Abstract
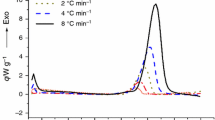
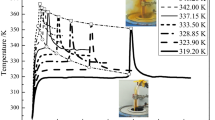
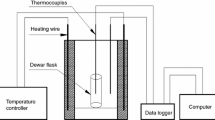
2-Ethylhexyl nitrate (EHN) is an important material, which is produced by concentrated HNO3–H2SO4 nitration process. But EHN is not a stable material, especially mixed with acids. To analyze the stability of EHN with concentrated acid under serious condition, four samples (pure EHN, concentrated sulfuric acid with EHN, concentrated nitric acid with EHN, and mixed acid with EHN) and three acids (sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and mixed acid) were measured by differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and accelerating rate calorimeter (ARC) in this paper. The results indicated that concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated nitric acid, and mixed acid all could decrease the onset decomposition temperature of EHN, especially concentrated sulfuric acid. DSC results also showed that the heat of EHN decomposition with nitric acid is larger than other samples. Based on ARC data, the kinetic parameters and T D24 (temperature at which TMR ad is 24 h) were calculated. The activation energy and T D24 of the EHN with acids, especially with concentrate sulfuric acid, were much lower than the pure EHN. It can be concluded that acids could decrease the stability of EHN and that is an important reason for frequent accidents.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TMR/min:
-
Time to maximum rate
- T D24/°C:
-
Temperature when TMR = 24 h
- T onset/°C:
-
Onset temperature of decomposition
- T peak/°C:
-
Peak temperature of decomposition
- ΔH/J g−1 :
-
Specific heat of material
- P/bar:
-
Pressure
- T/K:
-
Temperature
- E/J mol−1 :
-
Activation energy
- A/s−1 :
-
Pre-exponential factor
- c 0/mol L−1 :
-
Initial concentration of sample
- ΔT/K:
-
Adiabatic temperature rise
- T f/°C:
-
Final temperature of decomposition
- n :
-
Reaction order
- Φ :
-
Thermal inertia factor
- C/J mol−1 K−1 :
-
Specific heat capacity
- ΔT s/K:
-
Adiabatic temperature rise corrected by Φ
- TMR s/min:
-
Time to maximum rate corrected by Φ
- P f/bar:
-
Final pressure of decomposition
References
Suppes GJ, Rui Y, Rome AC, Chen Z. Cetane-improver analysis and impact of activation energy on the relative performance of 2-ethylhexyl nitrate and tetraethylene glycol dinitrate. Ind Eng Chem Res. 1997;36(10):4397–404.
Oxley JC, Smith JL, Rogers E, Ye W. Heat-release behavior of fuel combustion additives. Energy Fuels. 2001;15(5):1194–9.
Zeng XL, Chen WH, Wang FW. Experiment study on thermal stability of EHN. Chin Saf Sci J. 2009;19(8):67–72.
Pritchard HO. Thermal decomposition of isooctyl nitrate. Combust Flame. 1989;75(3):415–6.
Bornemann H, Scheidt F, Sander W. Thermal decomposition of 2-ethylhexyl nitrate (2-EHN). Int J Chem Kinet. 2002;34(1):34–8.
Hu YX, Lv JZ. Cetane number improvers in diesel fuel (I): synthesis of isooctyl nitrate. J. Petrochem Univ. 1997;10(4):16–8.
Chen LP, Liu TT, Yang Q, et al. Thermal hazard evaluation for iso-octanol nitration with mixed acid. J Loss Prevent Proc. 2012;25(3):631–5.
Shen JN, Zhao YC, Chen GW, Yuan Q. Investigation of nitration processes of iso-octanol with mixed acid in a microreactor. Chin J Chem Eng. 2009;17(3):412–8.
Chou HC, Chen NC, Hsu ST, Wang CH, Wu SH, Wen IJ, Shen SJ, Shu CH. Thermal hazard evaluation of tert-butyl hydroperoxide mixed with four acids using calorimetric approaches. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117(2):851–5.
Grewer T, Frurip DJ, Keith HB. Prediction of thermal hazards of chemical reactions. J Loss Prevent Proc. 1999;12(5):391–8.
Hsueh KH, Chen WT, Chu YC, Tsai LC, Shu CM. Thermal reactive hazards of 1,1-bis (tert-butylperoxy) cyclohexane with nitric acid contaminants by DSC. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;109(3):1253–60.
Chen YL, Chou YP, Hou HY, I YP, Shu CM. Reaction hazard analysis for cumene hydroperoxide with sodium hydroxide or sulfuric acid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95(2):535–9.
Wang KQ. Chemical production accident analysis and prevention. China: China Petrochemical Press; 2005. p. 191.
Roduit B, Borgeat C, Berger B, Folly P, Andres H, Schadeli U, Vogelsanger B. Up-scaling of DSC data of high energetic materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;85(1):195–202.
Singh G, Pandey DK. Thermal studies on energetic compounds. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2004;76(2):507–19.
Pourmortazavi SM, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M, Kohsari I, Hajimirsadeghi SS. Non-isothermal kinetic studies on thermal decomposition of energetic materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110(2):857–63.
Tou JC, Whiting LF. The thermokinetic performance of an accelerating rate calorimeter. Thermochim Acta. 1981;48(1):21–42.
Townsend DI, Tou JC. Thermal hazard evaluation by an accelerating rate calorimeter. Thermochim Acta. 1980;37(1):1–30.
Stoessel F. Thermal safety of chemical processes. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 2008. p. 279–82.
Cooper PW. Explosives engineering. New York: VCH; 1996. p. 104.
Dimoplon W. Estimating specific-heat of liquid mixtures. Chem Eng. 1972;79(22):64–6.
Acknowledgements
This investigation was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51204099) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. The authors thank for these supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., Chen, L., Chen, W. et al. Thermal stability of 2-ethylhexyl nitrate with acid. J Therm Anal Calorim 119, 205–212 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4134-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4134-3