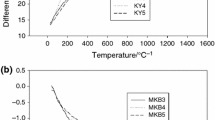
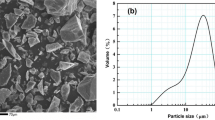
Abstract
Fine needles of mullite grains were obtained successfully in a compact and low porous matrix using solid state sintering. We treated high-grade kaolin and sand-rich kaolin at 750 °C to amorphous metakaolins, and bauxite at 1,000 °C to metastable alumina. By designing a stochiometric composition of mullite, each amorphous metakaolin was added to metastable alumina. Fine grains of mullite with almost complete crystallization were obtained from 1,350 °C in a case of amorphous metakaolin from high-grade kaolin and at 1,550 °C in the other case where amorphous metakaolin is from sand-rich kaolin. The difference in the temperatures of mullitization was linked to the late dissolution of silica from the cristobalite and quartz phases which were still present in the sand-rich metakaolin sample at 1,350 °C. The use of metastable alumina and metakaolin instead of kaolin to design the mullite matrix allows the increase in number of mullite nucleation sites. This results to high densification and crystallization, fine grain size, and high mechanical properties of the final matrix.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksay IA, Dabbs DM, Sarikaya M. Mullite for structural, electronic and optical applications. J Am Ceram Soc. 1991;74:2343–58.
Brindley GW, Nakahira M. The kaolinite-mullite reactions series: III, the high temperature phases. J Am Ceram Soc. 1959;42(7):319–24.
Komarneni S, Suwa Y, Roy R. Application of compositionally diphase xerogels for enhanced densification: the system Al2O3–SiO2. J Am Ceram Soc. 1984;69:C155–6.
Sonuparlak B. Sol–gel processing of infrared transparent mullite. Adv Ceram Mater. 1988;3:263–7.
Fahrenholtz WL, Smith DM, Cesarano J III. Effect of precursor particle size on the densification and crystallization behavior of mullite. J Am Ceram Soc. 1993;76:433–7.
Ha JS, Chawla KK. The effect of precursor characteristics on the crystallization and densification of diphasic mullite gels. Ceram Int. 1993;19:299–305.
Jeng DY, Rahaman MN. Sintering and characterization of mullite powder prepared by sol–gel processing. J Mater Sci. 1993;28:4904–9.
Pach L, Iratni A, Kovar V, Mankos P, Komarnemi S. Sintering of diphasic mullite gel. J Eur Ceram Soc. 1996;16:561–6.
Sacks MD, Pask JA. Sintering of mullite containing materials: II, effect of agglomeration. J Am Ceram Soc. 1982;65:70–7.
Kanzaki S, Tabata H. Sintering and mechanical properties of stoichiometric mullite. J Am Ceram Soc. 1985;68:C6–7.
Sacks MD, Bozkurt N, Scheiffele GW. Fabrication of mullite and mullite-matrix composites by transient viscous sintering of composite powders. J Am Ceram Soc. 1991;74(10):2428–37.
Sacks MD, Lee HW, Pask JA. A review of powder preparation methods of densification procedures for fabricating high density mullite. In Ceramic transactions. vol. 6. Westerville: American ceramic Society; 1990. pp. 167–207.
Ambroise J, Murat M, Pera J. Hydratation reaction and hardening of calcined clays and related minerals: V. Extension of the research and general conclusions. Cem Concr Res. 1985;15:261–8.
Davidovits J. Geopolymer chemistry and applications. Morrisville: Geoplymer Institute; 2008.
Lee S, Kim YJ, Moon HS. Energy-filtering transmission electron microscopy (EFTEM) study of modulated structure in metakaolinite, represented by 14 Å modulation. J Am Ceram Soc. 2003;86:174–6.
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J. An introduction to rock forming minerals. 2nd ed. London: Longman Scientific and Technical; 1992.
Igor L, David B. Metastable alumina polymorphs: crystal structures and transition sequences. J Am Ceram Soc. 1998;81(8):1995–2012.
Paulik J, Paulik F, Naumann R, Kohnke K, Petzold D. Kinetics and mechanism of the dehydration of hydrargilites. Part. 1. Thermochim Acta. 1983;64:1–14.
