Abstract
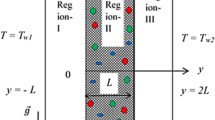
Mixed convection in vertical parallel channels is analyzed with the viscous fluid sandwiched between nanofluids within porous material filled in a vertical channel. The concept of single-phase transport of nanofluids is employed to define the nanofluid flow and heat transfer and the Darcy approach is incorporated to describe the circulation within the porous material. Formulated ordinary differential equations which are non-linear and coupled along with the corresponding boundary and interface conditions are solved by the regular perturbation method. The main objective is to investigate the effects of the Grashof and Brinkman numbers, solid volume fraction, porous parameter on the velocity and temperature fields. Results are shown in the graphical and tabular form. The physical characteristics governing the flow such as skin friction and rate of heat transfer are also investigated considering five different materials of nanoparticles.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Br :
-
Brinkman number \(\left( {Br = \frac{{\mu_{{\text{f}}}^{3} }}{{\rho_{{\text{f}}}^{2} h^{2} \left( {T_{{{\text{w1}}}} - T_{\rm w2} } \right)k_{{\text{f}}} }}} \right)\)
- G :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- Gr :
-
Grashof number \(\left( {Gr = \frac{{g\beta_{{\text{f}}} \left( {T_{{{\text{w1}}}} - T_{{{\text{w2}}}} } \right)\;h^{3} }}{{\upsilon_{{\text{f}}}^{2} }}} \right)\)
- h :
-
Channel width
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- P :
-
Non-dimensional pressure \(\left( {P = - \frac{{\rho_{{\text{f}}} h^{3} }}{{\mu_{{\text{f}}}^{2} }} \;\frac{\partial p}{{\partial x}}} \right)\)
- T :
-
Temperature
- u :
-
Dimensional velocity
- y :
-
Space coordinate
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient
- θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- ρ :
-
Density
- σ :
-
Porous parameter \(\left( {\sigma = {h \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {h {\sqrt \kappa }}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\sqrt \kappa }}} \right)\)
- τ :
-
Skin friction
- ϕ :
-
Volume fraction of the solid nanoparticles
- nf :
-
Nanofluid
- f :
-
Base fluid
- s :
-
Solid nanoparticles
- i :
-
Quantities for the fluids in region-I, region-II and region-III
References
Maxwell JA. Treatise on electricity and magnetism. 2nd ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1873.
Selimefendigil F, Chamkha AJ. Magnetohydrodynamics mixed convection in a power law nanofluid-filled triangular cavity with an opening using Tiwari and Das’ nanofluid model. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135:419–36.
Izadi M, Hashemi Pour SMR, Yasuri AK, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection of a nanofluid in a three-dimensional channel. Effect of opposed buoyancy force on hydrodynamic parameters, thermal parameters and entropy generation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136:2461–75.
Ahmed SE, Mansour MA, Hussein AK, Mallikarjuna B, Almeshaal MA, Kolsi L. MHD mixed convection in an inclined cavity containing adiabatic obstacle and filled with Cu–water nanofluid in the presence of the heat generation and partial slip. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138:1443–600.
Bondarenko DS, Sheremet MA, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Mixed convection heat transfer of a nanofluid in a lid-driven enclosure with two adherent porous blocks. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135:1095–105.
Abu-Nada E, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection flow in a lid-driven inclined square enclosure filled with a nanofluid. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2010;29:472–82.
Tiwari RK, Das MK. Heat transfer augmentation in a two sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50:2002–188.
Mittal N, Satheesh A, Kumar DS. Numerical simulation of mixed-convection flow in a lid-driven porous cavity using different nanofluids. Heat Transf Asian Res. 2014;43:1–16.
Bianco V, Manca O, Nardini S, Vafai K. Heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. New York: CRC Press; 2015.
Bianco V, Manca O, Nardini S. Second law analysis of Al2O3-water nanofluid turbulent forced convection in a circular cross section tube with constant wall temperature. Adv Mech Eng. 2013;5:1–12.
Bianco V, Manca O, Nardini S. Performance analysis of turbulent convection heat transfer of Al2O3 water-nanofluid in circular tubes at constant wall temperature. Energy. 2014;77:403–13.
Lee S, Choi SUS, Li S, Eastman JA. Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles. J Heat Transf. 1999;121:280–9.
Mostafizur RM, Saidur R, Abdul Aziz AR, Bhuiyan MHU. Thermo physical properties of methanol based Al2O3 nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;85:414–9.
Choi SUS, Zhang ZG, Lockwood FE, Grulke EA. Anomalous thermal conductivity enhancement in nanotube suspensions. Appl Phys Lett. 2001;79:2252–4.
Ellahi R, Hassan M, Zeeshan A. Shape effects of nanosize particles in Cu-H2O nanofluid on entropy generation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;81:449–56.
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R, Hassan M, Soleimani S. A study of natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid filled enclosure with elliptic inner cylinder. Int. J. Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2014;24:1906–27.
