Abstract
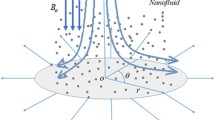
In this paper, the nanofluid flow near an infinite disk which stretches in the radial direction in the presence of exponential space-based heat source (ESHS) and thermal-based heat source (THS) is investigated. The Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects are accounted to study the nanofluids. Effects of radial magnetism and the Coriolis force are also deployed. The pertinent nonlinear equations are approximated under boundary layer notion and modified von Kármán transformations. The subsequent nonlinear differential system is treated via shooting method. The impacts of controlling parameters on flow profiles are discussed and depicted with the aid of graphs. Results show that as the ESHS and THS parameters increase, the thermal field increases. However, ESHS phenomenon is highly influential than THS phenomenon on energy transport and its gradient. Further, it is found that thermophoresis slip mechanism has more effect on heat transport rate than the Brownian motion.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SUS. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: ASME, FED 231/MD, vol 66, p 99–105. 1995.
Kuznetsov AV, Nield DA. Natural Convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate: a revised model. Int J Therm Sci. 2014;77:126–9.
Sheikholeslami M, Mustafa MT, Ganji DD. Effect of Lorentz forces on forced convection nanofluid flow over a stretched surface. Particuology. 2016;26:108–13.
Hayat T, Aziz A, Muhammad T, Alsaedi A, Mustafa M. On magnetohydrodynamic flow of second-grade nanofluid over a convectively heated nonlinear stretching surface. Adv Powder Technol. 2016;27:1992–2004.
Hsiao KL. Micropolar nanofluid flow with MHD and viscous dissipation effects towards a stretching sheet with multimedia feature. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;112:983–90.
Reddy JR, Sugunamma V, Sandeep N. Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on unsteady MHD nanofluid flow over a slendering stretching surface with slip effects. Alex Eng J. 2018;57(4):2465–73.
Makinde OD, Animasaun IL. Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on MHD bioconvection of nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation and quartic chemical reaction past an upper horizontal surface of a paraboloid of revolution. J Mol Liq. 2016;221:733–43.
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Raju CSK. Cattaneo–Christov heat flux on UCM nanofluid flow across a melting surface with double stratification and exponential space dependent internal heat source. Inform Med Unlocked. 2017;9:26–34.
Kumar RK, Raju CS, Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Varma SV. Chemical reaction effects on nano carreau liquid flow past a cone and a wedge with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Int J Chem React Eng. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2017-0108.
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD, Javed MY, Ellahi R. Effect of thermal radiation on magnetohydrodynamics nanofluid flow and heat transfer by means of two phase model. J Magn Magn Mater. 2015;374:36–43.
Hayat T, Hussain Z, Muhammad T, Alsaedi A. Effects of homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions in flow of nanofluids over a nonlinear stretching surface with variable surface thickness. J Mol Liq. 2016;221:1121–7.
Hayat T, Muhammad K, Muhammad T, Alsaedi A. Melting heat in radiative flow of carbon nanotubes with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. Commun Theor Phys. 2018;69(4):441.
Koriko OK, Omowaye AJ, Sandeep N, Animasaun IL. Analysis of boundary layer formed on an upper horizontal surface of a paraboloid of revolution within nanofluid flow in the presence of thermophoresis and Brownian motion of 29 nm CuO. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;124:22–36.
Hayat T, Waqas M, Shehzad SA, Alsaedi A. On model of Burgers fluid subject to magneto nanoparticles and convective conditions. J Mol Liq. 2016;222:181–7.
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Gorla RSR, Abbasi FM, Shehzad SA. Numerical solutions for magnetohydrodynamic flow of nanofluid over a bidirectional non-linear stretching surface with prescribed surface heat flux boundary. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;417:189–96.
Mebarek-oudina F, Bessaïh R. Numerical modeling of MHD stability in a cylindrical configuration. J Frankl Inst. 2014;351:667–81.
Mahender D, Srikanth Rao P. Unsteady MHD free convection and mass transfer flow past a porous vertical plate in presence of viscous dissipation”. J Phys Conf Ser. 2015;662:012012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/662/1/012012.
Mebarek-Oudina F, Bessaih R. Oscillatory magnetohydrodynamic natural convection of liquid metal between vertical coaxial cylinders. J Appl Fluid Mech. 2016;9(4):1655–65.
Mebarek-Oudina F. Numerical modeling of the hydrodynamic stability in vertical annulus with heat source of different lengths. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2017;20(4):1324–33.
Gireesha BJ, Mahanthesh B, Rashidi MM. MHD boundary layer heat and mass transfer of a chemically reacting Casson fluid over a permeable stretching surface with non-uniform heat source/sink. Int J ind Math. 2015;7(3):247–60.
Von Karman T. Uber laminar and turbulent reibung. ZAMM. 1921;1:233–5.
Fang T. Flow over a stretchable disk. Phys Fluids. 2007;19(12):128105.
Turkyilmazoglu M. MHD fluid flow and heat transfer due to a stretching rotating disk. Int J Therm Sci. 2012;51:195–201.
Mushtaq A, Mustafa M. Computations for nanofluid flow near a stretchable rotating disk with axial magnetic field and convective conditions. Results Phys. 2017;7:3137–44.
Aziz A, Alsaedi A, Muhammad T, Hayat T. Numerical study for heat generation/absorption in flow of nanofluid by a rotating disk. Results Phys. 2018;8:785–92.
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Shashikumar NS, Shehzad SA. Marangoni convective MHD flow of SWCNT and MWCNT nanoliquids due to a disk with solar radiation and irregular heat source. Phys E. 2017;94:25–30.
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Prasannakumara BC, Kumar PBS. Magneto-Thermo-Marangoni convective flow of Cu–H2O nanoliquid past an infinite disk with particle shape and exponential space based heat source effects. Results Phys. 2017;7:2990–6.
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Shehzad SA, Rauf A, Kumar PBS. Nonlinear radiated MHD flow of nanoliquids due to a rotating disk with irregular heat source and heat flux condition. Phys B. 2018;537:98–104.
Acknowledgements
The author (B Mahanthesh) is thankful to the Management of CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bangalore, India, for their support to complete this research work. We would also like to thank the Editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahanthesh, B., Lorenzini, G., Oudina, F.M. et al. Significance of exponential space- and thermal-dependent heat source effects on nanofluid flow due to radially elongated disk with Coriolis and Lorentz forces. J Therm Anal Calorim 141, 37–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08985-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08985-0