Abstract
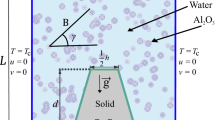
Numerical simulation of mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven triangular cavity filled with power law nanofluid and with an opening was performed under the effect of an inclined magnetic field. The left vertical wall of the cavity moves in + y-direction, and the bottom wall of the cavity is partially heated. Galerkin weighted residual finite element method was used to solve the governing equations. Influence of Richardson number, Hartmann number, inclination angle, opening ratio and nanoparticle volume fraction on the fluid flow and heat transfer is examined for various power law indices. It was observed that average heat transfer deteriorates as the value of Richardson number and Hartmann number enhances. At the lowest value of Richardson number, the discrepancy between the average heat transfer corresponding to different power law indices is higher. The inclination angle of the magnetic field where the minimum of the average Nusselt number is seen depends on the fluid type. Average heat transfer number is the highest for the highest value of the opening ratio. The average Nusselt number enhances with solid particle volume fraction, and there are slight variations in the reduction in the average Nusselt number when base fluid and nanofluid are considered for various power law indices.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\mathbf {B}_0\) :
-
Magnetic field strength
- Gr :
-
Grashof number
- h :
-
Local heat transfer coefficient (\(\hbox {W m}^{-2}\; \hbox {K}^{-1}\))
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W \(\hbox {m}^{-1}\; \hbox {K}^{-1}\))
- H :
-
Length of the enclosure (m)
- h :
-
Length of the heater (m)
- m :
-
Consistency coefficient
- n :
-
Power law index
- \({Nu}_\mathrm{x}\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \({Nu}_\mathrm{m}\) :
-
Average Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Ri :
-
Richardson number
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u, v :
-
x–y velocity components (m \(\hbox {s}^{-1}\))
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity (\(\hbox {m}^2\hbox { s}^{-1}\))
- \(\beta\) :
-
Expansion coefficient (\(\hbox {K}^{-1}\))
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Inclination angle (°)
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (\(\hbox {m}^2\hbox { s}^{-1}\))
- \(\theta\) :
-
Non-dimensional temperature
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of the fluid (\(\hbox {kg m}^{-3}\))
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Electrical conductivity (\(\hbox {S m}^{-1}\))
- c:
-
Cold
- h:
-
Hot
- m:
-
Average
References
Varol Y, Koca A, Oztop H. Natural convection in a triangle enclosure with flush mounted heater on the wall. Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transf. 2006;33:951–8.
Yucel N, Turkoglu H. Natural convection in rectangular enclosures with partial heating and cooling. Heat Mass Transf. 1994;29:471–7.
Oztop FH, Estelle P, Yan WM, Al-Salem Khaled, Orfi J, Mahian O. A brief review of natural convection in enclosures under localized heating with and without nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;60:37–44.
Oztop HF, Abu-Nada E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2008;29:1326–36.
Yucel A. Convection and radiation in a square enclosure. Numer Heat Transfer Part A. 1989;15:261–78.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF, Chamkha AJ. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid filled lid driven cavity under the influence of inclined magnetic fields imposed to its upper and lower diagonal triangular domains. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;406:266–81.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Effect of a rotating cylinder in forced convection of ferrofluid over a backward facing step. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;71:142–8.
Banerjee S, Mukhopadhyay A, Sen S, Ganguly R. Thermomagnetic convection in square and shallow enclosures for electronics cooling. Numer Heat Transfer Part A Appl. 2009;55:931–51.
Polat O, Bilgen E. Conjugate heat transfer in inclined open shallow cavities. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2003;46:1563–73.
Ostrach S. Natural convection heat transfer in cavities and cells. In: Proceedings 7th international heat transfer conference, Toronto, Canada; 1978
Yu P, Qiu J, Qin Q, Tian ZF. Numerical investigation of natural convection in a rectangular cavity under different directions of uniform magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;67:1131–44.
