Abstract
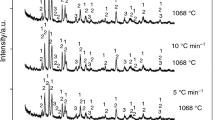
The precipitation of primary Fe-bearing compounds in a secondary AlSi9Cu3(Fe) alloy has been investigated over three levels of iron (0.80, 1.00, 1.20 mass%) and manganese (0.25, 0.40, 0.55 mass%), and two levels of chromium (0.06, 0.10 mass%), as well as different cooling rates (2, 10, 20 °C min−1). Differential scanning calorimetry and metallographic techniques have been used in order to quantitatively evaluate the nucleation temperature and the phase fraction of sludge particles. The temperature of sludge formation increases by increasing the initial concentrations of Fe, Mn and Cr, while an increase in the cooling rate shifts the sludge nucleation towards lower temperature. The amount of sludge particles increases progressively with the sludge factor but even more by decreasing the cooling rate. The combination of Fe, Mn and Cr levels, as well as cooling rate, allows to determine a threshold value that prevents the sludge formation. In the analysed range of composition and cooling conditions, functional equations have been developed in order to accurately predict the precipitation temperature and the phase fraction of sludge in AlSi9Cu3(Fe) die-casting alloys.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kearney A. Melting furnaces: reverberatory furnaces and crucible furnaces. In: ASM International Handbook Committee, editors. Casting, ASM Handbook, Vol. 15. Materials Park, OH: ASM International, The Materials Information Society; 1992. p. 816–34.
Crepeau PN. Effect of iron in Al–Si casting alloys: a critical review. AFS Trans. 1995;103:361–6.
Ji S, Yang W, Gao F, Watson D, Fan Z. Effect of iron on the microstructure and mechanical property of Al–Mg–Si–Mn and Al–Mg–Si diecast alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;564:130–9.
Taghaddos E, Hejazi MM, Taghiabadi R, Shabestari SG. Effect of iron-intermetallics on the fluidity of 413 aluminum alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2009;468:539–45.
Zedan Y, Samuel FH, Samuel AM, Doty HW. Effects of Fe intermetallics on the machinability of heat-treated Al-(7–11)% Si alloys. J Mater Process Technol. 2010;210:245–57.
Chen CL, Richter A, Thomson RC. Investigation of mechanical properties of intermetallic phases in multi-component Al–Si alloys using hot-stage nanoindentation. Intermet. 2010;18:499–508.
Ferraro S, Timelli G. Influence of sludge particles on the tensile properties of die-cast secondary aluminum alloys. Metall Mater Trans B. 2015;46:1022–34.
Wallace J. A guide to correcting soldering. 1st ed. Des Plaines, IL: North American Die Casting Association; 2006.
Wang L, Makhlouf MM, Apelian D. Aluminium die casting alloys: alloy composition, microstructure, and properties-performance relationships. Int Mater Rev. 1995;40:221–38.
Jorstad JL. Understanding sludge. Die Cast Eng. 1986;30:30–6.
Gobrecht J. Settling-out of Fe, Mn and Cr in Al–Si casting alloys. Giesserei. 1975;62:263–6.
Dunn R. Aluminum melting prob1ems and their influence on furnace selection. Die Cast Eng. 1965;9:8–30.
Makhlouf MM, Apelian D. Casting characteristics of aluminum die casting alloys. http://metalcasting.govtools.us/reports/casting_characteristics_of_aluminum.pdf. Accessed 5 Feb 2002.
Shabestari SG. The effect of iron and manganese on the formation of intermetallic compounds in aluminium-silicon alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2004;383:289–98.
Flores A, Escobedo JC, Mendez M, Mendez J. Kinetics of the formation, growth and sedimentation of the phase Al15Fe, Mn3Si2 in Al–Si–Cu alloys. Proceedings of international die casting congress and exposition, Detroit, Michigan, USA, Sept 30–Oct 3, 1991, p. 293–7.
Ghomashchi MR. Intermetallic compounds in an Al–Si alloy used in high pressure die-casting. Z Metallkunde. 1987;78:784–7.
Gustafsson G, Thorvaldsson T, Dunlop GL. The influence of Fe and Cr on the microstructure of cast Al–Si–Mg alloys. Met Trans A. 1986;17:45–52.
Mackay RI, Gruzleski JE. Quantification of iron in aluminium-silicon foundry alloys via thermal analysis. Int J Cast Met Res. 1997;10:131–45.
Timelli G, Bonollo F. The influence of Cr content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi9Cu3(Fe) die casting alloys. Mat Sci Eng A. 2010;528:273–82.
Wang L, Nguyen TT, Savage G, Davidson CJ. Thermal and flow modelling of ladling and injection in high pressure die casting process. Int J Cast Met Res. 2003;16:409–17.
EN 1706:2010. Aluminium and aluminium alloys—castings—chemical composition and mechanical properties.
