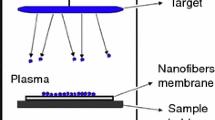
Abstract
The objective of this study was to explore an innovative type of form-stable phase-change materials (PCMs) with flexible cellulose acetate (CA) nano-fibrous felts (nano-felts) absorbed with capric–myristic–stearic acid ternary eutectic mixture for thermal energy storage/retrieval. Capric–myristic–stearic acid (CMS) ternary eutectic mixture as model PCM was firstly prepared. The developed CA nano-felts as supporting material was mechanically flexible and was made from CA/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) precursor composite nanofibers followed by removal of PVP components. The effects of original mass ratio of CA/PVP on absorption capacities of CA nano-felts were studied. The modified CA nano-felts with groove/porous structure and rough surfaces were capable of absorbing a large amount of PCMs. The morphological structures, as well as the properties of thermal energy storage, thermal stability and reliability, and thermal insulation of composite PCMs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermal performance measurement, respectively. The results showed that CMS eutectic was absorbed in and/or supported by modified CA nano-felts. The heat enthalpy values of composite PCMs have slightly decreased in comparison with the corresponding theoretical values. The composite PCMs demonstrated good thermal stability and reliability after thermal cycles. The composite PCMs had high thermal insulation capability for temperature regulation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pomianowski M, Heiselberg P, Zhang YP. Review of thermal energy storage technologies based on PCM application in buildings. Energy Build. 2013;67:56–69.
Tang QQ, Sun J, Yu SM, Wang GC. Improving thermal conductivity and decreasing supercooling of paraffin phase change materials by n-octadecylamine-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2014;4:36584–90.
Pielichowska K, Pielichowski K. Phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Prog Mater Sci. 2014;65:67–123.
Yuan YP, Zhang N, Tao WQ, Cao XL, He YL. Fatty acids as phase change materials: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2014;29:482–98.
Fu XW, Liu ZM, Wu B, Wang JL, Lei JX. Preparation and thermal properties of stearic acid/diatomite composites as form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage via direct impregnation method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123(2):1173–81.
Liang W, Chen PS, Sun HX, Zhu ZQ, Li A. Innovative spongy attapulgite loaded with n-carboxylic acids as composite phase change materials for thermal energy storage. RSC Adv. 2014;4:38535–41.
Zhu FR, Zhang L, Zeng JL, Zhu L, Zhu Z, Zhu XY, Li RH, Xiao ZL, Cao Z. Preparation and thermal properties of palmitic acid/polyaniline/copper nanowires form-stable phase change materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115(2):1133–41.
Genc ZK, Canbay CA, Acar SS, Sekerci M, Genc M. Preparation and thermal properties of heterogeneous composite phase change materials based on camphene-palmitic acid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120(3):1679–88.
Zhao P, Yue QY, He HT, Gao BY, Wang Y, Li Q. Study on phase diagram of fatty acids mixtures to determine eutectic temperatures and the corresponding mixing proportions. Appl Energy. 2014;115:483–90.
Ke HZ, Pang ZY, Peng B, Wang J, Cai YB, Huang FL, Wei QF. Thermal energy storage and retrieval properties of form-stable phase change nanofibrous mats based on ternary fatty acid eutectics/polyacrylonitrile composite by magnetron sputtering of silver. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123(2):1293–307.
Cao L, Tang YJ, Fang GY. Preparation and properties of shape-stabilized phase change materials based on fatty acid eutectics and cellulose composites for thermal energy storage. Energy. 2015;80:98–103.
Yang XJ, Yuan YP, Zhang N, Cao XL, Liu C. Preparation and properties of myristic–palmitic–stearic acid/expanded graphite composites as phase change materials for energy storage. Sol Energy. 2014;99:259–66.
Zhang N, Yuan YP, Wang X, Cao XL, Yang XJ, Hu SC. Preparation and characterization of lauric-myristic-palmitic acid ternary eutectic mixtures/expanded graphite composite phase change material for thermal energy storage. Chem Eng J. 2013;231:214–9.
Yuan YG, Yuan YP, Zhang N, Du YX, Cao XL. Preparation and thermal characterization of capric–myristic–palmitic acid/expanded graphite composite as phase change material for energy storage. Mater Lett. 2014;125:154–7.
Meng X, Zhang HZ, Sun LX, Xu F, Jiao QZ, Zhao ZM, Zhang J, Zhou HY, Sawada Y, Liu YL. Preparation and thermal properties of fatty acids/CNTs composite as shape-stabilized phase change materials J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111(1):377–84.
Zhang N, Yuan YP, Yuan YG, Li TY, Cao XL. Lauric–palmitic–stearic acid/expanded perlite composite as form-stable phase change material: preparation and thermal properties. Energy Build. 2014;82:505–11.
