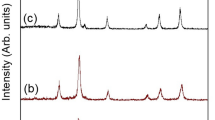
Abstract
Thermal transformation of water-dispersible magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles formed by the thermal decomposition of [Fe(NH2CONH2)6](NO3)3 in triethylene glycol (TEG) was studied to explore the possibilities of the synthesis of water-dispersible maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) using X-ray diffraction, differential thermal analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, and Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy. The structural and magnetic properties of resulting γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles were characterized using N2 adsorption–desorption, transmission electron microscopy, UV–Vis absorption spectroscopy, and vibrating sample magnetic measurements. The results show that the oxidation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles at 150 °C for 6 h can produce superparamagnetic γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles less than 10 nm in size coated with a TEG layer. The obtained γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles are highly dispersible in water owing to the hydrophilic properties of the TEG coating.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu S, Chow GM. Carboxyl group (–CO2H) functionalized ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for potential bio-applications. J Mater Chem. 2004;14:2781–6.
Shkilnyy A, Munnier E, Hervé K, Soucé M, Benoit R, Cohen-Jonathan S, Limelette P, Saboungi M-L, Dubois P, Chourpa I. Synthesis and evaluation of novel biocompatible super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as magnetic anticancer drug carrier and fluorescence active label. J Phys Chem C. 2010;11:45850–8.
Dobson J. Magnetic micro- and nano-particle-based targeting for drug and gene delivery. Nanomedicine. 2006;1:31–7.
Latham AH, Williams ME. Controlling transport and chemical functionality of magnetic nanoparticles. Acc Chem Res. 2008;41:411–20.
Kluchova K, Zboril R, Tucek J, Pecova M, Zajoncova L, Safarik I, Mashlan M, Markova I, Jancik D, Sebela M, Bartonkova H, Bellesi V, Novak P, Petridis D. Superparamagnetic maghemite nanoparticles from solid-state synthesis—their functionalization towards peroral MRI contrast agent and magnetic carrier for trypsin immobilization. Biomaterials. 2009;30:2855–63.
Wang Y-XJ, Hussain SH, Krestin GP. Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2001;11:2319–31.
Gálvez N, Kedracka EJ, Carmona F, Céspedes-Guirao FJ, Font-Sanchis E, Fernández-Lázaro F, Sastre-Santos Á, Domínguez-Vera JM. Water soluble fluorescent-magnetic perylenediimide-containing maghemite-nanoparticles for bimodal MRI/OI imaging. J Inorg Biochem. 2012;117:205–11.
Lu A-H, Salabas EL, Schüth F. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46:1222–44.
Wei X, Wei Z, Zhang L, Liu Y, He D. Highly water-soluble nanocrystal powders of magnetite and maghemite coated with gluconic acid: preparation, structure characterization, and surface coordination. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011;354:76–81.
Petcharoen K, Sirivat A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater Sci Eng B. 2012;177:421–7.
Wu S, Sun A, Zhai F, Wang J, Xu W, Zhang Q, Volinsky AA. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Mater Lett. 2011;65:1882–4.
Hyeon T, Lee SS, Park J, Chung Y, Na HB. Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse maghemite nanocrystallites without a size-selection process. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:12798–801.
Cheon J, Kang N-J, Lee S-M, Lee J-H, Yoon J-H, Oh SJ. Shape evolution of single-crystalline iron oxide nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:1950–1.
Cozzoli PD, Snoeck E, Garcia MA, Giannini C, Guagliardi A, Cervellino A, Gozzo F, Hernando A, Achterhold K, Ciobanu N, Parak FG, Cingolani R, Manna L. Colloidal synthesis and characterization of tetrapod-shaped magnetic nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2009;6:1966–72.
Haviv AH, Greneche J-M, Lellouche J-P. Aggregation control of hydrophilic maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles by surface doping using cerium atoms. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:12519–21.
Utech S, Scherer C, Maskos M. Multifunctional, multicompartment polyorganosiloxane magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Magn Magn Mater. 2009;321:1386–8.
Rajamathi M, Ghosh M, Seshadri R. Hydrolysis and amine-capping in a glycol solvent as a route to soluble maghemite γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem Commun. 2002;10:1152–3.
Wei Y, Lu F, Zhang X, Chen D. Polyol-mediated synthesis of water-soluble LaF3:Yb:Er upconversion fluorescent nanocrystals. Mater Lett. 2007;61:1337–40.
Zhao L, Chano T, Morikawa S, Saito Y, Shiino A, Shimizu S, Maeda T, Irie T, Aonuma S, Okabe H, Kimura T, Inubushi T, Komatsu N. Hyperbranched polyglycerol-grafted superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, functionalization, size separation, magnetic properties, and biological applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2012;22:5107–17.
