Abstract
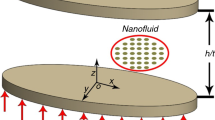
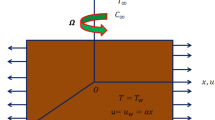
In current research, MAPLE software was utilized to scrutinize the heat transfer of copper–H2O nanomaterial migration over a sheet. Entropy production in existence of magnetic field was scrutinized, and Bejan number was reported as main outputs. Converting PDEs into ODEs was done via similarity transformation, and final ODEs were analyzed via RK4. The influence of different variables, including fraction of nanomaterial and Lorentz force on flow distribution and temperature field, also on surface tension and Nu was demonstrated. Besides, Be and NG were calculated for various ranges of scrutinized variables.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nayak MK, Akbar NS, Tripathi D, Khan ZH, Pandey VS. MHD 3D free convective flow of nanofluid over an exponentially stretching sheet with chemical reaction. Adv Powder Technol. 2017;28(9):2159–66.
Kumari M, Nath G. Analytical solution of unsteady three-dimensional MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer due to impulsively stretched plane surface. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2009;14(8):3339–50.
Prasad KV, Pal D, Umesh V, Rao NSP. The effect of variable viscosity on MHD viscoelastic fluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching sheet. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2010;15(2):331–44.
Hayat T, Qayyum S, Alsaedi A, Ahmad B. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) nonlinear convective flow of Walters-B nanofluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet with variable thickness. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;110:506–14.
Szilágyi IM, Kállay-Menyhárd A, Šulcová P, Kristóf J, Pielichowski K, Šimon P. Recent advances in thermal analysis and calorimetry. In: Presented at the 1st journal of thermal analysis and calorimetry conference and 6th V4 (Joint Czech-Hungarian-Polish-Slovakian) thermoanalytical conference (2017), J Therm Anal Calorim 133 (2018), 1–4.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Thermal radiation of ferrofluid in existence of Lorentz forces considering variable viscosity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;109:82–92.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical investigation of nanofluid free convection under the influence of electric field in a porous enclosure. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:1212–21.
Tlili I, Alkanhal TA, Othman M, Dara RN, Shafee A. Water management and desalination in KSA view 2030: case study of solar humidification and dehumidification system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08700-z.
Sheikholeslami M. Effect of uniform suction on nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a cylinder. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. 2015;37:1623–33.
Alrobaian AA, Alsagri AS, Ali JA, Hamad SM, Shafee A, Nguyen TK, Li Z. Investigation of convective nanomaterial flow and exergy drop considering CVFEM within a porous tank. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08564-3.
Ma X, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Nguyen-Thoi T, Li Z. Solidification inside a clean energy storage unit utilizing phase change material with copper oxide nanoparticles. J Clean Prod. 2020;245:118888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118888.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical modeling of Nano enhanced PCM solidification in an enclosure with metallic fin. J Mol Liq. 2018;259:424–38.
Manh TD, Nam ND, Abdulrahman GK, Moradi R, Babazadeh H. Impact of MHD on hybrid nanomaterial free convective flow within a permeable region. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09008-8.
Rezaeianjouybari B, Sheikholeslami M, Shafee A, Babazadeh H. A novel Bayesian optimization for flow condensation enhancement using nanorefrigerant: a combined analytical and experimental study. Chem Eng Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2019.115465.
Sheikholeslami M, Arabkoohsar A, Jafaryar M. Impact of a helical-twisting device on nanofluid thermal hydraulic performance of a tube. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08683-x.
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R. Three dimensional mesoscopic simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;89:799–808.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Nanofluid two phase model analysis in existence of induced magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:288–99.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical simulation for solidification in a LHTESS by means of nano-enhanced PCM. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2018;86:25–41.
Li Y, Aski FS, Barzinjy AA, Dara RN, Shafee A, Tlili I. Nanomaterial thermal treatment along a permeable cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08706-7.
Manh TD, Nam ND, Abdulrahman GK, Shafee A, Shamlooei M, Babazadeh H, Jilani AK, Tlili I. Effect of radiative source term on the behavior of nanomaterial with considering Lorentz forces. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09077-9.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid convection in a porous enclosure considering heat flux boundary condition. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;106:1261–9.