Prakash C, Kaminski D. Conjugate natural convection in square enclosure: effect of conduction in one of the vertical walls. HTD ASME. 1984;39:49–54.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF, Al-Salem K. Natural convection of ferrofluids in partially heated square enclosures. J Magn Magn Mater. 2014;372:122–33.
Rahman M, Alim M, Sarker M. Numerical study on the conjugate effect of joule heating and magnato-hydrodynamics mixed convection in an obstructed lid-driven square cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37(37):524–34.
Oztop HF, Al-Salem K, Pop I. MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with corner heater. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:494–3504.
Finlayson B. Convective instability of ferromagnetic fluids. J Fluid Mech. 1970;40:753–67.
Tiwari RK, Das MK. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50:2002–18.
Armaghani T, Chamkha AJ, Maghrebi M, Nazari M. Numerical analysis of a nanofluid forced convection in a porous channel: a new heat flux model in LTNE condition. J Porous Med. 2014;17:637–46.
Ismael MA, Armaghani T, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate heat transfer and entropy generation in a cavity filled with a nanofluid-saturated porous media and heated by a triangular solid. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2016;59:138–51.
Kakac S, Pramuanjaroenkij A. Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52:3187–96.
Meibodi SS, Kianifar A, Mahian O, Wongwises S. Second law analysis of a nanofluid-based solar collector using experimental data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:617–25.
Rashidi S, Mahian O, Languri EM. Applications of nanofluids in condensing and evaporating systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017; 1–13 (in press)
Mahian O, Kianifar A, Kalogirou SA, Pop I, Wongwises S. A review of the applications of nanofluids in solar energy. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;57:582–94.
Abu-Nada E, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection flow in a lid-driven inclined square enclosure filled with a nanofluid. Eur J Mechs B Fluids. 2010;29:472–82.
Armaghani T, Kasaeipoor A, Alavi N, Rashidi M. Numerical investigation of water-alumina nanofluid natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation in a baffled l-shaped cavity. J Mol Liq. 2016;223:243–51.
Chamkha AJ, Abu-Nada E. Mixed convection flow in single- and double-lid driven square cavities filled with water–Al2O3 nanofluid: Effect of viscosity models. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2012;36:82–96.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Identification of forced convection in pulsating flow at a backward facing step with a stationary cylinder subjected to nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2013;45:111–21.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Mixed convection of nanofluids in a three dimensional cavity with two adiabatic inner rotating cylinders. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;117:331–43.
Abu-Nada E. Application of nanofluids for heat transfer enhancement of separated flows encountered in a backward facing step. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2008;29:242–9.
Shenoy A, Sheremet M, Pop I. Convective flow and heat transfer from wavy surfaces: viscous fluids. Porous media and nanofluids. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group; 2016.
Das SK, Choi SUS, Yu W, Pradeep Y. Nanofluids: science and technology. Hoboken: Wiley; 2008.
Grosan T, Sheremet MA, Pop I. In: Heat transfer enhancement in cavities filled with nanofluids. 2017; 267–284
Bahiraei M. A numerical study of heat transfer characteristics of Cuo–water nanofluid by euler–lagrange approach. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123:1591–9.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Modeling and optimization of MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven trapezoidal cavity filled with alumina–water nanofluid: effects of electrical conductivity models. Int J Mech Sci. 2018;136:264–78.
Sheikholeslami M, Bandpy MG, Ganji D. Numerical investigation of MHD effects on Al2o3–water nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a semi-annulus enclosure using LBM. Energy. 2013;60:501–10.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Numerical study of MHD mixed convection in a nanofluid filled lid driven square enclosure with a rotating cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;78:741–54.
Sheikholeslami M, Bandpy MG, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A. Simulation of MHD Cuo–water nanofluid flow and convective heat transfer considering lorentz forces. J Magn Magn Mater. 2014;369:69–80.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Conjugate natural convection in a nanofluid filled partitioned horizontal annulus formed by two isothermal cylinder surfaces under magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;108:156–71.
