Abstract
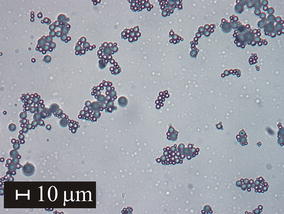
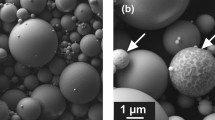
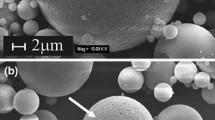
Yttrium aluminate glasses with eutectic AY-E and near-eutectic composition AY-NE were prepared in the form of glass microspheres. Their basic characterization was carried out by XRD, optical microscopy and SEM. In DSC records of both samples, two exothermic peaks in temperature interval 940–1027 °C were observed. In both samples, YAG phase crystallized in two steps, as determined by HT XRD. DSC experiments conducted in the temperature interval 35–1200 °C at heating rates 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 °C min−1 were performed, and the kinetic parameters of crystallization were determined with the use of the JMAK model. Crystallization in both samples was controlled by diffusion flow with linear nucleation rate time dependence. One-dimensional growth and formation of needle-like (dendritic) YAG crystals was observed in AY-E glass crystallized at 932 °C corresponding to the first exothermic maximum at the DSC curve. Two-dimensional growth and the presence of plate-like YAG crystals were observed in AY-NE glass crystallized at 996 °C. For the second exothermic effect, plate-like crystals crystallized at higher temperatures (996 and 1020 °C) in both compositions. The results of SEM analysis are in agreement with the results of kinetic calculations in the prepared systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ochiai S, Ikeda S, Iwamoto S, Sha JJ, Okuda H, Waku Y, Nakagawa N, Mitani A, Sato M, Ishikawa T. Residual stresses in YAG phase of melt growth Al2O3/YAG eutectic composite estimated by indentation fracture test and finite element analysis. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2008;28:2309–17.
Song K, Zhang J, Liu L. An Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 eutectic nanocomposite rapidly solidified by a new method: liquid–metal quenching. Scr Mater. 2014;92:39–42.
Buyuk U, Engin S, Marasli N. Directional solidification of Zn–Al–Cu eutectic alloy by the vertical Bridgman method. J Min Metall B. 2015;51:67–72.
Mesa MC, Oliete PB, Pastor YJ. Mechanical properties up to 1900 K of Al2O3/Er3Al5O12/ZrO2 eutectic ceramics grown by laser floating zone method. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2014;34:2081–7.
Yu JZ, Zhang J, Su H-J. Fabrication and characterization of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 eutectic in situ composite ceramics by double side laser zone remelting method. J Inorg Mater. 2012;27:843–8.
Kurosawa S, Suzuki A, Yamaji A. Luminiscent properties of Cr-doped gallium garnet crystals grown by the micro-pulling- down method. J Cryst Growth. 2016;452:95–100.
Dianguang L, Yan G, Jinling L, Fangzhoung L, Kai L, Haijun S, Yiguang W, Linan A. Preparation of Al2O3–Y3Al5O12–ZrO2 eutectic ceramic by flash sintering. Scr Mater. 2016;14:108–11.
Harada Y, Ayabe K, Uekawa N. Formation of GdAlO3–Al2O3 composite having fine pseudo-eutectic microstructure. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2008;28:2941–6.
Harada Y, Uekawa N, Kojima T, Kokegawa K. Fabrication of Y3Al5O12–Al2O3 eutectic materials having ultra fine microstructure. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2008;28:235–40.
Harada Y, Uekawa N, Kojima T, Kakegawa K. Formation of Y3Al5O12–Al2O3 eutectic microstructure with off-eutectic composition. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2008;28:1973–8.
Yao B, Su H, Zhang J, Ren Q, Ma W, Liu L, Henghzhi F. Sintering densification and microstructure formation of bulk Al2O3/YAG autectic ceramics by hot pressing based on fine eutectic microstructure. Mater Des. 2016;92:213–22.
Harada Y, Uekawa N, Kojima T, Kakegawa K. Development of formation method for homogenous and fine eutectic like microstructures with off eutectic composition in various rare-earth oxide—Al2O3 systems. Adv Appl Ceram. 2009;108:78–83.
