Abstract
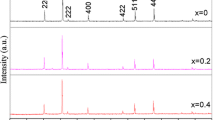
Nanocrystalline nickel ferrite and copper nickel ferrite materials were synthesized through surfactant Tween 80-assisted hydrothermal reaction at low temperature using metallic copper, nickel, and iron as raw materials. Thermogravimetric (TG) and differential thermal analysis (DTA) were used to determine the decomposition of the precursors. Phase composition, microstructural characterization, and distribution of cations in tetrahedral and octahedral sites of crystal structure properties of synthesized ferrite materials were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) absorption, and Mössbauer spectroscopy. The impedance spectroscopic studies of copper nickel ferrite sintered ceramics were carried out at room temperature. TG and DTA of precursors revealed that the crystallization temperature for spinel ferrites phases formation was around 650 °C which were being synthesized through Tween 80-assisted hydrothermal process in highly basic reaction at 180–200 °C for 11–13 h in PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave. XRD analysis and Rietveld refinement study confirm the formation of single-phase cubic spinel nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) and copper nickel ferrite (Ni0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4) with cell parameters 8.3385, 8.3595 Å and space group Fd3 m, respectively. The synthesized ferrite products showed extensive XRD line broadening, and the average crystallite sizes of NiFe2O4 and Cu0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 ferrites were in range of 21–29 nm and 18–23 nm, respectively. Mössbauer parameters are characteristic of substituted Cu-Ni-Fe2O4 ferrite material. Isothermal shrinkage characteristic and coefficient of thermal expansion were determined by dilatometry. The ferrite specimens showed excellent densification at 1,050 °C temperature, and uniformly fine grain-sintered ceramics with submicron grain size (10–18 μm) were obtained after sintering at 850 and 1,050 °C. Sintering at 1,050 °C, results in the formation of depletion layer at grain boundaries which act as trapping centers for the carriers and an increase in the impedance values are conferred.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Safarik I, Safarikova M. Magnetic nanoparticles and bioscience. In: Rahman Z, Schubert U, editors. Hofmann H. Nanostructured materials: Springer Vienna; 2002. p. 1–23.
Xu Q, Wei Y, Liu Y, Ji X, Yang I, Gu M. Preparation of Mg/Fe spinel ferrite nanoparticles from Mg/Fe-LDH microcrystallites under mild conditions. Solid State Sci. 2009;11:472–8.
Candeiaa RA, Bernardib MIB, Longoc E, Santosa IMG, Souza AG. Synthesis and characterization of spinel pigment CaFe2O4 obtained by the polymeric precursor method. Mater Lett. 2001;58:569–72.
Rosi NL, Mirkin CA. Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem Rev. 2005;105:1547–62.
Lee AH, Huh YM, Jun YW, Seo JW, Jang JT, Song HT, Kim S, Cho EJ, Yoon HG, Suh JS, Cheon J. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat Med. 2007;13:95–9.
Prasad NK, Rathinasamy K, Panda D, Bahadur D. Mechanism of cell death induced by magnetic hyperthermia with nanoparticles of γ-MnxFe2-xO3 synthesized by a single step process. J Mater Chem. 2007;17:5042–51.
Kinemuchi Y, Ishizaka K, Suematsu H, Jiang W, Yatsui K. Magnetic properties of nanosize NiFe 2 O 4 particles synthesized by pulsed wire discharge. Thin Solid Films. 2002;407:109–13.
Alarif A, Deraz NM, Shaban S. Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd. 2009;486:501–6.
Sanpo N, Wang J, Berndt CC. Influence of chelating agents on the microstructure and antibacterial property of cobalt ferrite nanopowders. J Austra Ceram Soc. 2013;49:84–91.
Uitert JV. Nickel copper ferrites for microwave applications. J Appl Phys. 1956;27:723–6.
Luders U, Barthelemy A, Bibes M, Bouzehouane K, Fusil S, Jacquet E, Contour JP, Bobo JF, Fontcuberta J, Fert A. NiFe2O4: a versatile spinel material brings new opportunities for spintronics. Adv Mater. 2006;18:1733–6.
Lee H, Jung JC, Kim H, Chung YM, Kim TJ, Lee SJ, Oh SH, Kim YS, Song IK. Effect of Divalent Metal Component (MeII) on the Catalytic Performance of MeIIFe2O4 Catalysts in the Oxidative Dehydrogenation of n-Butene to 1,3-Butadiene. Catal Lett. 2008;124:364–8.