Hatami M, Sheikholeslami M, Hosseini M, Ganji DD. Analytical investigation of MHD nanofluid flow in non-parallel walls. J Mol Liq. 2014;194:251–9.
Chamkha AJ, Rashad AM, Mansour MA, Armaghani T, Ghalambaz M. Effects of heat sink and source and entropy generation on MHD mixed convection of a cu-water nanofluid in a lid-driven square porous enclosure with partial slip. Phys Fluids. 2017;29:052001.
Chamkha AJ, Rashad AM, Armaghani T, Mansour MA. Effects of partial slip on entropy generation and MHD combined convection in a lid-driven porous enclosure saturated with a cu-water nanofluid. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. 2017 (in press)
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. MHD mixed convection of nanofluid filled partially heated triangular enclosure with a rotating adiabatic cylinder. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2014;45:2150–62.
Mahmoudi A, Mejri I, Abbassi MA, Omri A. Lattice boltzmann simulation of MHD natural convection in a nanofluid-filled cavity with linear temperature distribution. Powder Technol. 2014;256:257–71.
Sheikholeslami M, Abelman S. Two-phase simulation of nanofluid flow and heat transfer in an annulus in the presence of an axial magnetic field. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol. 2015;14:561–9.
Rashad A, Armaghani T, Chamkha A, Mansour M. Entropy generation and MHD natural convection of a nanofluid in an inclined square porous cavity: effects of a heat sink and source size and location. Chin J Phys. 2018;56:193–211.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Influence of inclination angle of magnetic field on mixed convection of nanofluid flow over a backward facing step and entropy generation. Adv Powder Technol. 2015;26:1663–75.
Sheikholeslami M, Rashidi M, Ganji D. Effect of non-uniform magnetic field on forced convection heat transfer of image-water nanofluid. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2015;294:299–312.
Selimefendigil F, Chamkha AJ. Natural convection of a hybrid nanofluid-filled triangular annulus with an opening. Comput Thermal Sci. 2016;8:555–66.
Muftuoglu A, Bilgen E. Natural convection in an open square cavity with discrete heaters at their optimized positions. Int J Therm Sci. 2008;47:369–77.
Hsu TH, Hong KY. Natural convection of micropolar fluids in an open cavity. Numer Heat Transf Part A. 2006;50:281–300.
Bilgen E, Muftuoglu A. Natural convection in an open square cavity with slots. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2008;35:896–900.
Kefayati G. Simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of non-newtonian power-law fluids in a sinusoidal heated cavity using FDLBM. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;53:139–53.
Kefayati G. FDLBM simulation of magnetic field effect on non-newtonian blood flow in a cavity driven by the motion of two facing lids. Powder Technol. 2014;253:325–37.
Mendu SS, Das P. Flow of power-law fluids in a cavity driven by the motion of two facing lids—a simulation by lattice boltzmann method. J Non Newton Fluid Mech. 2012;175:10–24.
Polat O, Bilgen E. Laminar natural convection in shallow open cavities. Int J Therm Sci. 2002;41:360–8.
Maxwell J. A treatise on electricity and magnetism. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1873.
Brinkman H. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys. 1952;20:571–81.
Pirmohammadi M, Ghassemi M. Effect of magnetic field on convection heat transfer inside a tilted square enclosure. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2009;36:776–80.
Sarris I, Zikos G, Grecos A, Vlachos N. On the limits of validity of the low magnetic reynolds number approximation in MHD natural-convection heat transfer. Numer Heat Transf Part B. 2006;50:158–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selimefendigil, F., Chamkha, A.J. Magnetohydrodynamics mixed convection in a power law nanofluid-filled triangular cavity with an opening using Tiwari and Das’ nanofluid model. J Therm Anal Calorim 135, 419–436 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7037-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7037-x