Raj R, Cologna M, Francis JS. Influence of externally imposed and internally generated electrical fields on grain growth, diffusional creep, sintering and related phenomena in ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc. 2011;94:1941–65.
Tarafder A, Molla AR, Karmakar B. Effects of nano-YAG (Y3Al5O12) crystallization on the structure and photoluminiscence properties of Nd3+-doped K2O–SiO2–Y2O3–Al2O3 glasses. Sol Sci. 2010;12:1756–63.
Prnová A, Galusek D, Hnatko M, Kozánková J, Vávra I. Composites with eutectic microstructure by hot pressing of Al2O3–Y2O3 glass microspheres. Ceram Silik. 2011;55:208–13.
Šesták J, Šimon P, editors. Thermal analysis of micro, nano- and non-crystalline materials: transformation, crystallization, kinetics and thermodynamics. New York: Springer; 2013. p. 225–46.
Avrami M. Kinetics of phase change. III. Granulation, phase change, and microstructure kinetics of phase change. J Chem Phys. 1941;9:177–84.
Avrami M. Kinetics of phase change. I. General theory. J Chem Phys. 1939;7:1103–12.
Avrami M. Kinetics of phase change. II. Transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei. J Chem Phys. 1940;8:212–24.
Kolmogorov AE. On the statistic theory of metal crystallization. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Ser Mat. 1937;1:355–9 (in Russian).
Johnson WA, Mehl RF. Reaction kinetics in processes of nucleation and growth. Trans Am Inst Min Metall Pet Eng. 1939;135:416–58.
Tanaka H. Thermal analysis and kinetics of solid state reactions. Thermochim Acta. 1995;267:29–44.
Šesták J, Šatava V, Wendlandt WW. The study of heterogeneous processes by thermal analysis. Thermochim Acta. 1973;7:333–556.
Málek J. The applicability of Johnson–Mehl–Avrami model in thermal analysis of crystallization kinetics of glasses. Thermochim Acta. 1995;267:61–73.
Vyazovkin S, Burnham AK, Criado JM, Perez-Maqueda LA, Popescu C, Sbirrazzuoli N. ICTAC kinetic committee recommendation for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520:1–19.
Johnson JB, Omland KS. Model selection in ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol Evol. 2004;19:101–8.
Cavanaugh JE. Criteria for linear model selection based on Kullback’s symmetric divergence. Aust N Y Stat. 2004;46:257–74.
Akaike H. Information theory and an extension of maximum likehood principle. In: Petrov BN, Csáki F, editors. 2nd international symposium on information theory. Budapest: Akadémia Kiadó; 1973. p. 267–81.
Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control. 1974;19:716–23.
Kim HJ, Cavanaugh JE. Model selection criteria based on Kullback information measures for nonlinear regression. J Stat Plan Inference. 2005;134:332–49.
Roduit B, Hartmann M, Folly P, Sarbach A, Baltensperger R. Prediction of thermal stability of materials by modified kinetic and model selection approaches based on limited amount of experimental points. Thermochim Acta. 2014;579:31–9.
Pechini MP. Method of preparing lead and alkaline-earth titanates and niobates and coating method using the same to form a capacitor. US Patent No. 3 330 697, 1967.
Prnová A, Bodišová K, Klement R, Migát M, Veteška P, Škrátek M, Bruneel E, Driessche IV, Galusek D. Preparation and characterization of Yb2O3–Al2O3 glasses by the Pechini sol–gel method combined with flame synthesis. Ceram Int. 2013;40:6179–84.
Prnová A, Klement R, Bodišová K, Valúchová J, Galusek D, Bruneel E, Driessche IV. Thermal behaviour of ytrium aluminate glasses studied by DSC, high temperature X-ray diffraction, SEM and SEM-EDS. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128:1407–15.
Acknowledgements
The financial support of this work by the project SAS-MOST JRP 2015/6, VEGA 1/0631/14, VEGA 2/0026/17 and APVV 0014-15 is gratefully acknowledged. This publication was created in the frame of the project “Centre of excellence for ceramics, glass, and silicate materials” ITMS code 262 201 20056, based on the Operational Program Research and Development funded from the European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prnová, A., Plško, A., Valúchová, J. et al. Crystallization kinetics of yttrium aluminate glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim 133, 227–236 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6948-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6948-2