Abstract
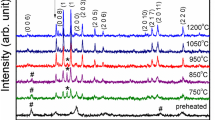
Citrate precursor method has been used to obtain nanosized particles of barium hexaferrite at low temperatures. Samples were annealed at 450 °C for 3 and 5 h. Quenching of the third sample was done by taking the crucible out from the muffle furnace after annealing it for 5 h and putting it abruptly into an ice bath. The saturation magnetization has been found to be 4.36 and 0.04 emu g−1 for the samples obtained upon annealing at 450 °C for 3 and 5 h, respectively, while that of the quenched sample has been found to be 4.61 emu g−1. In case of the sample obtained after 5-h annealing, the squareness value was found to be maximum indicating significance in memory and switching applications. For the quenched and the 3-h annealing products, the magnetic data values are similar. Creation of spin disorders on the surface upon prolonged annealing, due to disappearance of oxygen ions and subsequent breakage of superexchange interactions between cations, has been undone upon quenching. The XRD and TEM data indicate that the particle size (9–17 nm) gets lower in case of the quenched samples. Photoluminescence study of the quenched sample furnished prominent peaks in UV, visible and near-IR regions under 200-nm excitation. The TG–DSC data were analysed for the kinetic parameters, activation energy (E), pre-exponential factor (A) using the Kissinger isoconversion and the Ozawa–Flynn–Wall methods for the first-step decomposition of the quenched sample.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ri CH, Li L, Qi Y. Anisotropy of the electrical conductivity in W-type hexagonal ferrites BaFe18O27 and BaCo2Fe16O27 from first principles. J Magn Magn Mater. 2012;324(8):1498–502.
Pullar RC, Bdikin IK, Bhattacharya AK. Magnetic properties of randomly oriented BaM, SrM, Co2Y, Co2Z and Co2W hexagonal ferrite fibres. J Europ Cer Soc. 2012;32(4):905–13.
Campbell P. Permanent magnet materials and their application. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1994.
Topal U, Ozkan H, Sozeri H. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline BaFe12O19 obtained at 850 °C by using ammonium nitrate melt. J Magn Magn Mater. 2004;284:416–22.
Molaei MJ, Ataie A, Raygan S, Picken SJ, Tichelaar FD. The effect of heat treatment and re-calcination on magnetic properties of BaFe12O19/Fe3O4 nano-composite. Ceram Int. 2012;38(4):3155–9.
Liu Y, Drew MGB, Liu Y. Optimizing the methods of synthesis for barium hexagonal ferrite—An experimental and theoretical study. Mater Chem Phys. 2012;134:266–72.
Li CJ, Wang B, Wang JN. Magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of electrospun Ba(1−x)La x Fe12O19 nanofibers. J Magn Magn Mater. 2012;324(7):1305–11.
Chang S, Kangning S, Pengfei C. Microwave absorption properties of Ce-substituted M-type barium ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater. 2012;324(5):802–5.
Topal U. Towards further improvements of the magnetization parameters of B2O3-Doped BaFe12O19 particles: etching with hydrochloric acid. J Supercond Nov Magn. 2012;25:1485–8.
Dursun S, Topkaya R, Akdogan N, Alkoy S. Comparison of the structural and magnetic properties of submicron barium hexaferrite powders prepared by molten salt and solid state calcination routes. Ceram Int. 2012;38(5):3801–6.
Singh RK, Narayan A, Prasad K, Yadav RS, Pandey AC, Singh AK, Verma L, Verma RK. Structural, magnetic and photoluminescence studies on cobalt ferrite nanoparticles obtained by citrate precursor method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:573–80.
Singh RK, Yadav A, Narayan A, Singh AK, Verma L, Verma RK. Thermal, structural and magnetic studies on chromite spinel, synthesized by citrate precursor method and annealed at temperature 450 °C and 650 °C. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:197–204.
Singh RK, Yadav A, Narayan A, Chandra M, Verma RK. Thermal, XRD and magnetization studies on ZnAl2O4 and NiAl2O4 spinels, synthesized by citrate precursor method and annealed at temperature 450 °C and 650 °C. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:205–10.
Verma RK, Hill JO, Niinisto L, Mojumdar SC, Kumar DD. A curriculum framework for education in thermal analysis. J Mater Educ. 2012;34:133–50.
