Abstract
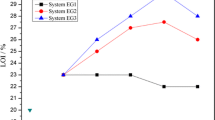
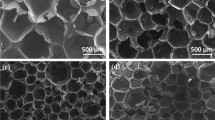
In this study, the flame-resistant epoxy syntactic foams with different content of hollow glass microspheres (HGM) were prepared by using aluminum diisobutylphosphinate (AlPBu) as flame retardant. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of the fracture surface of different epoxy syntactic foams showed that AlPBu particles had good compatibility with the matrix due to their similar polarities. And the limiting oxygen index, UL 94 test, cone calorimeter and thermogravimetric analysis were applied to characterize the flame retardation and thermal behavior of the foams. These results showed that AlPBu improved the flame retardancy of epoxy syntactic foams, while the HGM exhibit a complicated influence on the flame retardation, although both AlPBu and HGM enhanced the char residues and decreased the peak heat release rate as well as the total heat release of composites. In addition, swollen char layers mainly containing the HGM were generated after adding AlPBu. Then, the char residues of the foams after combustion were observed by SEM, and the results were applied to reveal the different fire behaviors of foams with different densities.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang L, Zhang J, Yang X, Zhang C, Gong W, Yu J. Flexural properties of epoxy syntactic foams reinforced by fiberglass mesh and/or short glass fiber. Mater Des. 2014;55:928–36.
Hu G, Yu D. Tensile, thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of hollow polymer particle-filled epoxy syntactic foam. Mater Sci Eng A. 2011;528:5177–83.
Wang L, Yang X, Zhang J, Zhang C, He L. The compressive properties of expandable microspheres/epoxy foams. Composites B. 2014;56:724–32.
Colloca M, Gupta N, Porfiri M. Tensile properties of carbon nanofiber reinforced multiscale syntactic foams. Composites B. 2013;44:584–91.
Zhuo JL, Xie LB, Liu GD, Chen XL, Wang YG. The synergistic effect of hollow glass microsphere in intumescent flame-retardant epoxy resin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;129:357–66.
Gupta N, Maharsia R. Enhancement of energy absorption in syntactic foams by nanoclay incorporation for sandwich core applications. Appl Compos Mater. 2005;12:247–61.
Tang Q, Wang B, Shi Y, Song L, Hu Y. Microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate with glycidyl methacrylate shell: application to flame retardant epoxy resin. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52:5640–7.
Qu H, Wu W, Hao J, Wang C, Xu J. Inorganic–organic hybrid coating encapsulated ammonium polyphosphate and its flame retardancy and water resistance in epoxy resin. Fire Mater. 2014;38:312–22.
Wang X, Hu Y, Song L, Xing W, Lu H, Lv P, Jie G. Flame retardancy and thermal degradation mechanism of epoxy resin composites based on a DOPO substituted organophosphorus oligomer. Polymer. 2010;51:2435–45.
Zhang W, Li X, Li L, Yang R. Study of the synergistic effect of silicon and phosphorus on the blowing-out effect of epoxy resin composites. Polym Degrad Stab. 2012;97:1041–8.
Luo H, Zhou F, Yang YY, Cao XL, Cai XF. Synergistic flame-retardant behavior and mechanism of tris(3-nitrophenyl) phosphine and DOPO in epoxy resins. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132:483–91.
Liu X, Liu J, Cai S. Comparative study of aluminum diethylphosphinate and aluminum methylethylphosphinate filled epoxy flame-retardant composites. Polym Compos. 2012;33:918–26.
Zhong L, Zhang KX, Wang X, Chen MJ, Xin F, Liu ZG. Synergistic effects and flame-retardant mechanism of aluminum diethyl phosphinate in combination with melamine polyphosphate and aluminum oxide in epoxy resin. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7699-4.
Hu Q, Peng PR, Peng S, Liu JY, Liu XQ, Zou LY, Chen J. Flame-retardant epoxy resin based on aluminum monomethylphosphinate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128:201–10.
Lv Q, Huang JQ, Chen MJ, Zhao J, Tan Y. An effective flame retardant and smoke suppression oligomer for epoxy resin. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52:9397–404.
Sun D, Yao Y. Synthesis of three novel phosphorus-containing flame retardants and their application in epoxy resins. Polym Degrad Stab. 2011;96:1720–4.
Guo WW, Yu B, Yuan Y, Song L, Hu Y. In situ preparation of reduced graphene oxide/DOPO-based phosphonamidate hybrids towards high-performance epoxy nanocomposites. Compos Part B Eng. 2017;123:154–64.