Dheep GR, Sreekumar A. Influence of nanomaterials on properties of latent heat solar thermal energy storage materials: a review. Energy Convers Manag. 2014;83:133–48.
Sari A, Karli A, Alkan C, Karaipekli A. Polyethyl methacrylate (PEMA)/fatty acids blends as novel phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Energy Sources Part A: Recov Util Environ Eff. 2013;35:1813–9.
Kenisarin MM, Kenisarina KM. Form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Renew Sust Energy Rev. 2012;16:1999–2040.
Cai YB, Gao CT, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Wei QF, Du JM, Hu Y, Song L. Influences of expanded graphite on structural morphology and thermal performance of composite phase change materials consisting of fatty acid eutectics and electrospun PA6 nanofibrous mats. Renew Energy. 2013;57:163–70.
Cai YB, Zong X, Zhang JJ, Hu YY, Wei QF, He GF, Wang XX, Zhao Y, Fong H. Electrospun nanofibrous mats absorbed with fatty acid eutectics as an innovative type of form-stable phase change materials for storage and retrieval of thermal energy. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2013;109:160–8.
Cai YB, Xu XL, Gao CT, Bian TY, Qiao H, Wei QF. Structural morphology and thermal performance of composite phase change materials consisting of capric acid series fatty acid eutectics and electrospun polyamide6 nanofibers for thermal energy storage. Mater Lett. 2012;89:43–6.
Zong X, Cai YB, Sun GY, Zhao Y, Huang FL, Song L, Hu Y, Fong H, Wei QF. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun SiO2 nanofibers absorbed with fatty acid eutectics for thermal energy storage/retrieval. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2015;132:183–90.
Xiang T, Zhang ZL, Liu HQ, Yin ZZ, Li L, Liu XM. Characterization of cellulose-based electrospun nanofiber membrane and its adsorptive behaviours using Cu(II), Cd(II), Pb(II) as models. Sci China-Chem. 2013;56:567–75.
Saljoughi E, Mohammadi T. Cellulose acetate (CA)/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) blend asymmetric membranes: preparation, morphology and performance. Desalination. 2009;249:850–4.
Castillo-Ortega MM, Najera-Luna A, Rodriguez-Felix DE, Encinas JC, Rodriguez-Felix F, Romero J, Herrera-Franco PJ. Preparation, characterization and release of amoxicillin from cellulose acetate and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) coaxial electrospun fibrous membranes. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2011;31:1772–8.
Zavastin D, Cretescu I, Bezdadea M, Bourceanu M, Dragan M, Lisa G, Mangalagiu I, Vasic V, Savic J. Preparation, characterization and applicability of cellulose acetate-polyurethane blend membrane in separation techniques. Colloid Surf A-Physicochem Eng Asp. 2010;370:120–8.
Ramesh S, Shanti R, Morris E. Characterization of conducting cellulose acetate based polymer electrolytes doped with “green” ionic mixture. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;91:14–21.
Bai J, Li YX, Zhang CQ, Liang XF, Yang QB. Preparing AgBr nanoparticles in poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) nanofibers. Colloid Surf A-Physicochem Eng Asp. 2008;329:165–8.
Gao MJ, Sun L, Wang ZQ, Zhao YB. Controlled synthesis of Ag nanoparticles with different morphologies and their antibacterial properties. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33:397–404.
Fang GY, Li H, Liu X. Preparation and properties of lauric acid/silicon dioxide composites as form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Mater Chem Phys. 2010;122:533–6.
Fang GY, Li H, Chen Z, Liu X. Preparation and properties of palmitic acid/SiO2 composites with flame retardant as thermal energy storage materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2011;95:1875–81.
Cai YB, Sun GY, Liu MM, Zhang J, Wang QQ, Wei QF. Fabrication and characterization of capric–lauric–palmitic acid/electrospun SiO2 nanofibers composite as form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage/retrieval. Sol Energy. 2015;118:87–95.
Mehrali M, Latibari ST, Mehrali M, Metselaar HSC, Silakhori M. Shape-stabilized phase change materials with high thermal conductivity based on paraffin/graphene oxide composite. Energy Convers Manag. 2013;67:275–82.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2015T80496), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP51621A), Jiangsu Universities “Qing Lan” Project (No. 2016 [15]), National Undergraduate Innovation and Training Program (No. 201610295043) and High-level Innovative and Entrepreneurial Talents in Jiangsu Province (No. 2015 [26]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Song, X., Liu, M. et al. Flexible cellulose acetate nano-felts absorbed with capric–myristic–stearic acid ternary eutectic mixture as form-stable phase-change materials for thermal energy storage/retrieval. J Therm Anal Calorim 128, 661–673 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5937-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5937-1