Abstract
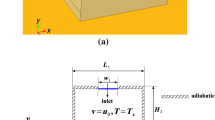
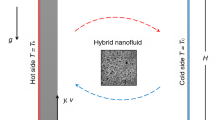
The present paper investigates numerically the effect of an external magnetic field on heat transfer and entropy generation of Ag–MgO (50:50 vol%)/water hybrid nanofluid flow in a partially heated irregular ventilated cavity. A finite-volume FORTRAN code has been written to solve the governing partial differential equations. New empirical correlations specifically dedicated to predict the dynamic viscosity and the thermal conductivity of the considered hybrid nanofluid were employed. After validation of model, the analysis has been done for a wide range of Reynolds number (10 ≼ Re ≼ 600), Hartmann number (0 ≼ Ha ≼ 80) and total nanoparticle volume fraction (0 ≼ φ ≼ 0.02). The results are presented in terms of streamlines, isotherms and isentropic lines as well as the average Nusselt number (Num), the average entropy generation (Sgen,m) and the Bejan number (Beavg). The criterion ξ = Sgen,m/Num is adopted to discuss the thermal performances of the system. The results reveal that the intensification of the magnetic field tends to attenuate the heat transfer convection and to reduce the thickness of the thermal boundary layer, close to the active walls. Globally, adding nanoparticles to the base fluid improves the heat transfer but increases the total entropy generation.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B 0 :
-
Magnetic induction (T)
- Be avg :
-
Average Bejan number
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity (J kg−1 K−1)
- d :
-
Dimensional length of the heat source (m)
- D :
-
Dimensionless distance of heat source from the entrance e1/W
- e 1 :
-
Distance of heat source from the entrance (m)
- e 2 :
-
Distance of heat source from the right vertical wall (m)
- Ec :
-
Eckert number
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m s−2)
- Gr :
-
Grashof number
- h :
-
Opening width (m)
- H :
-
Height of the cavity (m)
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- Nu l :
-
Local Nusselt number
- Nu m :
-
Average Nusselt number
- Nu * :
-
Normalized Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Ri :
-
Richardson number
- S ′gen :
-
Dimensional local entropy generation (W K−1 m−3)
- S gen :
-
Dimensionless local entropy generation
- S avg,θ :
-
Dimensionless average entropy generation due to heat transfer
- S avg,ψ :
-
Dimensionless average entropy generation due to fluid friction
- S avg, Mag :
-
Dimensionless average entropy generation due to magnetic field
- S * :
-
Normalized entropy generation
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u, v :
-
Velocity components (m s−1)
- U 0 :
-
Velocity of the flow at the inlet (m s−1)
- U, V :
-
Dimensionless velocity components
- x, y :
-
Dimensional Cartesian coordinates (m)
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless Cartesian coordinates
- W :
-
Width of the cavity (m)
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (K−1)
- ε :
-
Dimensionless length of the heat source d/W
- ξ :
-
Thermal performance criterion (Sgen,m/Num)
- φ :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- υ :
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2 s−1)
- θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- σ :
-
Fluid electrical conductivity (Ω−1 m−1)
- χ :
-
Irreversibility factor
- C:
-
Cold
- H:
-
Hot
- f:
-
Base fluid
- l:
-
Local
- m:
-
Average
- hyb,nf:
-
Hybrid nanofluid
- 0:
-
Reference state
References
Rashidi S, Bovand M, Abolfazli J, Ahmadi G. Discrete particle model for convective Al2O3-water nanofluid around a triangular obstacle. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;100:39–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.01.076.
Akbarzadeh M, Rashidi S, Karimi N, Omar N. First and second laws of thermodynamics analysis of nanofluid flow inside a heat exchanger duct with wavy walls and a porous insert. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7044-y.
Rashidi S, Eskandarian M, Mahian O, Poncet S. Combination of nanofluid and inserts for heat transfer enhancement. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;9:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7070-9.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, et al. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows-Part I: fundamental and theory. Phys Rep. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2018.11.004.
Rashidi S, Karimi N, Mahian O, Esfahani JA. A concise review on the role of nanoparticles upon the productivity of solar desalination systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;8:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7500-8.
Rashidi S, Mahian O, Languri EM. Applications of nanofluids in condensing and evaporating systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;131:2027–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6773-7.
Rahimi A, Sepehr M, Lariche MJ, Mesbah M, Kasaeipoor A, Malekshah EH. Analysis of natural convection in nanofluid-filled H-shaped cavity by entropy generation and heatline visualization using lattice Boltzmann method. Phys E Low Dimens Syst Nanostructures. 2018;97:347–62.
Sidik NAC, Adamu IM, Jamil MM, Kefayati GHR, Mamat R, Najafi G. Recent progress on hybrid nanofluids in heat transfer applications: a comprehensive review. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;78:68–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.08.019.