Wan J, Cai W, Meng X, Liu E. Monodisperse water-soluble magnetite nanoparticles prepared by polyol process for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Chem Commun. 2007;47:5004–6.
Hu F, MacRenaris KW, Waters EA, Liang T, Schultz-Sikma EA, Eckermann AL, Meade TJ. Ultrasmall, water-soluble magnetite nanoparticles with high relaxivity for magnetic resonance imaging. J Phys Chem C. 2009;113:20855–60.
Jia X, Chen D, Jiao X, Zhai S. Environmentally-friendly preparation of water-dispersible magnetite nanoparticles. Chem Commun. 2009;8:968–70.
Asuha S, Wan HL, Zhao S, Deligeer W, Wu HY, Song L, Tegus O. Water-soluble, mesoporous Fe3O4: synthesis, characterization, and properties. Ceram Int. 2012;38:6579–84.
Asuha S, Zhao S, Wu HY, Song L, Tegus O. One step synthesis of maghemite nanoparticles by direct thermal decomposition of Fe–urea complex and their properties. J Alloys Compd. 2009;472:L23–4.
Przepiera K, Przepiera A. Kinetics of thermal transformations of precipitated magnetite and goethite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;65:497–503.
Maity D, Agrawal DC. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles under oxidizing environment and their stabilization in aqueous and non-aqueous media. J Magn Magn Mater. 2007;308:46–55.
Alibeigi S, Vaezi MR. Phase transformation of iron oxide nanoparticles by varying the molar ratiao of Fe2+:Fe3+. Chem Eng Technol. 2008;31:1591–6.
Correa JR, Canetti D, Castillo R, Llópiz JC, Dufour J. Influence of the precipitation pH of magnetite in the oxidation process to maghemite. Mater Res Bull. 2006;41:703–13.
Zhao S, Wu HY, Song L, Tegus O, Asuha S. Preparation of γ-Fe2O3 nanopowders by direct thermal decomposition of Fe-urea complex: reaction mechanism and magnetic properties. J Mater Sci. 2009;44:926–30.
Sutka A, Lagzdina S, Kaambre T, Parna R, Kisand V, Kleperis J, Maiorov M, Kikas A, Kuusik I, Jakovlevs D. Study of the structural phase transformation of iron oxide nanoparticles from an Fe2+ ion source by precipitation under various synthesis parameters and temperatures. Mater Chem Phys. 2015;149–150:473–9.
Singh M, Ulbrich P, Prokopec V, Svoboda P, Santava E, Stepanek F. Vapour phase approach for iron oxide nanoparticle synthesis from solid precursors. J Solid State Chem. 2013;200:150–6.
Darezereshki E. Synthesis of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles by wet chemical method at room temperature. Mater Lett. 2010;64:1471–2.
Al-Ghamdi AA, Al-Hazmi F, Al-Tuwirqi RM, Alnowaiser F, Al-Hartomy OA, El-Tantawy F, Yakuphanoglu F. Synthesis, magnetic and ethanol gas sensing properties of semiconducting magnetite nanoparticles. Solid State Sci. 2013;19:111–9.
Morales MP, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, Montero MI, Serna CJ, Roig A, Casas L, Martínez B, Sandiumenge F. Surface and internal spin canting in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem Mater. 1999;11:3058–64.
Xia HB, Yi J, Foo PS, Liu B. Facile fabrication of water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles and their spherical aggregates. Chem Mater. 2007;19:4087–97.
Aghaie-Khafri M, Kakaei Lafdani MH. A novel method to synthesize Cr2O3 nanopowders using EDTA as a chelating agent. Powder Technol. 2012;222:152–9.
Ercuta A, Chirita M. Highly crystalline porous magnetite and vacancy-ordered maghemite microcrystals of rhombohedral habit. J Cryst Growth. 2013;380:182–6.
Gilbert B, Katz JE, Denlinger JD, Yin Y, Falcone R, Waychunas GA. Soft X-ray spectroscopy study of the electronic structure of oxidized and partially oxidized magnetite nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114:21994–2001.
He YP, Miao YM, Li CR, Wang SQ, Cao L, Xie SS, Yang GZ, Zou BS, Burda C. Size and structure effect on optical transitions of iron oxide nanocrystals. Phys Rev B. 2005;71:125411–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21267016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wurendaodi, W., Dujiya, J., Zhao, S. et al. Thermal transformation of water-dispersible magnetite nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim 130, 681–688 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6431-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6431-0