Abstract
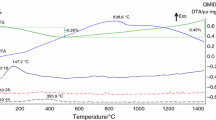
During a heating–cooling cycle, zirconia (ZrO2) undergoes a martensitic transformation from monoclinic to tetragonal structure phases, which presents special hysteresis loop in the dilatometry curve at temperatures between 800 and 1100 °C. Monoclinic zirconia (m-ZrO2) particles reinforced ceramic matrix composites not always present this behavior. In order to elucidate this fact a series of zircon–zirconia (ZrSiO4–ZrO2) ceramic composites have been obtained by slip casting and characterized. The final properties were also correlated with the zirconia content (0–30 vol.%). The influence of the martensitic transformation (m–t) in well-dispersed zirconia grains ceramic composite on the thermal behavior was analyzed. Thermal behavior evaluation was carried out; the correlation between the thermal expansion coefficients with the zirconia content showed a deviation from the mixing rule applied. A hysteresis loop was observed in the reversible dilatometric curve of composites with enough zirconia grains (≥10 vol.%). Over this threshold the zirconia content is correlated with the loop area. The transformation temperatures were evaluated and correlated with the zirconia addition. When detected the m–t temperature transformation is slightly influenced by the zirconia content (due to the previously evaluated decrease in the material stiffness) and similar to the temperature reported in literature. The reverse (cooling) transformation temperature is strongly decreased by the ceramic matrix. The DTA results are consistent with the dilatometric analysis, but this technique showed more reliable results. Particularly the endothermic m–t transformation temperature showed to be easily detected even when the only m-ZrO2 present was the product of the slight thermal dissociation of the zircon during the processing of the pure zircon material.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torrecillas R, Moya JS, De Aza S, Gros H, Fantozzi G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of mullite-zirconia reaction-sintered composites. Acta Metall Mater. 1993;41(6):1647–52.
Lathabai S, Hay DG, Wagner F, Claussen N. Reaction-bonded mullite/zirconia composites. J Am Ceram Soc. 1996;79(1):248–56.
Hamidouche M, Bouaouadja N, Osmani H, Torrecillias R, Fantozzi G. Thermomechanical behavior of mullite-zirconia composite. J Eur Ceram Soc. 1996;16(4):441–5.
Jang B-K. Microstructure of nano SiC dispersed Al2O3-ZrO2 composites. Mater Chem Phys. 2005;93(2–3):337–41.
Hirvonen A, Nowak R, Yamamoto Y, Sekino T, Niihara K. Fabrication, structure, mechanical and thermal properties of zirconia-based ceramic nanocomposites. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2006;26(8):1497–505.
Sarkar D, Adak S, Mitra NK. Preparation and characterization of an Al2O3-ZrO2 nanocomposite, Part I: Powder synthesis and transformation behavior during fracture. Compos Part A. 2007;38(1):124–31.
Yugeswaran S, Selvarajan V, Dhanasekaran P, Lusvarghi L. Transferred arc plasma processing of mullite-zirconia composite from natural bauxite and zircon sand. Vacuum. 2008;83(2):353–9.
Rendtorff N, Garrido L, Aglietti E. Thermal shock behavior of dense Mullite-Zirconia composites obtained by two processing routes. Ceram Int. 2008;34(8):2017–24.
Belhouchet H, Hamidouche M, Bouaouadja N, Garnier V, Fantozzi G. Elaboration and characterization of mullite-zirconia composites from gibbsite, boehmite and zircon. Ceramics-Silikaty. 2009;53(3):205–10.
Ibarra Castro MN, Almanza Robles JM, Cortés Hernández DA, Escobedo Bocardo JC, Torres Torres J. Development of mullite/zirconia composites from a mixture of aluminum dross and zircon. Ceram Int. 2009;35(2):921–4.
Mecif A, Soro J, Harabi A, Bonnet JP. Preparation of mullite- and zircon-based ceramics using kaolinite and zirconium oxide: a sintering study. J Am Ceram Soc. 2010;93(5):1306–12.
