Abstract
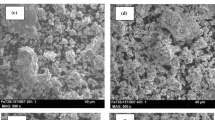
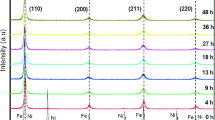
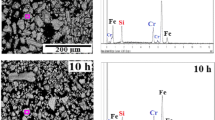
In this paper, Fe50Se50 alloy powders were synthesized from pure elemental powder by mechanical allowing. The structure, microstructure, morphology, chemical composition and thermal behavior at a function of milling times (0–39 h) were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy attached with energy-dispersive spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). In addition, the interaction hyperfine and magnetic proprieties was examined by transmission Mössbauer spectroscopy (TMS) and thermomagnetic measurements (VSM) respectively. For milling times up to 6 h, the results of refinement of the X-ray diffraction pattern by MAUD software reveal the formation of the β-FeSe hexagonal, amorphous selenium and nanocrystalline α-Fe. The DSC curves show several exothermic and endothermic peaks associated with various phases’ transitions such as the exothermic peak at 103 °C related to crystallization amorphous selenium. However, after prolonging the milling time to 39 h, the XRD shows the formation of α-FeSe phase tetragonal which has plenty of technological interests especially the superconductivity. The Mössbauer spectroscopy confirmed the formation the two-phase paramagnetic hexagonal β-FeSe and α-FeSe tetragonal, according to the XRD and DSC. Measurement of magnetization (VSM) displays that saturation magnetization (MS) decreases as the milling time increases.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu XJ, Shen DZ, Zhang ZZ, Zhang JY, Liu KW, Li BH, Lu YM, Yoa B, Zahao DX, Li BS, Shan CX, Fan XW, Lin HJ, Yang CL. On nature of the carriers in ferromagnetic FeSe. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;90:112105.
Wu XJ, Zhang ZZ, Zhang JY, Ju ZG, Shan DZ, Li BH, Shan CX, Lu YM. Structural and electrical characterization of single tetragonal FeSe on Si substrate. J Cryst Growth. 2007;300(2):246–63.
Ouertani B, Ouertfelli J, Saadoum M, Bessais B, Ezzaouia H, Bernède JC. Transformation of amorphous iron oxide thin films predeposited by spray pyrolysis into a single FeSe2 phase by selenisation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2005;87(1–4):501–11.
Zhang S, Liu J, Feng J, Shao B, Li C, Zhang P. Optimization of FeSe superconducting tapes with different sheath materials and precursor powders. J Supercond Novel Magn. 2018;31–9:2747–51.
Ubale AU, Sakhare YS, Belkhedkar MR. Synthesis and characterization of spray deposited nonostructured FeSe thin films. Mater Lett. 2013;92:111–4.
Ubale AU, Skhare YS. Effet of substrate temperature on optical, structural and electrical properties of FeSe thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. J Phys Chem Solids. 2013;74(10):1459–64.
Jin R, Zhao K, Pu X, Zhang M, Cai F, Yang X, Kim H, Zhao Y. Structural and photovolataic properties of FeSe2 films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Mater Lett. 2016;179:179–81.
Sobhani A, Salavati-Niasari M. Synthesis and characterization of FeSe2 nanoparticles and FeSe2/FeO(OH) nanocomposites by hydrothermal method. J Alloy Compd. 2015;625(15):26–33.
Tao YR, Fan L, Wu ZY, Wu XC, Wang ZH. Synthesis and characterization of superconducting FeSe nanowires. J Alloy Compd. 2018;75:20–7.
Li ML, Yao QZ, Zhou GT, Fu SQ. Microwave-assisted synthesis of flower-like β-FeSe microstructure. CrystEngComm. 2010;12:3138–44.
Onar K, Yakinci ME. Solid state synthesis and characterization of bulk β-FeSe superconductors. J Alloy Compd. 2015;620(25):210–6.
Chebli A, Djekoun A, Sunol JJ, Niznansky D. Structural, thermal and hyperfine properties of Fe75Se25 powders prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater Chem Phys. 2018;217:477–85.
Feng JQ, Zhang SN, Liu JX, Ma XB, Zhang PX. Fabrication of FeSe superconducting tapes with high-energy ball milling aided PIT process. Mater Lett. 2016;170:31–4.
Xiaoting L, Zhiming G, Yongchang L, Zongqing M, Liming Y. Influence of premilling time on the sintering process and superconductive properties of FeSe. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond. 2012;22(6):7300105.
Ulbrich KF, Campos CEM. Nanosized tetragonal β-FeSe phase obtained by mechanical alloying: structural and microstructural, magnetic and electrical characterization. RCA Adv. 2018;8:8190–8.
Neikov OD. Handbook of non-ferrous metal powders technologies and application. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2019. p. 91–124.
Lutterotti L. MAUD program, CPD, Newsletter(IUCr). 2000. p P24.
Rietveld HM. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J Appl Cryst. 1969;2:65–71.
Stewart RF, Bently J, Goodman B. Generalized x-ray scattering factors in diatomic molecules. J Chem Phys. 1975;63(9):3786–93.
Campos CEM, De Lima JC, Grandi TA, Machado KD, Pizani PS. Structural studies of iron selenides prepared by mechanical alloying. Solid State Commun. 2002;123:179–84.
Elabbar AA, Abu-Sehly AA. Crystallization kinetics of amorphous selenium prepared by ball milling technique: evidence of three crystallization regimes. Mater Chem Phys. 2013;141(2–3):713–8.