Verma RK, Verma L, Chandra M. Thermoanalytical studies on the non-isothermal dehydration and decomposition of dl-lactates of a series of transition metals. Indian J Chem. 2003;42A:2982–7.
Bhattacharjee NC, Kumar M, Kumar S, Verma RK. Kinetic and mechanistic studies on non-isothermal decomposition of potassium dioxalatocuprate(II) dihydrate. J Indian Chem Soc. 1998;75(5):317–8.
Verma RK, Verma L, Chandra M, Bhushan A. Non-isothermal dehydration and decomposition of dl-lactates of transition metals and alkaline earth metals: a comparative study. J Therm AnalCalorim. 2005;80:351–4.
Kumar M, Verma RK, Verma L, Bhattacharjee NC, Kumar S, Verma BP. Thermal decomposition of potassium trioxalato chromate(III) trihydrate: a kinetic and mechanistic study. Asian J Chem. 1996;8(3):543–6.
Agrawal HL, Mishra A, Ambasta RK, Verma L, Verma RK, Verma BP. Kinetic parameters of thermolysis of complexes of rhodium(III), palladium(II) and platinum(II) with substituted morpholines from their non-isothermal thermogravimetric data. Asian J Chem. 1994;6:130–4.
Verma BP, Verma RK, Chandra M, Pandey S, Mallick AK, Verma L. A study of non-isothermal decomposition of calcium dl-lactate pentahydrate. Asian J Chem. 1994;6:606–12.
Verma RK, Verma L, Ranjan M, Verma BP, Mojumdar SC. Thermal analysis of 2-oxocyclopentanedithiocarboxylato complexes of iron(III), copper(II) and zinc(II) containing pyridine or morpholine as the second ligand. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:27–31.
Verma RK, Verma L, Bhushan A, Verma BP. Thermal decomposition of complexes of cadmium(II) and mercury(II) with triphenylphosphanes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;90:725–9.
Brown ME, Gallagher PK. Introduction to recent advances, techniques and applications of thermal analysis and calorimetry. In: Brown ME, Gallagher PK, editors. Hand book of thermalanalysis and calorimetry. New York: Elsevier; 2008. p. 1–12.
Verma RK, Verma L, Chandra M, Verma BP. Kinetic parameters of thermal dehydration and decomposition from thermoanalytical curves of zinc dl-lactate. J Indian Chem Soc. 1998;75:162–4.
Wang J, Chen Q, Che S. Magnetic properties in BaFe12O19 nanoparticles prepared under a magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater. 2004;280:281–6.
Kissinger HE. Variation of peak temperature with heating rate in differential thermal analysis. J Res Natl Bur Stand. 1956;57:217–21.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29:1702–6.
Flynn JH, Wall LA. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. Polym Lett. 1966;4:323–8.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38:1881–6.
Wohlfarh EP. Fundamental properties of hexaferrite with magnetoplumbite structure in ferromagnetic materials. NewYork: North-Holland Publishing Company; 1982.
Martirosyan KS, Galstyan Hossain, Wang YJ, Litvinov D. Barium hexaferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and magnetic properties. Mater Sci Eng, B. 2011;176:8–13.
Kodama RH, Berkowitz AE, Mcniff EJ, Foner S. Surface disorder in NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys Rev Lett. 1996;77:394–7.
Misra RDK, Gubbala S, Kale A. Egelhoff Jr WF.A comparison of the magnetic characteristics of nanocrystalline nickel, zinc, and manganese ferrites synthesized by reverse micelle technique. Mater Sci Eng, B. 2004;111(2–3):164–74.
Mishra DK, Qi X. Energy levels and photoluminescence properties of nickel-doped bismuth ferrite. J Alloys Compd. 2010;504:27–31.
Ghatak AK, Loknathan S. quantum mechanics, theory and applications. India: Macmillan India Ltd; 1984. p. 503.
Siwach OP, Sen P. Synthesis and study of fluorescence properties of Cu nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. 2008;10:107–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, R.K., Singh, R.K., Narayan, A. et al. Low-temperature synthesis of hexagonal barium ferrite (BaFe12O19) nanoparticles by annealing at 450 °C followed by quenching. J Therm Anal Calorim 129, 691–699 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6247-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6247-y