Chockalingam S, Traver HK. Microwave sintering of β-SiAlON-ZrO2 composites. Mater Des. 2010;31(8):3641–6.
Tür YK, Sünbül AE, Yilmaz H, Duran C. Effect of mullite grains orientation on toughness of mullite/zirconia composites. Ceram Trans. 2010;210:273–8.
Curran DJ, Fleming TJ, Towler MR, Hampshire S. Mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite-zirconia compacts sintered by two different sintering methods. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2010;21(4):1109–20.
Ma W, Wen L, Guan R, Sun X, Li X. Sintering densification, microstructure and transformation behavior of Al2O3/ZrO2(Y2O3) composites. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;477(1–2):100–106.
Sahnoune F, Saheb N, Chegaar M, Goeuriot P. Microstructure and sintering behavior of mullite-zirconia composites. Mater Sci Forum. 2010;638–642:979–84.
Calderon-Moreno JM, Yoshimura M. Al2O3–Y3AlO12(YAG)-ZrO2 ternary composite rapidly solidified from the eutectic melt. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2005;25(8):1365–8.
Hamidouche M, Bouaouadja N, Torrecillas R, Fantozzi G. Thermomechanical behavior of a zircon–mullite composite. Ceram Int. 2007;33(4):655–62.
Naglieri V, Palmero P, Montanaro L. Preparation and characterization of alumina-doped powders for the design of multi-phasic nano-microcomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97(1):231–7.
Shevchenko AV, Dudnik EV, Ruban AK, Redko VP, Lopato LM. Sintering of self-reinforced ceramics in the ZrO2–Y2O3–CeO2–Al2O3 system. Powder Metall Metal Ceram. 2010;49(1–2):42–9.
Malek O, Vleugels J, Perez Y, De Baets P, Liu J, Van den Berghe S, Lauwers B. Electrical discharge machining of ZrO2 toughened WC composites. Mater Chem Phys. 2010;123(1):114–20.
Sarkar SK, Lee BT. Evaluation and comparison of the microstructure and mechanical properties of fibrous Al2O3-(m-ZrO2)/t-ZrO2 composites after multiple extrusion steps. Ceram Int. 2010;36(6):1971–6.
Pan C, Zhang L, Zhao Z, Qu Z, Yang Q, Huang X. Changes in microstructures and properties of Al2O3/ZrO2(Y2O3) with different content of ZrO2. Adv Mater Res. 2010;105–106(1):1–4.
Rendtorff N, Garrido L, Aglietti E. Mullite-zirconia-zircon composites: properties and thermal shock resistance. Ceram Int. 2009;35(2):779–86.
Rendtorff N, Garrido L, Aglietti E. Zirconia toughening of mullite-zirconia-zircon composites obtained by direct sintering. Ceram Int. 2010;36(2):781–8.
Zender H, Leistner H, Searle H. ZrO2 materials for applications in the ceramic industry. Interceram. 1990;39(6):33–6.
Kelly P, Rose LF. The martensitic transformation in ceramics-its role in transformation toughening. Prog Mater Sci. 2002;47:463–557.
Rendtorff NM, Garrido LB, Aglietti EF. Thermal behavior of mullite–zirconia–zircon composites. Influence of zirconia phase transformation. J Therm Anal Calorim. doi:10.1007/s10973-010-1030-3.
Wang C, Zinkevich M, Aldinger F. The zirconia-Hafnia system: DTA measurements and thermodynamic calculations. J Am Ceram Soc. 2006;89(12):3751–8.
Luo X, Zhou W, Ushakov SV, Navrotsky A, Demkov AA. Monoclinic to tetragonal transformations in hafnia and zirconia: a combined calorimetric and density functional study. Phys Rev B. 2009;80(13):134119.
Wang C, Zinkevich M, Aldinger F. On the thermodynamic modeling of the Zr-O system. Calphad. 2004;28(3):281–92.
Chevalier J, Gremillard L, Virkar AV, Clarke DR. The tetragonal-monoclinic transformation in zirconia: lessons learned and future trends. J Am Ceram Soc. 2009;92(9):1901–20.