Esfe MH, Arani AAA, Rezaie M, Yan W-M, Karimipour A. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:189–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.06.003.
Kasaeipoor A, Malekshah EH, Kolsi L. Free convection heat transfer and entropy generation analysis of MWCNT-MgO (15%–85%)/water nanofluid using Lattice Boltzmann method in cavity with refrigerant solid body-Experimental thermo-physical properties. Powder Technol. 2017;322:9–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.08.061.
Toghraie D, Chaharsoghi VA, Afrand M. Measurement of thermal conductivity of ZnO–TiO2/EG hybrid nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125:527–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5436-4.
Ismael MA, Abu-Nada E, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection in a square cavity filled with CuO-Water nanofluid heated by corner heater. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;133:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.08.029.
Astanina MS, Sheremet MA, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Mixed convection of Al2O3-water nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity having two porous layers. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;118:527–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.11.018%0A.
Sun C, Yu B, Oztop HF, Wang Y, Wei J. Control of mixed convection in lid-driven enclosures using conductive triangular fins. 2011;54:894–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.09.068.
Akar S, Rashidi S, Esfahani AJ. Second law of thermodynamic analysis for nanofluid turbulent flow around a rotating cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;132:1189–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6907-y.
Shirejini ZS, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Recovery of drop in heat transfer rate for a rotating system by nanofluids. J Mol Liq. 2016;220:961–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.05.039.
Mansour MA, Siddiqa S, Gorla RSR, Rashad AM. Effects of heat source and sink on entropy generation and MHD natural convection of Al2O3–Cu/water hybrid nanofluid filled with square porous cavity. Therm Sci Eng Prog. 2018;6:57–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2017.10.014.
Radhakrishnan TV, Verma AK, Balaji C, Venkateshan SP. An experimental and numerical investigation of mixed convection from a heat generating element in a ventilated cavity. 2007;32:502–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2007.06.001.
Tmartnhad I, El M, Najam M, Oubarra A. Numerical investigation on mixed convection flow in a trapezoidal cavity heated from below. Energy Convers Manag. 2008;49:3205–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2008.05.017.
Minaei A, Ashjaee M, Goharkhah M. Experimental and numerical study of mixed and natural convection in an enclosure with a discrete heat source and ventilation ports. Heat Transf Eng. 2014;35:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/01457632.2013.810455.
Parvin S, Chamkha AJ. An analysis on free convection flow, heat transfer and entropy generation in an odd-shaped cavity filled with nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;54:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2014.02.031.
Rehena N, Alim MA. Control volume finite element simulation of MHD forced and natural convection in a vertical channel with a heat-generating pipe. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55:2813–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.02.023.
Kalidasan K, Velkennedy R, Kanna PR. Laminar natural convection of Copper–Titania/Water hybrid nanofluid in an open ended C-shaped enclosure with an isothermal block. J Mol Liq. 2017;246:251–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.09.071.
Kalidasan K, Kanna PR. Natural convection on an open square cavity containing diagonally placed heaters and adiabatic square block and filled with hybrid nanofluid of nanodiamond-cobalt oxide/water. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2017;81:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.12.005.
Kalidasan K, Kanna PR. Effective utilization of MWCNT-water nanofluid for the enhancement of laminar natural convection inside the open square enclosure. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2016;65:331–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.05.035.
Sourtiji E, Gorgi-Bandpy M, Ganji D, Hosseinizadeh SF. Numerical analysis of mixed convection heat transfer of Al2O3-water nanofluid in a ventilated cavity considering different positions of the outlet port. Powder Technol. 2014;262:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.04.061.
Mehrizi AA, Farhadi M, Afroozi HH, Sedighi K, Darz AAR. Mixed convection heat transfer in a ventilated cavity with hot obstacle: effect of nanofluid and outlet port location. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2012;39:1000–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2012.04.002.
Shahi M, Mahmoudi AH, Talebi F. Numerical study of mixed convective cooling in a square cavity ventilated and partially heated from the below utilizing nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37:201–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2009.10.002.
Yousefi-Lafouraki B, Ramiar A, Mohsenian S. Entropy generation analysis of a confined slot impinging jet in a converging channel for a shear thinning nanofluid. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;105:675–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.03.067.
Rashidi S, Javadi P, Esfahani AJ. Second law of thermodynamics analysis for nanofluid turbulent flow inside a solar heater with the ribbed absorber plate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7164-4.
Bejan A. A study of entropy generation in fundamental convective heat transfer. J Heat Transf. 1979;101:718–25.
Biswal P, Basak T. Entropy generation vs energy efficiency for natural convection based energy flow in enclosures and various applications: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;80:1412–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.04.070.
Kasaeipoor A, Ghasemi B, Aminossadati SM. Convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a vented T-shaped cavity in the presence of magnetic field. Int J Therm Sci. 2015;94:50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.02.014.
