Abstract
In this article, an efficient flame-retardant and smoke-suppressant agent HGM@AMP was prepared by coated hollow glass microspheres (HGM) with ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP) and applied in thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). The fire safety characteristics including heat and smoke production of TPU composites were investigated using cone calorimeter test (CCT), smoke density test (SDT), thermogravimetric analysis/infrared spectrometry (TG-IR), etc. The CCT results revealed that HGM@AMP could significantly decrease the heat release rate (HRR), total smoke release, smoke factor and so on. For example, when the loading of HGM@AMP was 0.5 mass%, the peak HRR value of the sample was decreased to 512.4 kW m−2, reduced by 55.1% compared with the sample containing the same loading of HGM (1141.8 kW m−2). The SDT results indicated that HGM@AMP could obviously improve the luminous flux of TPU composites in the test with or without flame, decreasing the production of smoke. And the TG-IR results showed that HGM@AMP can improve the thermal stability of TPU composites at high temperature. In all, HGM@AMP would make a great influence in improving the fire safety of TPU.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saralegi A, Rueda L, Fernández-D’Arlas B, Mondragon I, Eceiza A, Corcuera M. Thermoplastic polyurethanes from renewable resources: effect of soft segment chemical structure and molecular weight on morphology and final properties. Polym Int. 2013;62:106–15.
Chen X, Jiang Y, Jiao C. Smoke suppression properties of ferrite yellow on flame retardant thermoplastic polyurethane based on ammonium polyphosphate. J Hazard Mater. 2014;266:114–21.
Finnigan B, Martin D, Halley P, Truss R, Campbell K. Morphology and properties of thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposites incorporating hydrophilic layered silicates. Polymer. 2004;45:2249–60.
Chattopadhyay D, Webster D. Thermal stability and flame retardancy of polyurethanes. Prog Polym Sci. 2009;34:1068–133.
Lin M, Li B, Li Q, Li S, Zhang S. Synergistic effect of metal oxides on the flame retardancy and thermal degradation of novel intumescent flame-retardant thermoplastic polyurethanes. J Appl Polym Sci. 2011;121:1951–60.
Weil E. Levchik S Current practice and recent commercial developments in flame retardancy of polyamides. Flame Retard. 2009;22:85–104.
Covaci A, Harrad S, Abdallah M. Novel brominated flame retardants: a review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour. Env Inter. 2011;37:532–56.
Laoutid F, Bonnaud L, Alexandre M, Lopez-Cuesta J, Dubois P. New prospects in flame retardant polymer materials: from fundamentals to nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng. 2009;63:100–25.
Ricciardi M, Antonucci V, Zarrelli M, Giordano M. Fire behavior and smoke emission of phosphate-based inorganic fire-retarded polyester resin. Fire Mater. 2012;36:203–15.
Chen X, Ma C, Jiao C. Synergistic effects between iron-graphene and ammonium polyphosphate in flame-retardant thermoplastic polyurethane. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:1–10.
Liu Y, Wang Q. Preparation of microencapsulated red phosphorus through melamine cyanurate self-assembly and its performance in flame retardant polyamide 6. Polym Eng Sci. 2010;46:1548–53.
Almeras X, Bras M, Hornsby P, Bourbigot S, Marosi G, Keszei S, et al. Effect of fillers on the fire retardancy of intumescent polypropylene compounds. Polym Degrad Stab. 2003;82:325–31.
Park S, Jin F, Lee C. Preparation and physical properties of hollow glass microspheres-reinforced epoxy matrix resins. Mater Sci Eng. 2005;402:335–40.
Hu Y, Mei R, An Z, Zhang J. Silicon rubber/hollow glass microsphere composites: influence of broken hollow glass microsphere on mechanical and thermal insulation property. Compos Sci Technol. 2013;79:64–9.
Jiao Y, Xiao G, Xu W, Zhu R, Lu Y. Factors influencing the deposition of hydroxyapatite coating onto hollow glass microspheres. Mater Sci Eng. 2013;33:2744–51.