Moriya Y, Navrotsky A. High-temperature calorimetry of zirconia: heat capacity and thermodynamics of the monoclinic-tetragonal phase transition. J Chem Thermodyn. 2006;38(3):211–23.
Skovgaard M, Ahniyaz A, Sørensen BF, Almdal K, van Lelieveld A. Effect of microscale shear stresses on the martensitic phase transformation of nanocrystalline tetragonal zirconia powders. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2010;30:2749–55.
Ownby PD, Burt DD, Stewart DV. Experimental study of the thermal expansion of yttria stabilized zirconia ceramics. Thermochim Acta. 1991;190(1):39–42.
Mori T, Yamamura H, Kobayashi H, Mitamura T. Preparation of high-purity ZrSi04 using sol-gel processing and mechanical properties of the sintered body. J Am Ceram Soc. 1990;75(9):2420–6.
Moreno R, Moya JS, Requena J. Slip casting of zircon by using an organic surfactant. Ceram Int. 1991;17(1):37.
Garrido LB, Aglietti EF. Zircon based ceramics by colloidal processing. Ceram Int. 2001;27(5):491–7.
Shi Y, Huang X, Yan D. Fabrication of hot-pressed zircon ceramics: mechanical properties and microstructure. Ceram Int. 1997;23(5):457–62.
Carbonneau X, Hamidouche M, Olagnon C, Fantozzi G, Torrecillas R. High temperature behavior of a zircon ceramic. Key Eng Mater. 1997;132–136:571–4.
Shi Y, Huang X, Yan D. Mechanical properties and toughening behavior of particulate-reinforced zircon matrix composites. J Mater Sci Lett. 1999;18(3):213–6.
Singh RN. High-temperature mechanical properties of a uniaxially reinforced zircon-silicon carbide composite. J Am Ceram Soc. 1990;73(8):2399–406.
Singh RN. Mechanical properties of a zircon matrix composite reinforced with silicon carbide whiskers and filaments. J Mater Sci. 1991;26(7):1839–46.
Singh RN. SiC fibre-reinforced zircon composites. Am Ceram Soc Bull 1991;70(I):55–56.
Shi Y, Huang X, Yan D. Toughening of hot-pressed ZrSiO4 ceramics by addition of Y-TZP. Mater Lett. 1998;35(3–4):161–5.
Alahakoon WPCM, Burrows SE, Howes AP, Karunaratne BSB, Smith ME, Dobedoe R. Fully densified zircon co-doped with iron and aluminium prepared by sol-gel processing. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2010;30(12):2515–23.
Kondoh I, Tanaka T, Tamari N. Sintering of zircon-silicon carbide whisker composites and their mechanical properties. J Jpn Ceram Soc. 1993;101(3):369–72.
Shi Y, Huang X, Yan D. Synergistic strengthening and toughening of zircon ceramics by the additions of SiC whisker and 3Y-TZP simultaneously. J Eur Ceram Soc. 1997;17:1003–10.
Rendtorff NM, Garrido LB, Aglietti EF. Mechanical and fracture properties of zircon–mullite composites obtained by direct sintering. Ceram Int. 2009;35(7):2907–13.
Tartaj P, Sanz J, Serna CJ, Ocana M. Zircon formation from amorphous spherical ZrSiO4 particles obtained by hydrolysis of aerosols. J Mater Sci. 1994;29(24):6533–8.
Kaiser A, Lobert M, Telle R. Thermal stability of zircon (ZrSiO4). J Eur Ceram Soc. 2008;28(11):2199–211.
Váczi T, Nasdala L, Wirth R, Mehofer M, Libowitzky E, Häger T. On the breakdown of zircon upon “dry” thermal annealing. Miner Petrol. 2009;97:1–129.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rendtorff, N.M., Suarez, G., Sakka, Y. et al. Influence of the zirconia transformation on the thermal behavior of zircon–zirconia composites. J Therm Anal Calorim 110, 695–705 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1906-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1906-x