Benzema M, Benkahla YK, Ouyahia S-E. Etude numérique de la convection mixte lors de l’écoulement d’un nanofluide hybride (Ag-MgO/Eau) dans une cavité trapézoïdale ventilée soumise à l’action d’un champ magnétique. In: 23th Congrès Fr. Mec. Lille, Fr. 28 Aout- 1 Sept.; 2017.
Hussain S, Ahmed SE, Akbar T. Entropy generation analysis in MHD mixed convection of hybrid nanofluid in an open cavity with a horizontal channel containing an adiabatic obstacle. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:1054–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.06.135.
Mehrez Z, El Cafsi A, Belghith A, Le Quéré P. The entropy generation analysis in the mixed convective assisting flow of Cu-water nanofluid in an inclined open cavity. Adv Powder Technol. 2015;26:1442–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2015.07.020.
Mehrez Z, El Cafsi A, Belghith A, Le Quéré P. MHD effects on heat transfer and entropy generation of nanofluid flow in an open cavity. J Magn Magn Mater. 2015;374:214–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.08.010.
Mahmoudi HA, Hooman K. Effect of a discrete heat source location on entropy generation in mixed convective cooling of a nanofluid inside the ventilated cavity. Int J Exergy. 2013;13:299–319.
Al-Rashed AAAA, Kalidasan K, Kolsi L, Velkennedy R, Aydi A, Hussein AK, Malekshah EH. Mixed convection and entropy generation in a nanofluid filled cubical open cavity with a central isothermal block. Int J Mech Sci. 2018;135:362–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.11.033.
Zamzari F, Mehrez Z, El Cafsi A, Belghith A, Le Quéré P. Numerical investigation of entropy generation and heat transfer of pulsating flow in a horizontal channel with an open cavity. J. Hydrodyn. 2017;29:632–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60776-X.
Benzema M, Benkahla YK, Labsi N, Brunier E, Ouyahia S. Numerical mixed convection heat transfer analysis in a ventilated irregular enclosure crossed by Cu-water nanofluid. Arab J Sci Eng. 2017;42:4575–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2563-6.
Öztop HF, Estellé P, Yan W-M, Al-Salem K, Orfi J, Mahian O. A brief review of natural convection in enclosures under localized heating with and without nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;60:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2014.11.001.
Biswas N, Manna NK, Datta P, Mahapatra PS. Analysis of heat transfer and pumping power for bottom-heated porous cavity saturated with Cu-water nanofluid. Powder Technol. 2018;326:356–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.12.030.
Garoosi F, Bagheri G, Talebi F. Numerical simulation of natural convection of nanofluids in a square cavity with several pairs of heaters and coolers (HACs) inside. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;67:362–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.08.034.
Mahian O, Pop I, Sahin AZ, Oztop HF, Wongwises S. Irreversibility analysis of a vertical annulus using TiO2/water nanofluid with MHD flow effects. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;64:671–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.05.001.
Davarnejad R, Jamshidzadeh M. CFD modeling of heat transfer performance of MgO-water nanofluid under turbulent flow. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2015;18:536–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2015.03.011.
Smith DK, Leider HR. Low-temperature thermal expansion of LiH, MgO and CaO. J Appl Cryst. 1968;246:246–9. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889868005418.
Kolsi L, Mahian O, Öztop HF, Aich W, Borjini MN, Abu-Hamdeh N, Ben Aissia H. 3D Buoyancy-induced flow and entropy generation of nanofluid-filled open cavities having adiabatic diamond shaped obstacles. Entropy. 2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18060232.
Mahian O, Oztop H, Pop I, Mahmud S, Wongwises S. Entropy generation between two vertical cylinders in the presence of MHD flow subjected to constant wall temperature. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2013;44:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2013.03.005.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, et al. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows-part II: applications. Phys Rep. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2018.11.003.
Patankar SV. Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. New York: McGraw-Hil; 1980.
Ouyahia S, Benkahla YK, Labsi N. Numerical study of the hydrodynamic and thermal proprieties of titanium dioxide nanofluids trapped in a triangular geometry. Arab J Sci Eng. 2016;41:1995–2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2055-0.
Ismael MA, Armaghani T, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate heat transfer and entropy generation in a cavity filled with a nanofluid-saturated porous media and heated by a triangular solid. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2015;59:138–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.09.012.
Mahmoudi HA, Pop I, Shahi M, Talebi F. MHD natural convection and entropy generation in a trapezoidal enclosure using Cu–water nanofluid. Comput Fluids. 2013;72:46–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2012.11.014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benzema, M., Benkahla, Y.K., Labsi, N. et al. Second law analysis of MHD mixed convection heat transfer in a vented irregular cavity filled with Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim 137, 1113–1132 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08017-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08017-x