Sheikholeslami M. Solidification of NEPCM under the effect of magnetic field in a porous thermal energy storage enclosure using CuO nanoparticles. J Mol Liq. 2018;263:303–15.
Sheikholeslami M, Bhatti MM. Active method for nanofluid heat transfer enhancement by means of EHD. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;109:115–22.
Shafee A, Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Babazadeh H. Irreversibility of hybrid nanoparticles within a pipe fitted with turbulator. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09248-8.
Sheikholeslami M, Sadoughi M. Mesoscopic method for MHD nanofluid flow inside a porous cavity considering various shapes of nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;113:106–14.
Daniel YS, Aziz ZA, Ismail Z, Salah F. Thermal radiation on unsteady electrical MHD flow of nanofluid over stretching sheet with chemical reaction. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2019;31:804–12.
Hsiao K-L. Stagnation electrical MHD nanofluid mixed convection with slip boundary on a stretching sheet. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;98:850–61.
Animasaun I, Sandeep DN, Ali M. Unsteady liquid film flow of electrically conducting magnetic-nanofluids in the vicinity of a thin elastic sheet. J Comput Theor Nanosci. 2017;14:1140–7.
Sheikholeslami M, Bhatti MM. Forced convection of nanofluid in presence of constant magnetic field considering shape effects of nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;111:1039–49.
Seyednezhad M, Sheikholeslami M, Ali JA, Shafee A, Nguyen TK. Nanoparticles for water desalination in solar heat exchanger: review. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08634-6.
Sheikholeslami M, Seyednezhad M. Nanofluid heat transfer in a permeable enclosure in presence of variable magnetic field by means of CVFEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:1169–80.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Melting heat transfer influence on nanofluid flow inside a cavity in existence of magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:517–26.
Sheikholeslami M. Application of Darcy law for nanofluid flow in a porous cavity under the impact of Lorentz forces. J Mol Liq. 2018;266:495–503.
Gao W, Yan L, Shi L. Generalized Zagreb index of polyomino chains and nanotubes. Optoelectron Adv Mater Rapid Commun. 2017;11(1–2):119–24.
Szilágyi IM, Santala E, Heikkilä M, Kemell M, Nikitin T, Khriachtchev L, Räsänen M, Ritala M, Leskelä M. Thermal study on electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone/ammonium metatungstate nanofibers: optimising the annealing conditions for obtaining WO3 nanofibers. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;105(1):73.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. CVFEM for influence of external magnetic source on Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid behavior in a permeable cavity considering shape effect. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;115:180–91.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Simulation of nanofluid heat transfer in presence of magnetic field: a review. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;115:1203–33.
Sheikholeslami M, Haq R, Shafee A, Li Z, Elaraki YG, Tlili I. Heat transfer simulation of heat storage unit with nanoparticles and fins through a heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;135:470–8.
Qin Y, Zhang M, Hiller JE. Theoretical and experimental studies on the daily accumulative heat gain from cool roofs. Energy. 2017;129:138–47.
Sheikholeslami M. Influence of magnetic field on nanofluid free convection in an open porous cavity by means of Lattice Boltzmann method. J Mol Liq. 2017;234:364–74.
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A. On simulation of nanofluid radiation and natural convection in an enclosure with elliptical cylinders. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;115:981–91.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical approach for MHD Al2O3-water nanofluid transportation inside a permeable medium using innovative computer method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:306–18.
Qin Y, He H. A new simplified method for measuring the albedo of limited extent targets. Solar Energy. 2017;157(Supplement C):1047–55.
Sheikholeslami M, Sadoughi MK. Simulation of CuO-water nanofluid heat transfer enhancement in presence of melting surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;116:909–19.
Sheikholeslami M. Lattice Boltzmann Method simulation of MHD non-Darcy nanofluid free convection. Phys B. 2017;516:55–71.
Sandeep DN. Effect of aligned magnetic field on liquid thin film flow of magnetic-nanofluids embedded with graphene nanoparticles. Adv Powder Technol. 2017;28:865–75.