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R, Ashorynejad HR, Domairry G, Hayat T. Effects of heat transfer in flow of nanofluids over a permeable stretching wall in a porous medium. J Comput Theor Nanosci. 2014;11:486–96.
Akbar NS, Raza M, Ellahi R. Interaction of nanoparticles for the peristaltic flow in an asymmetric channel with the induced magnetic field. Eur Phys J Plus. 2014;129:155–67.
Akbar NS, Raza M, Ellahi R. Influence of heat generation and heat flux on peristaltic low with interacting nanoparticles. Eur Phys. 2014;129:185–99.
Sheikholeslami M, Bandpy MG, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A. Simulation of MHD CuO-water nanofluid flow and convective heat transfer considering Lorentz forces. J Magn Magn Mater. 2014;369:69–80.
Ding YL, Alias H, Wen DS, Williams RA. Heat transfer of aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes (CNT nanofluids). Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2006;49:240–50.
Bianco V, Manca O, Nardini S. Numerical simulation of water/Al2O3 nanofluid turbulent convection. Adv Mech Eng. 2010;2010:1–10.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Li Z, Ahmad S. Numerical modeling for alumina nanofluid magnetohydrodynamic convective heat transfer in a permeable medium using Darcy law. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:614–22.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Li Z, Ahmad S. Lorentz forces effect on NEPCM heat transfer during solidification in a porous energy storage system. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:665–74.
Shenoy A, Sheremet M, Pop I. Convective flow and heat transfer from wavy surfaces: viscous fluids, porous media and nanofluids. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2016.
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV. The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for the double-diffusive natural convective boundary layer flow in a porous medium saturated with a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:374–8.
Cheng P, Minkowycz W. Free convection about a vertical flat plate embedded in a porous medium with application to heat transfer from a dike. J Geophysical Research. 1977;82:2040–4.
Umavathi JC, Mohite MB. The onset of convection in a nanofluid saturated porous layer using Darcy model with cross diffusion. Meccanica. 2014;49:1159–75.
Ahmed S, Pop I. Mixed convection boundary layer flow from a vertical flat plate embedded in a porous medium filled with nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37:987–91.
Sheikholeslami M. Magnetic field influence on CuO-H2O nanofluid convective flow in a permeable cavity considering various shapes for nanoparticles. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2017;42:19611–21.
Cimpean D, Pop I. Fully developed mixed convection flow of a nanofluid through an inclined channel filled with a porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55:907–14.
Hajipour M, Dehkordi A. Analysis of nanofluid heat transfer in parallel-plate vertical channel filled with porous medium. Int J Therm Sci. 2012;55:103–13.
Amrei Hashemi SMH, Dehkordi AM. Modeling and CFD simulation of a mixed-convection flow of regular fluids and nanofluids in vertical porous and regular channels. Heat Transf Asian Res. 2014;43:243–69.
Hatami M, Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in an asymmetric porous channel with expanding or contracting wall. J Mol Liq. 2014;195:230–9.
Sheikholeslami M, Kataria HR, Mittal AS. Effect of thermal diffusion and heat-generation on MHD nanofluid flow past an oscillating vertical plate through porous medium. J Mol Liq. 2018;257:12–25.
Hajizadeh A, Shah NA, Shah SIA, Animasaun IL, Rahimi-Gorji M, Alarifi IM. Free convection flow of nanofluids between two vertical plates with damped thermal flux. J Mol Liq. 2019;289:110964.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical approach for MHD Al2O3-water nanofluid transportation inside a permeable medium using innovative computer method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:306–18.
Vafai K, Thiyagaraja R. Analysis of flow and heat transfer at the interface region of a porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1987;30:1391–405.
Brinkman HC. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys. 1952;20:571–81.
Shekhar M, Umavathi JC. Influence of viscous dissipation on non-Darcy mixed convection flow of nanofluid. Heat Transf Asian Res. 2017;46:176–99.
Umavathi JC, Liu IC, Sheremet MA. Convective heat transfer in a vertical rectangular duct filled with nanofluid. Heat Transf Asian Res. 2016;45:661–79.
Umavathi JC, Sheremet MA. Influence of temperature dependent conductivity of a nanofluid in a vertical rectangular duct. Int J Non-Linear Mech. 2016;78:17–28.
Umavathi JC, Ojjela O, Vajravelu K. Numerical analysis of natural convective flow and heat transfer of nanofluids in a vertical rectangular duct using Darcy–Forchheimer–Brinkman model. Int J Therm Sci. 2017;111:511–24.
Vajravelu K, Prasad KV, Abbasandy S. Convective transport of nanoparticles in multi-layer fluid flow. Appl Math Mech Engl Ed. 2013;34:177–88.
Acknowledgements
This work of Mikhail A. Sheremet was supported by the Regional Scientific and Educational Mathematical Centre of Tomsk State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umavathi, J.C., Sheremet, M.A. Heat transfer of viscous fluid in a vertical channel sandwiched between nanofluid porous zones. J Therm Anal Calorim 144, 1389–1399 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09664-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09664-1