Sun L, Wan S, Yu Z, Wang L. Optimization and modeling of preparation conditions of TiO2 nanoparticles coated on hollow glass microspheres using response surface methodology. Sep Purif Technol. 2014;125:156–62.
Jiao C, Wang H, Li S, Chen X. Fire hazard reduction of hollow glass microspheres in thermoplastic polyurethane composites. J Hazard Mater. 2017;332:176–84.
Chen X, Jiang Y, Jiao C. Synergistic effects between hollow glass microsphere and ammonium polyphosphate on flame-retardant thermoplastic polyurethane. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117:857–66.
Liu L, Hu J, Zhuo J, Jiao C, Chen X, Li S. Synergistic flame retardant effects between hollow glass microspheres and magnesium hydroxide in ethylene-vinyl acetate composites. Polym Degrad Stab. 2014;104:87–94.
Wang G, Hu Xiao-Ping LuZ, Song L, Zhang M, Zhang J. Preparation and characterization of ammonium molybdophosphate coated by microcapsule and flame retardancy and smoke suppression of its composites with UPR. Fine Chem. 2007;24:108–12.
Deng Q, Li M. Cheng Z Study of cesium recovery with zirconyl phosphate-ammonium molybdophosphate complex ion exchanger. Nucl Power Eng. 2006;27:94–6.
Ramgobin A, Fontaine G, Penverne C, Bourbigot S. Thermal stability and fire properties of salen and metallosalens as fire retardants in thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). Mater. 2017;10:665–83.
Kamikawa D, Kuroda K, Inoue M, Kubo S, Yoshida T. Evaluation of combustion properties of wood pellets using a cone calorimeter. J Wood Sci. 2010;55:453–7.
Schartel B, Hull T. Development of fire retarded materials—Interpretation of cone calorimeter data. Fire Mater. 2010;31:327–54.
Sacristán M, Hull T, Stec A, Ronda J, Galià M, Cádiz V. Cone calorimetry studies of fire retardant soybean-oil-based copolymers containing silicon or boron: comparison of additive and reactive approaches. Polym Degrad Stab. 2010;95:1269–74.
Jiao C, Wang H, Zhang Z. Preparation and properties of an efficient smoke suppressant and flame-retardant agent for thermoplastic polyurethane. Polym Adv Technol. 2017;28:1690–8.
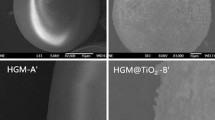
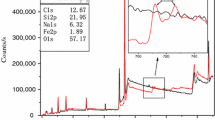
Wang H, Jiao C, Zhao L. Preparation and characterization of TiO2-coated hollow glass microsphere and its flame-retardant property in thermoplastic polyurethane. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:2729–40.
Savas L, Deniz T, Tayfun U, Dogan M. Effect of microcapsulated red phosphorus on flame retardant, thermal and mechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethane composites filled with huntite & hydromagnesite mineral. Polym Degrad Stab. 2017;135:121–9.
Zhou K, Gui Z, Hu Y. The influence of graphene based smoke suppression agents on reduced fire hazards of polystyrene composites. Composites. 2016;80:217–27.
Carty P, Creighton J, White S. TG and flammability studies on polymer blends containing acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene and chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;63:679–87.
Zhou K, Tang G, Jiang S. Combination effect of MoS2 with aluminum hypophosphite in flame retardant ethylene-vinyl acetate composites. RSC Adv. 2016;6:37672–80.
Chen X, Ma C, Jiao C. Enhancement of flame-retardant performance of thermoplastic polyurethane with the incorporation of aluminum hypophosphite and iron-graphene. Polym Degrad Stab. 2016;129:275–85.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51776101, 51206084) the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2017MB016) and the Project of the State Administration of Work Safety (shandong-0039-2017AQ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, C., Wang, H. & Chen, X. An efficient flame-retardant and smoke-suppressant agent by coated hollow glass microspheres with ammonium molybdophosphate for thermoplastic polyurethane. J Therm Anal Calorim 137, 1579–1589 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08044-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08044-8