Gedam NN, Kadu AV, Padole PR, Bodade AB, Chaudhari GN. Structural Properties of Nanosized NiFe2O4 for LPG Sensor. Sensors & Transducers J. 2009;110:86–95.
Patil KC, Hegde MS, Rattan T, Aruna ST. Chemistry of nanocrystalline oxide materials: combustion synthesis, properties and applications. Singapore: World Scientific; 2008.
Stewart SJ, Tueros M, Cernicciaro G, Scorzelli RB. Magnetic size growth in nonocrystalline copper ferrite. Solid State Commun. 2004;129:347–414.
Lavela P, Tirado JL. CoFe 2 O 4 and NiFe 2 O 4 synthesized by sol–gel procedures for their use as anode materials for Li ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2007;172:379–87.
Sutka A, Mezinskis G, Strikis G, Siskin A. Gas sensitivity of stoichiometric and excess-iron Ni-Zn ferrite prepared by sol-gel auto combustion. Energetika. 2012;58:166–72.
Kakade MB, Ramanathan S, Kothyiyal GP. Nano-alumina by gel combustion, its thermal characterization and slurry-based coating on stainless steel surface. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;112:133–40.
Durrani SK, Naz S, Hayat K. Thermal analysis and phase evolution of nonocrystalline perovskite oxide materials synthesized via hydrothermal and self-combustion methods. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:1371–80.
Durrani SK, Hussain SZ, Saeed K, Khan Y, Arif M, Ahmed N. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of nanosized transition metal chromite spinels. Turk J Chem. 2012;36:111–20.
Durrani SK, Naz S, Nadeem M, Khan AA. Thermal, structural, and impedance analysis of nanocrystalline magnesium chromite spinel synthesized via hydrothermal process. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116:309–20.
Brabers VAM. Infrared spectra of cubic and tetragonal manganese ferrites. Phys Status Solidi. 1969;33:563–72.
Cannas C, Falqui A, Musinu A, Peddis D, Piccaluga G. CoFe2O4 nanocrystalline powders prepared by citrate-gel methods: synthesis, structure and magnetic properties. J Nanopart Research. 2006;8:255–67.
McClune WF. Powder diffraction file, inorganic phases. Swarthmore: International centre for diffraction; 1989.
Culity BD, Stock SR. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction. 2nd ed. Reading: Addition-Wesley; 1978.
Hoque SM, Choudhury MA, Islam MF. Characterization of Ni-Cu Mixed Spinel Ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater. 2002;251:292–303.
Gabal MA, Al-Angari YM, Kadi MW. Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni1-xCuxFe2O4 prepared through oxalates precursors. Polyhedron. 2011;30:1185–90.
Askeland DR. The science and engineering of materials. 2nd ed. NY: Champman & Hall; 1990.
Siddique M, Butt NM, Shafi M, Abbass T, Misbah UI. Cation distribution in Ni-substituted Mn-Ferrite by Mössbour effect technique. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2003;258:525–9.
Siddique M, Khan RTA, Shafi M. Fluctuation in occupancy of Cu2+ ions in Zn- and Cd-substituted Cu-Ferrite. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2008;277:531–7.
Nadeem M, Mushtaq A. Thermal cycling induced reversibility/irreversibility in the ac electrical properties of La0.50Ca0.50MnO3+δ by impedance spectroscopy. J Appl Phys. 2009;106:0737131–6.
Iqbal MJ, Nadeem M, Hassan MM. Low temperature AC electrical study of Pr0.5-xLaxCa0.5MnO3 (x = 0.0–0.4) ceramics by employing impedance spectroscopy. J App Phys. 2013;114:1137081–8.
Acknowledgements
One of the author (Sumaira Naz) wishes to thank the financial support of the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan through the (5000) Indigenous PhD scholarship scheme in Science and Technology. Authors also wish to thank to Aurangzeb, M.M.R Baig, M. Shafi, M. Hussain, Z. Ahmed, Shahid Ayub, and Laquit Ali for their technical and lab assistance during XRD, SEM, Mössbauer data collection, and hydrothermal experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durrani, S.K., Naz, S., Nadeem, M. et al. Thermal, structural analysis, Mössbauer and impedance study of copper nickel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via Tween 80-assisted hydrothermal process. J Therm Anal Calorim 119, 253–263 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4090-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4090-y