Okamoto H. The Fe–Se (iron–selenium) system. J Phase Equilib. 1991;12:383.
Xia XJ, Huang FQ, Xie XM, Jiang MH. Preparation and superconductivity of stoichiometric β-FeSe. Europhys Lett. 2009;86:37008.
Grivel JC, Wulff AC, Zhao Y, Andersen NH, Bednareik J, Zimmermann MV. In situ observation of the formation of FeSe. Supercond Sci Technol. 2011;24:15007.
Hsu FC, Luo JY, Yeh KW, Chen TK, Huang TW, Wu PM, Lee YC, Huang YL, Chu YY, Yan DC, Wu MK. Superconductivity in the PbO-type structure α-FeSe. PNAS. 2008;105(38):1462–4.
Zahao PH, Yan W, Yang JY, Ham YL, Aldica G, Sandu V, Badica P, Nie JC. A simple fabrication of FeSe superconductors with high upper critical field. J Supercond Novel Magn. 2012;25:1781–5.
Zhang SN, Xiao BM, Liu JX, Jian FQ, Cheng SL, Ping X. Effect of high-energy ball milling time on the sintering process of FeSe superconductors. Mater Sci Forum. 2016;848:657–63.
Wu MK, Hsu FC, Yeh KW, Huang TW, Chang HH, Chen TK, Rao SM, Mok BH, Chen CL, Huang YL, Ke CT, Wu PM, Chang AM, Wu CT, Perng TP. The development of the superconducting PbO-type β-FeSe and related compounds. Phys C. 2009;469:340–9.
Zhang S, Feng J, Liu J, Shao B, Li C, Zhang P. Optimization of high-energy ball milling aided sintering process for FeSe superconductors. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond. 2017;27(5):1–4.
Takemura Y, Suto H, Honda N, Kukuno K, Saito K. Characterization of FeSe films prepared on GaAs substrate by selenization technique. J Appl Phys. 1997;81:5177.
Takemura Y, Honda N, Takahashi T, Suto H, Kakuno K. Isotropic magnetization in FeSe films on GaAs substrate. J Magn Mater. 1998;181:1319–20.
Hussain RA, Badshah A, La B. Fabrication, characterization and application of iron selenide. J Solid State Chem. 2016;243:179–89.
Chen N, Ma Z, Liu Y, Li X, Cai Q, Li H, Yu L. Influence of Sn doping on the phase formation and superconductivity of FeSe0.93. J Alloy Compd. 2014;588(5):418–21.
Harris SB, Camata RP. Double epitaxy of tetragonal and hexagonal phases in the FeSe system. J Cryst Growth. 2019;514(15):54–9.
Zhang S, Shao B, Zahao G, Liu J, Feng J, Li C, Zhang P. Influences of Fe content on the fabrication of FeSe superconductors with high-energy ball milling aided sintering process. J Alloy Compd. 2017;729:823–7.
Brand RA. The NORMOS program is available from WISSEL GmbH. D-82319 Starnberg, Germany. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res. 1987;B28:398.
Sklyarova A, Lindén J, Tewari GC, Rautama EL, Kappinen M. 57Fe Mössbauer study of a secondary phase in FeSe1−x with a large quadrupole splitting. Hyperfine Interact. 2014;226:341–9.
Blachowski A, Ruebenbauer K, Zukrowski J, Perzewoznik J, Wojciechowski K, Stadnik M. Mössbauer spectroscopy evidence for the lack of iron magnetic moment in superconducting FeSe. J Alloy Compd. 2010;494:1–4.
Mizuguchi Y, Furubayashi T, Deguchi K, Tsuda S, Yamagchi T, Takano Y. Mössbauer studies on FeSe and FeTe. Phys C. 2010;470:5339–83.
Khosravi S, Alizadeh M, Sharafi S, Maleh HK, Atar N. Structural, magnetic and electron transfer effect of Cr additive on Fe65Co35 nanopowder fabricated mechanical allowing. Powder Technol. 2015;279:262–8.
Ashokkumar T, Rajadurai A, Gopinath SCB. Saturation magnetization studies on iron-nickel ball milling nanopowders and spark plasma sintered specimens. J Magn Magn Mater. 2018;465:621–5.
Rathi A, Meka MV, Jayaraman TV. Synthesis of nanocrystalline equiatomic nickel-cobalt-iron alloy powders by mechanical alloying and their structural and magnetic characterization. J Magn Magn Mater. 2019;496(1):469–82.
Chebli A, Djekoun A, Boudinar N, Benabdeslem M, Otmani A, Bouzabata B, Sunol JJ. Synthesis and characterization of high-energy ball-milled nanostructured Fe25Se75. JOM. 2016;68(1):351–61.
de Lima JC, dos Santos VHF, Grandi TA. Structural study of the Zn–Se system by ball milling technique. Nano Struct Mater. 1999;11(1):51–7.
Liu G, Li J, Chen K. Reaction mechanism in fast combustion synthesis of superconducting FeSe and FeSe0.7Te0.3. Acta Mater. 2017;122:187–98.
Zhang S, Liu J, Feng J, Wang Y, Ma X, Li C, Zhang P. Fabrication mechanism of FeSe superconductors with high-energy ball milling aided sintering process. Mater Chem Phys. 2015;163(1):587–93.
Acknowledgements
Financial support from High School of Technological Education (ENSET)–Skikda is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chebli, A., Djekoun, A., Suñol, J.J. et al. Structural, magnetic and thermal characterization of Fe50Se50 powders obtained by mechanical alloying. J Therm Anal Calorim 140, 53–62 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08772-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08772-x