Abstract
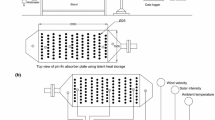
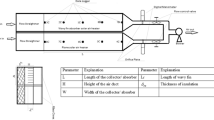
This research paper deals with the experimental thermodynamic analysis of a forced convection solar air heater using pin-fin absorber plate and compared with the standard flat absorber plate. The experiments were carried out during the months of February 2018 and March 2018 at Coimbatore city in India. The performance parameters such as, outlet air temperature, energy efficiency, thermohydraulic efficiency, and exergy efficiency are used for performance comparisons. The results showed that the pin-fin absorber plate has about 17 °C higher outlet air temperature when compared to the flat absorber plate. The energy efficiency of a forced convection solar air heater using pin-fin absorber plate was found to be 3% to 12% higher when compared to flat absorber plate with 2% to 11% higher exergy efficiency. The results confirmed that forced convection solar air heaters using pin-fin absorber plate is having significant performance improvement in thermodynamic performance with minimum pressure drop across the air heater duct.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Area (m2)
- c p :
-
Specific heat (J kg−1 K−1)
- D h :
-
Diameter mean diameter (m)
- \(\dot{E}x_{\text{des}}\) :
-
Exergy (W)
- f :
-
Friction coefficient
- h c :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- h r :
-
Radiation heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- h fg :
-
Latent heat of paraffin wax (J kg−1 K−1)
- h :
-
Specific enthalpy (J kg−1)
- I :
-
Intensity of radiation (W m−2)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- K :
-
Head loss factor
- L 1 :
-
Length of the solar air heater (m)
- L 2 :
-
Width of the solar air heater (m)
- L 3 :
-
Depth of the solar air heater (m)
- \(\dot{m}_{\text{a}}\) :
-
Mass flow rate of air (kg s−1)
- p :
-
Pressure (bar)
- P flow :
-
Pumping power (W)
- P blower :
-
Blower power (W)
- \(\dot{Q}\) :
-
Amount of heat transfer (W)
- \(\dot{Q}_{\text{s}}\) :
-
Energy incident on the solar air heater (W)
- R :
-
Gas constant (J kg−1 K−1)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number (–)
- s :
-
Specific entropy (J kg−1 K−1)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- U :
-
Over all heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- v :
-
Velocity (m s−1)
- x :
-
Thickness (m)
- 0:
-
Dead state
- a:
-
Air
- ab:
-
Absorbed
- amb:
-
Ambient
- ava:
-
Available
- b:
-
Bottom
- ch:
-
Charging
- des:
-
Destruction
- e:
-
Edge
- f:
-
Fluid
- g:
-
Glass
- h:
-
Hydraulic
- i:
-
Insulation
- loss:
-
Heat loss
- m:
-
Mean
- p:
-
Plate
- r, p-g:
-
Radiation heat exchange between plate and glass
- r, g-a:
-
Radiation heat exchange between glass and air
- s:
-
Stored
- t:
-
Top
- th-hy:
-
Thermohydraulic
- u:
-
Utilised
- w:
-
Wind
- \(\psi_{\text{i}}\) :
-
Specific exergy (J kg−1)
- τ :
-
Transmissivity
- α :
-
Absorptivity
- ε :
-
Emissivity
- σ :
-
Stefan Boltzmann constant (5.68 × 10−8 W m−2 K−4)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- η :
-
Efficiency (%)
- Δp :
-
Pressure drop (N m−2)
- Δp total :
-
Total pressure drop (N m−2)
- Δp ch :
-
Pressure drop across the channel (N m−2)
- Δp Entry :
-
Pressure drop at the entry (N m−2)
- Δp o :
-
Pressure drop in the orifice meter (N m−2)
- Δh :
-
Difference in liquid column (m)
References
Kalogirou SA. Solar thermal collectors and applications. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2004;30:231–95.
Tyagi VV, Pandey AK, Kaushik SC, Tyagi SK. Thermal performance evaluation of a solar air heater with and without thermal energy storage. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:1345–52.
Bhushan B, Singh R. A review on methodology of artificial roughness used in duct of solar air heaters. Energy. 2010;35:202–12.
Alam T, Saini RP, Salini JS. Use of turbulators for heat transfer augmentation in an air duct—a review. Renew Energy. 2014;62:689–715.
Singh OK, Panwar NL. Effects of thermal conductivity and geometry of materials on the temperature variation in packed bed solar air heater. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:839–47.
Ramadan MRI, El-Sebaii AA, Aboul-Enein S, El-Bialy E. Thermal performance of a packed bed double-pass solar air heater. Energy. 2007;32:1524–35.
Mohanraj M, Chandrasekar P. Performance of a solar drier with and without heat storage material for copra drying. Int J Global Energy Issues. 2009;32:112–21.
Akpinar EK, KocyIgit F. Energy and exergy analysis of a new flat-plate solar air heater having different obstacles on absorber plates. Appl Energy. 2010;87:3438–50.
Tanda G. Performance of solar air heater ducts with different types of ribs on the absorber plate. Energy. 2011;36:6651–60.
Yeh H-M, Ho C-D, Lin C-Y. Effect of collector aspect ratio on the collector efficiency of upward type baffled solar air heaters. Energy Convers Manag. 2000;41:971–81.
Chamoli S, Thakur NS. Exergetic performance evaluation of solar air heater having V-down perforated baffles on the absorber plate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117:909–23.
Ozgen F, Esen M, Esen H. Experimental investigation of thermal performance of a double-flow solar air heater having aluminum cans. Renew Energy. 2009;34:2391–8.
Nwosu NP. Employing exergy-optimized pin-fins in the design of an absorber in a solar air heater. Energy. 2010;35:571–5.
Arul Kumar R, Ganesh Babu B, Mohanraj M. Thermodynamic performance of a forced convection solar air heaters using pin-fin absorber plate packed with latent heat storage materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:1657–78.
Arul Kumar R, Ganesh Babu B, Mohanraj M. Experimental investigations on a forced convection solar air heater using packed bed absorber plates with phase change materials. Int J Green Energy. 2017;14(15):1330753
Tyagi VV, Pandey AK, Giridhar G, Bandhopdhayay B, Park SR, Tyagi SK. Comparative study based on exergy analysis of solar air dryer using temporary thermal energy storage. Int J Energy Res. 2012;36:724–36.
Shariah A, Al-Akhras MA, Al-Omari IA. Optimizing the tilt angle of solar collectors, Renew. Energy. 2002;26:587–98.
Kalaiarasi G, Velraj R, Muthusamy V. Swami, Experimental energy analysis of a flat plate solar air heater with a new design of integrated sensible heat storage. Energy. 2016;111:609–19.
Holman JP. Experimental methods for engineers. New Delhi: Tata Mcgraw hill Publishing Company; 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivakumar, S., Siva, K. & Mohanraj, M. Experimental thermodynamic analysis of a forced convection solar air heater using absorber plate with pin-fins. J Therm Anal Calorim 136, 39–47 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-07998-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-07998-5