O3 water hybrid nanofluids in a cavity equally divided into two parts by a vertical flexible partition membrane. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138(2):1723–43.
Sadeghi HM, Babayan M, Chamkha A. Investigation of using multi-layer PCMs in the tubular heat exchanger with periodic heat transfer boundary condition. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2020;147:118970.
Ghalambaz M, Chamkha AJ, Wen D. Natural convective flow and heat transfer of nano-encapsulated phase change materials (NEPCMs) in a cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;138:738–49.
Hajjar A, Mehryan S, Ghalambaz M. Time periodic natural convection heat transfer in a nano-encapsulated phase-change suspension. Int J Mech Sci. 2020;166:105243.
Ramazani HZ, Mohammadi O, Rahgozar I, Shafii MB, Ahmadi MH. Super-fast discharge of phase change materials by using an intermediate boiling fluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2020;115:104597.
Ghalambaz M, Zadeh SMH, Mehryan S, Pop I, Wen D. Analysis of melting behavior of PCMs in a cavity subject to a non-uniform magnetic field using a moving grid technique. Appl Math Model. 2020;77:1936–53.
Dhaidan NS, Khodadadi J, Al-Hattab TA, Al-Mashat SM. Experimental and numerical investigation of melting of phase change material/nanoparticle suspensions in a square container subjected to a constant heat flux. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;66:672–83.
Aguila B, Vasco DA, Galvez P, Zapata PA. Effect of temperature and CuO-nanoparticle concentration on the thermal conductivity and viscosity of an organic phase-change material. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;120:1009–19.
Nkurikiyimfura I, Wang Y, Pan Z. Heat transfer enhancement by magnetic nanofluids—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2013;21:548–61.
Gupta M. A review on the improvement in convective heat transfer properties using magnetic nanofluids. Int J Therm Technol E-ISSSN-2277-4114. 2016;6(1):40–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The Contributions of the first and second authors in the study are equal.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadegh, S.S., Aghababaei, A., Mohammadi, O. et al. An experimental investigation into the melting of phase change material using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles under magnetic field. J Therm Anal Calorim 146, 381–392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09958-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09958-4