Naumann R, Kohnke K, Paulik J, Paulik F. Kinetics and mechanism of the dehydration of hydrargilites. Part. 2. Thermochim Acta. 1983;64:15–26.
Mercury JMR, Pena P, Aza AH, Sheptyakov D, Turrillas X. On the decomposition of synthetic gibbsite studied by neutron thermodiffractometry. J Am Ceram Soc. 2006;89(12):3728–33.
Slade RCT, Southern JC, Thompson IM. Al-27 nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectroscopy investigation of thermal transformation sequences of alumina hydrates 1 gibbsite, gamma-Al(OH)3. J Mater Chem. 1991;1:563–8.
Djangang CN, Elimbi A, Melo UC, Lecomte GL, Nkoumbou C, Soro J, Yvon J, Blanchart P, Njopwouo D. Refractory ceramics from clays of Mayouom and Mvan in Cameroon. Appl Clay Sci. 2008;39(1–2):10–7.
Njoya A, Nkoumbou C, Grosbois C, Njopwouo D, Njoya D, Courtin-Nomade A, Yvon J, Martin F. Genesis of Mayouom kaolin deposit (western Cameroon). Appl Clay Sci. 2006;32(1–2):125–40.
Leonelli C, Kamseu E, Melo UC, Corradi A, Pellacani GC. Mullitization behavior during thermal treatment of three kaolinitic clays from Cameroon: densification sintering kinetics and microstructure. Interceram. 2008;57(6):396–401.
Kamseu E, Braccini S, Corradi A, Leonelli C. Microstructural evolution during thermal treatment of three kaolinitic clays from Cameroon. Adv Appl Ceram. 2009;108(6):338–46.
Kamseu E, Rizzuti A, Miselli P, Veronesi P, Leonelli C. Use of noncontact dilatometry for the assessment of the sintering kinetics during mullitization of three kaolinitic clays from Cameroon. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98(3):757–63.
Tchamba AB, Kamseu E, Melo UC, Yongué R, Djoya D, Njopwouo D. Caractérisation de la bauxite de Haléo-Danielle (Minim-Martap, Cameroun) en vue de son utilisation industrielle dans les matériaux à haute teneur en alumine. Silic Ind. 2008;73(5–6):77–84.
Tchamba AB, Melo UC, Kamseu E, Yongue R, Njopwouo D. Thermal and sintering behavior of bauxites from Haleo-Danielle, Minim-Martap (Cameroon). Ind Ceram. 2010;30(1):1–6.
Lee WE, Souza GP, McConville CCJ, Tarvornpanich T, Iqpal Y. Mullite formation in clays clay-derived vitreous ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2008;28:465–71.
Ferhat K, Olcay S. Improvement of sintering and microstructural homogeneity of a diphasic mullite. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2001;21:901–5.
Bartsch M, Saruhan B, Schmucker M, Hartmut S. Novel low-temperature processing route of dense mullite ceramics by reaction sintering of amorphous SiO2-coated γ-Al2O3 particle nanocomposites. J Am Ceram Soc. 1999;82(6):1388–92.
Askay I, Dabbs D, Sarikaya M. Mullite for structural electronic and optical applications. J Am Ceram Soc. 1991;74(10):2343–58.
Wei WC, Halloran JW. Phase transformation of diphasic aluminosilicate gels. J Am Ceram Soc. 1988;71(3):166–72.
Huling JC, Messing GL. Hybrid gels for homoepatic nucleation of mullite. J Am Ceram Soc. 1989;72(9):1725–9.
Huling JC, Messing GL. Hybrid Gels designed for mullite nucleation and phase crystallization control. In: Zelinski BJJ, Brinker CJ, Clark DE, Ulrich DR (eds) Better ceramics through chemistry IV, Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, vol 180. Materials Research Society, Pittsburg, PA; 1990. pp 515–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djangang, C.N., Tchamba, A.B., Kamseu, E. et al. Reaction sintering and microstructural evolution in metakaolin-metastable alumina composites. J Therm Anal Calorim 117, 1035–1045 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3937-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3937-6