Timelli G, Ferraro S, Grosselle F, Bonollo F, Voltazza F, Capra L. Mechanical and microstructural characterization of diecast aluminium alloys. Metall Ital. 2011;101:5–17.
Hohne GWH, Hemminger WF, Flammersheim H-J. Differential scanning calorimetry. 2nd ed. Germany: Springer; 2003.
Marchwica P, Sokolowski JH, Kierkus WT. Fraction solid evolution characteristics of AlSiCu alloys—dynamic baseline approach. J Achiev Mater Manuf Eng. 2011;47:115–36.
Bäckerud L, Chai G, Tamminen J. Solidification Characteristics of aluminum alloys, Vol. 2: foundry alloys. 1st ed. Des Plaines, IL: American Foundrymen’s Society Inc; 1990.
Gowri S, Samuel FH. Effect of alloying elements on the solidification characteristics and microstructure of Al–Si–Cu–Mg–Fe 380 Alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 1994;25:437–48.
Mondolfo LF. Aluminium alloys: structure and properties. 1st ed. London: Butterworths; 1976.
Samuel AM, Samuel FH. Effect of alloying elements and dendrite arm spacing on the microstructure and hardness of an Al–Si–Cu–Mg–Fe–Mn (380) aluminium die-casting alloy. J Mater Sci. 1995;30:1698–708.
Cao X, Campbell J. The solidification characteristics of Fe-rich intermetallics in Al-11.5Si-0.4 Mg cast alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 2004;35:1425–35.
Ferraro S, Fabrizi A, Timelli G. Evolution of sludge particles in secondary die-cast aluminum alloys as function of Fe, Mn and Cr contents. Mater Chem Phys. 2015;153:168–79.
Yang W, Ji S, Zhou X, Stone I, Scamans G, Thompson GE, et al. Heterogeneous nucleation of α-Al grain on primary α-AlFeMnSi intermetallic investigated using 3D SEM ultramicrotomy and HRTEM. Metall Mater Trans A. 2014;45:3971–80.
Warmuzek M, Ratuszek W, Sęk-Sas G. Chemical inhomogeneity of intermetallic phases precipitates formed during solidification of Al–Si alloys. Mater Charact. 2005;54:31–40.
Guo Z, Saunders N, Schillé JP, Miodownik AP. Material properties for process simulation. Mater Sci Eng A. 2009;499:7–13.
Fabrizi A, Ferraro S, Timelli G. The influence of Fe, Mn and Cr additions on the formation of iron-rich intermetallic phases in an Al–Si die-casting alloy. In: Tiryakioĝlu M, Campbell J, Byczynski G, editors. Shape casting 5: international symposium 2014. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley; 2014. p. 277–84.
Cao X, Saunders N, Campbell J. Effect of iron and manganese contents on convection-free precipitation and sedimentation of primary α-Al(FeMn)Si phase in liquid Al-11.5Si-0.4 Mg alloy. J Mater Sci. 2004;39:2303–14.
Samuel AM, Samuel FH, Doty HW, Valtierra S. Effect of superheat, cooling rate and impurities on the formation of iron intermetallics in Al–Si die casting alloys. AFS Trans. 2001;109:679–96.
Cao X, Campbell J. Effect of melt superheating on convection-free precipitation and sedimentation of primary α-Fe phase in liquid al-11.5Si-0.4 Mg alloy. Int J Cast Met Res 2003;15:595–608.
Khalifa W, Samuel FH, Gruzleski JE, Doty HW, Valtierra S. Nucleation of Fe-intermetallic phases in the Al–Si–Fe alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2005;36:1017–32.
Terzi S, Taylor JA, Cho YH, Salvo L, Suéry M, Boller E, et al. In situ study of nucleation and growth of the irregular α-Al/β-Al5FeSi eutectic by 3-D synchrotron X-ray microtomography. Acta Mater. 2010;58:5370–80.
Orozco-González P, Castro-Román M, Maldonado-Ruíz S, Haro-Rodríguez S, Equihua-Guillén F, Muñiz-Valdez R, et al. Nucleation of Fe-rich intermetallic phases on α-Al2O3 oxide films in Al–Si Alloys. J Miner Mater Charact Eng. 2015;3:15–25.
Acknowledgements
This work was developed within the European Project MUSIC (MUlti-layers control & cognitive System to drive metal and plastic production line for Injected Components, FP7-FoF-ICT-2011.7.1, Contract No. 314145). The author would like to acknowledge Raffineria Metalli Capra Spa (Brescia, Italy) for the financial support to the research and the skilful contribution of SAEN Snc (Brugine, Italy) for high-pressure die-casting experiments. Many thanks are also due to Dr. J. Dalla Barba for the experimental contribution to this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Timelli, G., Capuzzi, S. & Fabrizi, A. Precipitation of primary Fe-rich compounds in secondary AlSi9Cu3(Fe) alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim 123, 249–262 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4952-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4952-y