Govindaraju M, Saranya S, Hakeem AKA, Jayaprakash R, Ganga B. Analysis of slip MHD nanofluid flow on entropy generation in a stretching sheet. Proc Eng. 2015;127:501–7.
Baag S, Mishra SR, Dash GC, Acharya MR. Entropy generation analysis for viscoelastic MHD flow over a stretching sheet embedded in a porous medium. Ain Shams Eng J. 2017;8(4):623–32.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Shafee A, Li Z, Haq R. Heat transfer of nanoparticles employing innovative turbulator considering entropy generation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;136:1233–40.
Qin Y, He Y, Wu B, Ma S, Zhang X. Regulating top albedo and bottom emissivity of concrete roof tiles for reducing building heat gains. Energy Build. 2017;156(3):218–24.
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB. Numerical simulation for impact of Coulomb force on nanofluid heat transfer in a porous enclosure in presence of thermal radiation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;118:823–31.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Numerical analysis of Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid flow in permeable media under the effect of external magnetic source. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;118:182–92.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Hedayat M, Shafee A, Li Z, Nguyen TK, Bakouri M. Heat transfer and turbulent simulation of nanomaterial due to compound turbulator including irreversibility analysis. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;137:1290–300.
Qin Y, Liang J, Tan K, Li F. A side by side comparison of the cooling effect of building blocks with retro-reflective and diffuse-reflective walls. Sol Energy. 2016;133:172–9.
Sheikholeslami M, Ghasemi A, Li Z, Shafee A, Saleem S. Influence of CuO nanoparticles on heat transfer behavior of PCM in solidification process considering radiative source term. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;126:1252–64.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Saleem S, Li Z, Shafee A, Jiang Y. Nanofluid heat transfer augmentation and exergy loss inside a pipe equipped with innovative turbulators. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;126:156–63.
Qin Y, He H, Ou X, Bao T. Experimental study on darkening water-rich mud tailings for accelerating desiccation. J Clean Prod. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118235.
Rabbi KM, Sheikholeslami M, Karim A, Shafee A, Li Z, Tlili I. Prediction of MHD flow and entropy generation by Artificial Neural Network in square cavity with heater-sink for nanomaterial. Phys A Stat Mech Its Appl. 2020;541:123520.
Sheikholeslami M, Li Z, Shafee A. Lorentz forces effect on NEPCM heat transfer during solidification in a porous energy storage system. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:665–74.
Sheikholeslami M, Seyednezhad M. Simulation of nanofluid flow and natural convection in a porous media under the influence of electric field using CVFEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;120:772–81.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Li Z. Water based nanofluid free convection heat transfer in a three dimensional porous cavity with hot sphere obstacle in existence of Lorenz forces. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;125:375–86.
Sheikholeslami M. Finite element method for PCM solidification in existence of CuO nanoparticles. J Mol Liq. 2018;265:347–55.
Qin Y, Hiller JE, Meng D. Linearity between pavement thermophysical properties and surface temperatures. J Mater Civ Eng. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002890.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. Simulation of water based nanofluid convective flow inside a porous enclosure via Non-equilibrium model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;120:1200–12.
Sheikholeslami M, Keshteli AN, Babazadeh H. Nanoparticles favorable effects on performance of thermal storage units. J Mol Liq. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112329.
Sheikholeslami M, Darzi M, Li Z. Experimental investigation for entropy generation and exergy loss of nano-refrigerant condensation process. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;125:1087–95.
Qin Y, Luo J, Chen Z, Mei G, Yan L-E. Measuring the albedo of limited-extent targets without the aid of known-albedo masks. Sol Energy. 2018;171:971–6.
Sheikholeslami M, Darzi M, Sadoughi MK. Heat transfer improvement and pressure drop during condensation of refrigerant-based nanofluid: an experimental procedure. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;122:643–50.
Sheikholeslami M. Influence of magnetic field on Al2O3-H2O nanofluid forced convection heat transfer in a porous lid driven cavity with hot sphere obstacle by means of LBM. J Mol Liq. 2018;263:472–88.
