Abstract
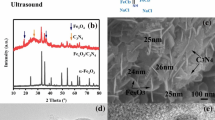
Flower-shaped Ni-doped Fe3O4/SnS2 composite was synthesized by a one-pot solvothermal method, where nanosized Ni-doped Fe3O4 particles were dispersed on the SnS2 sheets and these sheets built the flower-shaped structure. A microcalorimeter was employed to study the Ni-doped Fe3O4 formation processes with the SnS2. The experimental results indicated that the Ni-doped Fe3O4 formation mechanism is similar with and without the SnS2. Different endothermal processes demonstrated that the interaction between the cations (Fe3+, Fe2+ and Ni2+) and S2− induced various morphologies of the Ni-doped Fe3O4. Cluster-shaped Ni-doped Fe3O4 was synthesized without SnS2. The composite exhibited more excellent Fenton catalytic activity than the Ni-doped Fe3O4, SnS2, and the mixture is composed of the Ni-doped Fe3O4 and SnS2 with the same composition as the composite for the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB). RhB could be removed about 95% in 120 min at natural pH of the RhB solution (6.64) without irradiation for the Ni-doped Fe3O4/SnS2 composite as the catalyst. The present SnS2 enhanced adsorption capacity for RhB and the dispersed nanosized particles of Ni-doped Fe3O4, and the interaction between cations (Fe3+ and Fe2+) and S2− enhanced the conversion from Fe3+ to Fe2+, which induced excellent catalytic activity of the composite.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quan L, Zhang H, Xu L. The non-isothermal cyclization kinetics of amino-functionalized carbon nanotubes/polyacrylonitrile composites by in situ polymerization. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:1081–9.
Vasilakos SP, Tarantili PA. In situ monitoring by DSC and modeling of curing of vinyl polysiloxanes in layered silicate nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:2049–58.
Wang L, Ma Z, Liu S, Huang Z. In situ growth mechanism and the thermodynamic functions of zinc oxide nano-arrays and hierarchical structure. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:201–8.
Liu J, Nan Z, Gao S. In situ microcalorimetry study of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticle formation under solvothermal conditions. Dalton Trans. 2015;44:17293–301.
Zhu J, Nan Z. Zn-doped Fe3O4 nanosheet formation induced by EDA with high magnetization and an investigation of the formation mechanism. J Phys Chem C. 2017;121:9612–20.
Cen H, Nan Z. Monodisperse Zn-doped Fe3O4 formation and photo-Fenton activity for degradation of rhodamine B in water. J Phys Chem Solid. 2018;121:1–7.
Zhang A, Nan Z. In situ microcalorimetric investigation on effects of surfactants on cluster-shaped Ni-doped Fe3O4 formation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:859–68.
Wang Y, Zhao H, Li M, Fan J, Zhao G. Magnetic ordered mesoporous copper ferrite as a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of imidacloprid. Appl Catal B Environ. 2014;147:534–45.
Babuponnusami A, Muthukumar K. A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng. 2014;2:557–72.
Liu X, Sun C, Chen L, Yang H, Ming Z, Bai Y, Feng S, Yang ST. Decoloration of methylene blue by heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation on Fe3O4/SiO2/C nanospheres in neutral environment. Mater Chem Phys. 2018;213:231–8.
Navalon S, De MM, Martin R, Alvaro M, Garcia H. Enhancement of the catalytic activity of supported gold nanoparticles for the Fenton reaction by light. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:2218–26.
Navalon S, Martin R, Alvaro M, Garcia H. Gold on diamond nanoparticles as a highly efficient Fenton catalyst. Angew Chem. 2010;122:8581–5.
Kwan WP, Voelker BM. Rates of hydroxyl radical generation and organic compound oxidation in mineral-catalyzed Fenton-like systems. Environ Sci Technol. 2003;37:1150–8.
Qiu PP, Kang K, Kim K, Li W, Cuia M, Khim J. Facile synthesis of uniform yolk-shell structured magnetic mesoporous silica as an advanced photo-Fenton-like catalyst for degrading rhodamine B. RSC Adv. 2015;5:96201–4.
Han C, Huang G, Zhu D, Hu K. Facile synthesis of MoS2/Fe3O4 nanocomposite with excellent Photo-Fenton-like catalytic performance. Mater Chem Phys. 2017;200:16–22.
Zhang SW, Fan QH, Gao HH, Huang YS, Liu X, Li JX, Xu XJ, Wang XK. Formation of Fe3O4@MnO2 ball-in-ball hollow spheres as a high performance catalyst with enhanced catalytic performances. J Mater Chem A. 2016;4:1414–22.
