Abstract
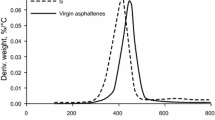
This study investigated the catalytic effect of NiO, Co3O4 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles toward asphaltene thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) under inert conditions. Asphaltene adsorbed onto the selected nanoparticles were subjected to thermal decomposition up to 800 °C in a thermogravimetric analyzer. The presence of nanoparticles caused a significant decrease in the asphaltene decomposition temperature and activation energy. Activation energies for the process were calculated using the Ozawa–Flynn–Wall method. All the selected metal oxide nanoparticles showed high catalytic activity toward asphaltene decomposition in the following order NiO > Co3O4 > Fe3O4. This study confirms that metal oxide nanoparticles can significantly enhance the thermal decomposition of heavy hydrocarbons, like asphaltenes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Governement of Alberta. Environmental management of Alberta’s oilsands. http://environment.gov.ab.ca/info/library/8042.pdf (2009). Accessed 30 Oct 2011.
Nassar NN, Hassan A, Pereira-Almao P. Metal oxide nanoparticles for asphaltene adsorption and oxidation. Energy Fuels. 2011;25(3):1017–23.
Hein FJ. Heavy oil and oil (Tar) sands in North America: an overview & summary of contributions. Nat Resour Res. 2006;15(2):67–84.
Herron, EH, King, SD. Heavy oil as the key to U.S. energy security. 2011. http://www.petroleumequities.com/cgi-bin/site.cgi?t=5&p=energysecurity.html. Accessed 11 June 2011
Nassar NN, Hassan A, Pereira-Almao P. Effect of surface acidity and basicity of aluminas on asphaltene adsorption and oxidation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011;360:233–8.
Nassar NN, Hassan A, Pereira-Almao P. Comparative oxidation of adsorbed asphaltenes onto transition metal oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A. 2011;384(1–3):145–9.
Nassar NN, Hassan A, Pereira-Almao P. Application of nanotechnology for heavy oil upgrading: catalytic steam gasification/cracking of asphaltenes. Energy Fuels. 2011;25(4):1566–70.
Nassar NN, Pereira-Almao P. Capturing H2S(g) by in situ-prepared ultradispersed metal oxide particles in an oilsand-packed bed column. Energy Fuels. 2010;24(11):5903–6.
Nassar NN, Husein MM, Pereira-Almao P. Ultradispersed particles in heavy oil: part II, sorption of H2S(g). Fuel Process Technol. 2010;91(2):169–74.
Nassar NN. Asphaltene adsorption onto alumina nanoparticles: kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Energy Fuels. 2010;24(8):4116–22.
Husein MM, Nassar NN. Nanoparticle preparation using the single microemulsions scheme. Curr Nanosci. 2008;4(4):370–80.
Nassar, NN, Hassan, A, Carbognani, L, Lopez-Linares, F, Pereira-Almao, P. Iron oxide nanoparticles for rapid adsorption and enhanced catalytic oxidation of thermally cracked asphaltenes. Fuel 2011. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2011.09.022.
Vyazovkin S, et al. ICTAC kinetics committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim Acta. 2011;520(1–2):1–19.
Flynn JH. The “temperature integral”—its use and abuse. Thermochim Acta. 1997;300(1–2):83–92.
Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1965;38(11):1881–6.
Doyle CD. Series approximations to the equation of thermogravimetric data. Nature. 1965;207(4994):290–1.
Doyle CD. Kinetic analysis of thermogravimetric data. J Appl Polym Sci. 1961;5(15):285–92.
Acknowledgements
Financial support provided by Carbon Management Canada, Inc. (CMC-NCE), a research network financed by the National Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC), is gratefully acknowledged. The authors would like to thank Mr. AbdelLatif Eldood for providing asphaltene samples and Mr. German Luna for his help in performing some calculations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nassar, N.N., Hassan, A. & Pereira-Almao, P. Thermogravimetric studies on catalytic effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on asphaltene pyrolysis under inert conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim 110, 1327–1332 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-2045-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-2045-0