Qin Y. A review on the development of cool pavements to mitigate urban heat island effect. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;52:445–59.
Sithole H, Mondal H, Sibanda P. Entropy generation in a second grade magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow over a convectively heated stretching sheet with nonlinear thermal radiation and viscous dissipation. Results Phys. 2018;9:1077–85.
Shit GC, Haldar R, Mandal S. Entropy generation on MHD flow and convective heat transfer in a porous medium of exponentially stretching surface saturated by nanofluids. Adv Powder Technol. 2017;28(6):1519–30.
Das S, Chakraborty S, Jana RN, Makinde OD. Entropy analysis of unsteady magneto-nanofluid flow past accelerating stretching sheet with convective boundary condition. Appl Math Mech. 2015;36(12):1593–610.
Qin Y, He Y, Hiller JE, Mei G. A new water-retaining paver block for reducing runoff and cooling pavement. J Clean Prod. 2018;199:948–56.
Sheikholeslami M, Ghasemi A. Solidification heat transfer of nanofluid in existence of thermal radiation by means of FEM. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;123:418–31.
Gao W, Wang WF, Farahani MR. Topological indices study of molecular structure in anticancer drugs. J Chem. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3216327.
Sheikholeslami M. New computational approach for exergy and entropy analysis of nanofluid under the impact of Lorentz force through a porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2019;344:319–33.
Gao W, Wang WF. The vertex version of weighted wiener number for bicyclic molecular structures. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/418106.
Sheikholeslami M, Jafaryar M, Li Z. Nanofluid turbulent convective flow in a circular duct with helical turbulators considering CuO nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;124:980–9.
Qin Y, Zhao Y, Chen X, Wang L, Li F, Bao T. Moist curing increases the solar reflectance of concrete. Constr Build Mater. 2019;215:114–8.
Gao W, Wang WF. The eccentric connectivity polynomial of two classes of nanotubes. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2016;89:290–4.
Gao W, Wang WF, Jamil MK, Farahani MR. Electron energy studying of molecular structures via forgotten topological index computation. J Chem. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1053183.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA. CVFEM simulation for nanofluid migration in a porous medium using Darcy model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;122:1264–71.
Gao W, Farahani MR, Shi L. The forgotten topological index of some drug structures. Acta Med Mediterr. 2016;32:579–85.
Sheikholeslami M. Magnetic field influence on CuO–H2O nanofluid convective flow in a permeable cavity considering various shapes for nanoparticles. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2017;42:19611–21.
Sheikholeslami M. CuO-water nanofluid flow due to magnetic field inside a porous media considering Brownian motion. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:921–9.
Gao W, Siddiqui MK, Imran M, Jamil MK, Farahani MR. Forgotten topological index of chemical structure in drugs. Saudi Pharm J. 2016;24(3):258–64.
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA, Li Z, Shafee A. Numerical modeling for Alumina nanofluid magnetohydrodynamic convective heat transfer in a permeable medium using Darcy law. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;127:614–22.
Sheikholeslami M, Rezaeianjouybari B, Darzi M, Shafee A, Li Z, Nguyen TK. Application of nano-refrigerant for boiling heat transfer enhancement employing an experimental study. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;141:974–80.
Gao W, Wang WF. Second atom-bond connectivity index of special chemical molecular structures. J Chem. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/906254.
Sheikholeslami M, Haq R, Shafee A, Li Z. Heat transfer behavior of Nanoparticle enhanced PCM solidification through an enclosure with V shaped fins. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;130:1322–42.
Sheikholeslami M. Numerical investigation for CuO-H2O nanofluid flow in a porous channel with magnetic field using mesoscopic method. J Mol Liq. 2018;249:739–46.
Brinkman HC. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys. 1952;20(4):571.
Bejan A. Entropy generation minimization. New York: CRC Press; 1996.
Wang CY. Free convection on a vertical stretching surface. ZAMM J Appl Math Mech. 1989;69(11):418–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balazadeh, N., Shafee, A. & Tlili, I. Irreversibility of nanomaterial due to MHD via numerical approach. J Therm Anal Calorim 144, 1041–1050 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09548-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09548-4