Abstract
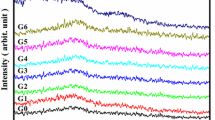
This article aims to shed some light on the structure and thermo-physical properties of lithium disilicate glasses in the system Li2O–SiO2–Al2O3–K2O. A glass with nominal composition 23Li2O–77SiO2 (mol%) (labelled as L23S77) and glasses containing Al2O3 and K2O with SiO2/Li2O molar ratios (3.13–4.88) were produced by conventional melt-quenching technique in bulk and frit forms. The glass-ceramics (GCs) were obtained from nucleation and crystallisation of monolithic bulk glasses as well as via sintering and crystallisation of glass powder compacts. The structure of glasses as investigated by magic angle spinning-nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS-NMR) depict the role of Al2O3 as glass network former with four-fold coordination, i.e., Al(IV) species while silicon exists predominantly as a mixture of Q 3 and Q 4 (Si) structural units. The qualitative as well as quantitative crystalline phase evolution in glasses was followed by differential thermal analysis (DTA), X-ray diffraction (XRD) adjoined with Rietveld-reference intensity ratio (R.I.R.) method, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The possible correlation amongst structural features of glasses, phase composition and thermo-physical properties of GCs has been discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shelby JE. Introduction to glass science and technology. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry; 2005.
Höland W, Beall G. Glass-ceramic technology. Ohio: The American Ceramic Society; 2002.
Vogel W. Structure and crystallization of glasses. 1st ed. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1971.
Fernandes HR, Tulyaganov DU, Goel A, Ribeiro MJ, Pascual MJ, Ferreira JMF. Effect of Al2O3 and K2O content on structure, properties and devitrification of glasses in the Li2O–SiO2 system. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2010;30:2017–30.
Barrett JM, Clark DE, Hench LL. Glass–ceramic dental restoration. U.S. Patent. 1980;4:189–325.
Wu M, Cannon WR, Panzera C. Castable glass–ceramic composition useful as dental restorative. U.S. Patent. 1985;4:515–634.
Larson AC, von Dreele RB. GSAS: general structure analysis system LANSCE, MS-H805. Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Laboratory; 1998.
Engelhardt G, Nofz M, Forkel K, Wihsmann FG, Magi M, Samoson A, Lippmaa E. Structural studies of calcium aluminosilicate glasses by high resolution solid state 29Si and 27A1 magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys Chem Glasses. 1985;26:157–65.
Mackenzie KJD, Smith ME. Multinuclear solid-state NMR of inorganic materials. Amsterdam: Pergamon; 2002.
Abo-Mosallam HA, Hill RG, Karpukhina N, Law RV. MAS-NMR studies of glasses and glass-ceramics based on a clinopyroxene–fluorapatite system. J Mater Chem. 2010;20:790–7.
Stebbins JF, Kroeker S, Lee SK, Kiczenski TJ. Quantification of five- and six-coordinated aluminium ions in aluminosilicate and fluoride-containing glasses by high-field, high-resolution 27Al NMR. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2000;275:1–6.
Silgardi C, D’Arrigo MC, Leonelli C. Sintering behaviour of glass ceramics frits. Am Ceram Soc Bull. 2000;9:88–93.
Fuss T, Mogus-Milankovic A, Ray CS, Lesher CE, Youngman R, Day DE. Ex situ XRD, TEM, IR, Raman and NMR spectroscopy of crystallization of lithium disilicate glass at high pressure. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2006;352:4101–11.
Bhaskar JS, Parthasarathy G, Sarmah NC. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic estimation of crystallinity in SiO2 based rocks. Bull Mater Sci. 2008;31(5):775–9.
Acknowledgements
Hugo R. Fernandes is grateful for the financial support of CICECO and for the PhD grant (SFRH/BD/41307/2007) from the FCT, Portugal. Ashutosh Goel is thankful to CICECO and FCT, Portugal (SFRH/BPD/65901/2009) for the post-doctoral research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, H.R., Tulyaganov, D.U., Goel, A. et al. Structural characterisation and thermo-physical properties of glasses in the Li2O–SiO2–Al2O3–K2O system. J Therm Anal Calorim 103, 827–834 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1049-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1049-5