Munoz M, Pedro ZMD, Casas JA, Rodriguez JJ. Preparation of magnetite-based catalysts and their application in heterogeneous Fenton oxidation-A review. Appl Catal B Environ. 2015;176:249–65.
López-Ramón MV, Álvarez MA, Moreno-Castilla C, Fontecha-Cámara MA, Yebra-Rodríguez A, Bailón-García E. Effect of calcination temperature of a copper ferrite synthesized by a sol-gel method on its structural characteristics and performance as Fenton catalyst to remove gallic acid from water. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;511:193–202.
Saha M, Mukherjee S, Kumar S, Dey S, Gayen A. Albumin matrix assisted wet chemical synthesis of nanocrystalline MFe2O4 (M = Cu, Co and Zn) ferrites for visible light driven degradation of methylene blue by hydrogen peroxide. RSC Adv. 2016;6:58125–36.
Zhang H, Liu J, Ou C, Faheem, Shen J, Yu H, Jiao Z, Han W, Sun X, Li J, Wang L. Reuse of Fenton sludge as an iron source for NiFe2O4 synthesis and its application in the Fenton-based process. J Environ Sci. 2017;53:1–8.
Tan X, Lu L, Wang L, Zhang J. Facile synthesis of bimodal mesoporous Fe3O4@SiO2 composite for efficient removal of Methylene Blue. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2015;37:2928–33.
Cui L, Lin H, Yang C, Han X, Zhang T, Qu F. Synthesis of multifunctional Fe3O4@mSiO2@Au core-shell nanocomposites for pH-responsive drug delivery. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2014;36:6156–64.
Hwang YK, Choi JN, Cho JH, Kwon H, Huh S. Fe3O4-nanoparticle- embedded multifunctional hollow mesoporous silica capsules. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2012;34:3379–83.
Yang ST, Zhang W, Xie J, Liao R, Zhang X, Yu B, Wu R, Liu X, Li H, Guo Z. Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles as a high performance Fenton-like catalyst in a neutral environment. RSC Adv. 2015;5:5458–63.
Chhowalla M, Shin HS, Eda G, Li LJ, Loh KP, Zhang H. The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat Chem. 2013;5:263–75.
Yang MQ, Zhang N, Wang Y, Xu YJ. Metal-free, robust, and regenerable 3D graphene–organics aerogel with high and stable photosensitization efficiency. J Catal. 2017;346:21–9.
Xie X, Zhang N, Tang ZR, Xu YJ. Adaptive geometry regulation strategy for 3D graphene materials: towards advanced hybrid photocatalysts. Chem Sci. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8sc03679a.
Ding X, Xiao D, Ji L, Jin D, Dai K, Yang Z, Wang S, Chen H. Simple fabrication of Fe3O4/C/g-C3N4 two-dimensional composite by hydrothermal carbonization approach with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible light. Catal Sci Technol. 2018;8:3484–92.
Zhu J, Cen H, Nan Z. Investigation on interaction induced cluster-shaped Zn-doped Fe3O4 formation by in situ calorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:1481–8.
Liu L, Zhang G, Wang L, Huang T, Qin L. Highly active S-modified ZnFe2O4 heterogeneous catalyst and its photo-Fenton behavior under UV–visible irradiation. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2011;50:7219–27.
Zhou R, Shen N, Zhao J, Su Y, Ren H. Glutathione-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with enhanced Fenton-like activity at neutral pH for degrading 2, 4-dichlorophenol. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6:1275–83.
Ma Z, Ren L, Xing S, Wu Y, Gao Y. Sodium dodecyl sulfate modified FeCo2O4 with enhanced Fenton-like activity at neutral pH. J Phys Chem C. 2015;40:23068–74.
Costa RCC, Moura FCC, Ardisson JD, Fabris JD, Lago RM. Highly active heterogeneous Fenton-like systems based on Fe0/Fe3O4 composites prepared by controlled reduction of iron oxides. Appl Catal B Environ. 2008;83:131–9.
Phan TTN, Nikoloski AN, Bahri PA, Li D. Heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of organics using highly efficient Cu-doped LaFeO3 under visible light. J Ind Eng Chem. 2018;61:53–64.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Nature Science Foundations of China (21673204 and 21273196) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, A., Nan, Z. Investigation on flower-shaped Ni-doped Fe3O4/SnS2 formation mechanism through a microcalorimetric method and catalytic property as a Fenton-like catalyst. J Therm Anal Calorim 139, 217–223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08432-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08432-0