Shi YQ, Yu B, Zheng YY, Yang J, Duan ZP, Hu Y. Design of reduced graphene oxide decorated with DOPO-phosphanomidate for enhanced fire safety of epoxy resin. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;521:160–71.
Xu MJ, Xu GR, Leng Y, Li B. Synthesis of a novel flame retardant based on cyclotriphosphazene and DOPO groups and its application in epoxy resins. Polym Degrad Stab. 2016;123:105–14.
Li JD, Chai SY, Kong L, Chen L, Chang CL. A preparation method of alkyl-substituted phosphinate salt. Patent 103073577 A, CN; 2012.
Brehme S, Schartel B, Goebbels J, Fischer O, Pospiech D. Phosphorus polyester versus aluminium phosphinate in poly (butylene terephthalate) (PBT): flame retardancy performance and mechanisms. Polym Degrad Stab. 2011;96:875–84.
Zhao B, Chen L, Long JW, Jian RK, Wang YZ. Synergistic effect between aluminum hypophosphite and alkyl-substituted phosphinate in flame-retarded polyamide 6. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52:17162–70.
Samyn F, Bourbigot S. Thermal decomposition of flame retarded formulations PA6/aluminum phosphinate/melamine polyphosphate/organomodified clay: interactions between the constituents? Polym Degrad Stab. 2012;97:2217–30.
Shi YQ, Yu B, Duan LJ, Gui Z, Wang BB, Hu Y, Yuen Richard KK. Graphitic carbon nitride/phosphorus-rich aluminum phosphinates hybrids as smoke suppressants and flame retardants for polystyrene. J Hazard Mater. 2017;332:87–96.
Shi YQ, Gui Z, Yuan BH, Hu Y, Zheng YY. Flammability of polystyrene/aluminim phosphinate composites containing modified ammonium polyphosphate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:1067–77.
Shi YQ, Fu LB, Chen XL, Guo J, Yang FQ, Wang JG, Zheng YY, Hu Y. Hypophosphite/graphitic carbon nitride hybrids: preparation and flame-retardant application in thermoplastic polyurethane. Nanomaterials. 2017;7:259–71.
Zhu YL, Shi YQ, Huang ZQ, Duan LJ, Tai QL, Hu Y. Novel graphite-like carbon nitride/organic aluminum diethylhypophosphites nanohybrid: preparation and enhancement on thermal stability and flame retardancy of polystyrene. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf. 2017;99:149–56.
Shao X, Wang L, Li M, Jia D. Synthesis, characterization and thermal degradation kinetics of aluminum diisobutylphosphinate. Thermochim Acta. 2012;547:70–5.
Yao Q, Levchik SV, Alessio GR. Phosphorus-containing flame retardant for thermoplastic polymers. Patent 8003722-B2, USA; 2010.
Lin TC, Gupta N, Talalayev A. Thermoanalytical characterization of epoxy matrix-glass microballoon syntactic foams. J Mater Sci. 2009;44:1520–7.
Shabde VS, Hoo KA, Gladysz GM. Experimental determination of the thermal conductivity of three-phase syntactic foams. J Mater Sci. 2006;41:4061–73.
Stefani PM, Cyras V, Tejeira Barchi A, Vazquez A. Mechanical properties and thermal stability of rice husk ash filled epoxy foams. J Appl Polym Sci. 2006;99:2957–65.
Xia Y, Jin F, Mao Z, Guan Y, Zheng A. Effects of ammonium polyphosphate to pentaerythritol ratio on composition and properties of carbonaceous foam deriving from intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene. Polym Degrad Stab. 2014;107:64–73.
Orhan T, Isitman NA, Hacaloglu J, Kaynak C. Thermal degradation mechanisms of aluminium phosphinate, melamine polyphosphate and zinc borate in poly (methyl methacrylate). Polym Degrad Stab. 2011;96:1780–7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science Foundation of Guizhou Province ([2018]1088), Science and Technological Project of Guizhou Province GXCX2016-010, Science and Technology Project of Guizhou Province ([2017]2806, [2015]2077) and Guizhou Province High-level Innovative Talents Training Project (2016/5667).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, Y., Wang, L., Yang, Z. et al. Effect of aluminum phosphinate on the flame-retardant properties of epoxy syntactic foams. J Therm Anal Calorim 137, 1645–1656 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08051-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08051-9