Abstract
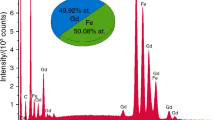
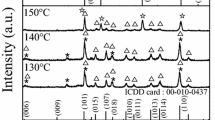
In the present study, the investigation of formation mechanism of holmium iron garnet (Ho3Fe5O12, HoIG) prepared by an aqueous sol–gel method was reported. We specifically focused on the identification of species released during the thermal decomposition of the Ho–Fe–O precursor gel using thermal analysis method. The formation of holmium iron garnet phase and some magnetic properties were investigated by X-ray diffraction analysis, Mössbauer spectroscopy and TG–DSC measurements. Evolved gas analysis of the decomposition products of gel precursor was performed by coupled TG–GC–MS method. In addition, the Curie temperatures of series of rare earth iron garnets were measured using thermal analyser with the small permanent magnet. The influence of the transition temperature from ferrimagnetic to paramagnetic state on the nature of lanthanide element in the iron garnets has been also investigated.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suchomski C, Reitz C, Pajic D, Jaglicic Z, Djerdj I, Brezesinski T. Large-pore mesoporous Ho3Fe5O12 thin films with a strong room-temperature perpendicular magnetic anisotropy by sol–gel processing. Chem Mater. 2014;26:2337–43.
Harris IR, Williams AJ. Magnetic materials. In: Rawlings RD, editor. Material science and engineering, vol. 2. Oxford: Eolls Publishers; 2009. p. 49–84.
Callister WD, Rethwisch DG. Materials science and engineering: an introduction. 9th ed. London: Wiley; 2013.
Coey JMD. Magnetism and magnetic materials. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2009.
Dobrzański LA, Drak M, Ziębowicz B. Materials with specific magnetic properties. J Achiev Mater Manuf Eng. 2006;17:37–40.
Suñol JJ, González A, Escoda L, Vilaró A. Curie temperature in Fe(Ni)Nb based mechanically alloyed materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;80:257–61.
Lin DM, Lin ML, Lin MH, Wu YC, Wang HS, Chen YJ. Studies of nanocrystalline phase and residual amorphous phase of FeCuNbSib alloy using TG(M) technique. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1999;58:355–62.
Brown ME. Introduction to thermal analysis: techniques and applications. London: Chapman and Hall; 1988.
Luciani G, Costantini A, Branda F, Scardi P, Lanotte L. Thermal evolution of ferromagnetic metallic glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;72:105–11.
Boyanov BS. Synthesis and neel temperature determination of ferrites from the CuO–ZnO−Fe2O3 system. J Therm Anal. 1995;44:707–16.
Sugimoto M. The past, present, and future of ferrites. J Am Ceram Soc. 1999;82:269–80.
Caffarena VR, Ogasawara T. Microstructure and hysteresis curves of samarium-holmium-iron garnet synthesized by coprecipitation. Mater Res. 2003;6:569–76.
Caffarena VR, Ogasawara T, Pinho MS, Capitaneo JL. Samarium-iron garnet nanopowder obtained by co-precipitation. Latin Am Appl Res. 2006;36:137–40.
Cheng Z, Yang H. Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sm–Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticles. Phys E. 2007;39:198–202.
Ramesh T, Shinde RS, Murthy SR. Nanocrystalline gadolinium iron garnet for circulator applications. J Magn Magn Mater. 2012;324:3668–73.
McCloy JS, Walsh B. Sublattice magnetic relaxation in rare earth iron garnets. Trans Magn IEEE. 2013;49:4253–6.
Nguyet DTT, Duong NP, Satoh T, Anh LN, Hien TD. Magnetization and coercivity of nanocrystalline gadolinium iron garnet. J Magn Magn Mater. 2013;332:180–5.
Suchomski C, Reitz C, Sousa CT, Araujo JP, Brezesinski T. Room temperature magnetic rare-earth iron garnet thin films with ordered mesoporous structure. Chem Mater. 2013;25:2527–37.
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW. Sol–gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol–gel processing. San Diego: Academic Press; 1990.
Di Maggio R, Campostrini R, Guella G. Gels from modified zirconium n-butoxide: a pyrolysis study by coupled thermogravimetry, gas chromatographic, and mass spectrometric analyses. Chem Mater. 1998;10:3839–47.
Egger P, Dirè S, Ischia M, Campostrini R. Pyrolysis study of sol–gel derived zirconia by TG–GC–MS. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;81:407–15.
Oja Açik I, Madarász J, Krunks M, Tõnsuaadu K, Janke D, Pokol G, Niinistö L. Thermoanalytical studies of titanium(IV) acetylacetonate xerogels with emphasis on evolved gas analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;88:557–63.
Pinkas J, Reichlova V, Serafimidisova A, Moravec Z, Zboril R, Jancik D, Bezdicka P. Sonochemical synthesis of amorphous yttrium iron oxides embedded in acetate matrix and their controlled thermal crystallization toward garnet (Y3Fe5O12) and perovskite (YFeO3) nanostructures. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114:13557–64.
Xie W, Pan W-P. Thermal characterization of materials using evolved gas analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;65:669–85.
Opuchovic O, Kareiva A, Mazeika K, Baltrunas D. Magnetic nanosized rare earth iron garnets R3Fe5O12: sol–gel fabrication, characterization and reinspection. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.09.041.
Masoudpanah SM, Mirkazemi SM, Shabani S, Dolat Abadi PT. The effect of the ethylene glycol to metal nitrate molar ratio on the phase evolution, morphology and magnetic properties of single phase BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Ceram Int. 2015;41:9642–6.
Opuchovic O, Beganskiene A, Kareiva A. Sol–gel derived Tb3Fe5O12 and Y3Fe5O12 garnets: synthesis, phase purity, micro-structure and improved design of morphology. J Alloys Compd. 2015;647:189–97.
Wang Y, Jiang X, Xia Y. A solution-phase, precursor route to polycrystalline SnO2 nanowires that can be used for gas sensing under ambient conditions. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:16176–7.
Arun T, Vairavel M, Gokul Raj S, Justin JR. Crystallization kinetics of Nd-substituted yttrium iron garnet prepared through sol–gel auto-combustion method. Ceram Int. 2012;38:2369–73.
Lataifeh M, Lehlooh AF, Mahmood S. Mössbauer spectroscopy of Al substituted Fe in holmium iron garnet. Hyperfine Interact. 1999;122:253–8.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by a Grant (No. S-LZ-17-6) from the Research Council of Lithuania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Opuchovic, O., Niznansky, D. & Kareiva, A. Thermoanalytical (TG/DSC/EVG–GC–MS) characterization of the lanthanide (Ho) iron garnet formation in sol–gel. J Therm Anal Calorim 130, 1085–1094 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6492-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6492-0