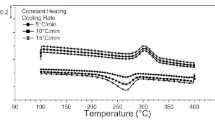
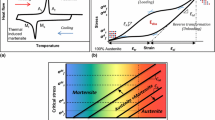
Abstract
Shape memory alloy mechanical performance and phase transformation temperatures depend on the composition of the alloy, on the thermo-mechanical history, and on the applied load. For this reason is important to execute a deep investigation of the SMA material before its final use. In this study we investigate the thermo-mechanical behavior of a NiTiCu wire under stress-free condition through the differential scanning calorimetry and the electrical resistance measurements and under load through tensile and hysteresis tests. The phase transformation temperature dependence on the applied load, by means of the Clausius–Clapeyron equation, as well as on the thermal treatment temperature are also studied.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Funakubo H. Shape memory alloys. London: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers; 1984.
Otsuka K, Wayman CM. Shape memory materials. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1998.
Nam TH, Saburi T, Nakata Y, Shimizu K. Shape memory characteristics and lattice deformation in Ti–Ni–Cu alloy. Mater Trans. 1990;31:1050–6.
Degeratu S, Rotaru P, Manolea Gh, Manolea HO, Rotaru A. Thermal characteristics of Ni–Ti SMA (shape memory alloy) actuators. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97:695–700.
Torra V, Auguet C, Isalgue A, Lovey FC, Sepulveda A, Soul H. Metastable effects on martensitic transformation in SMA. Part VIII Temperature effects on cycling. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009. doi:10.1007/s10973-009-0613-3.
Carreras G, Isalgue A, Torra V, Lovey FC, Soul H. Metastable effects on martensitic transformation in SMA. Part V. Fatigue-life and detailed hysteresis behavior in NiTi and Cu-based alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;91(2):575–9.
Auguet C, Isalgue A, Lovey FC, Pelegrina JL, Ruiz S, Torra V. Metastable effects on martensitic transformation in SMA. Part III. Tentative temperature effects in a NiTi alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;89(2):537–42.
Miller DA, Lagoudas DC. Influence of cold work and heat treatment on the shape memory effect and plastic strain development of NiTi. Mater Sci Eng A. 2001;308:161–75.
Fukuda T, Kakeshita T, Kitayama M, Saburi T. Effect of aging on martensitic transformation in a shape memory Ti–40.5Ni–10Cu alloy. J Phys IV. 1995;5:717–22.
Uchil J. Shape memory alloys—characterization techniques. J Phys. 2002;58:1131–9.
Duerig TW, Melton KN, Stockel D, Wayman CM. Engineering aspects of shape memory alloys. London: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1990.
Auguet C, Isalgue A, Torra V, Lovey FC, Pelegrina JL. Metastable effects on martensitic transformation in SMA. PartVII Aging problems in NiTi. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:63–71.
Artiaga R, García A, García L, Varela A, Mier JL, Naya S, Gra M. DMTA study of a nickel-titanium wire. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2002;70:199–207.
Lo YC, Wu SK, Horng HE. A study of B2-B19-B19′ two-stage martensitic transformation in a Ti50Ni40Cu10 alloy. Acta Metall Mater. 1993;41:747–59.
Uchil J, Mohanchandra KP, Ganesh Kumara K, Mahesh KK. Study of critical dependence of stable phases in nitinol on heat treatment using electrical resistivity probe. Mater Sci Eng A. 1998;251:58–63.
Wu SK, Lin HC, Lin TY. Electrical resistivity of Ni–Ti binary and Ti–Ni-X (X = Fe, Cu) ternary shape memory alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2006;438–440:536–9.
Shaw JA, Kyriakides S. Thermomechanical aspects of NiTi. J Mech Phys Solids. 1995;43:1243–81.
Marony Sousa Farias Nascimento M, de Araújo CJ, da Rocha Neto JS, Nogueira de Lima AM. Electro-thermomechanical characterization of Ti–Ni shape memory alloy thin wires. Mater Res. 2006;9:15–9.
Nam TH, Saburi T, Shimizu K. Cu-content dependence of shape memory characteristics in Ti–Ni–Cu alloys. Mater Trans. 1990;31:956–67.
Otsuka K, Ren X. Physical metallurgy of Ni–Ti-based shape memory alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2005;50:511–678.
Wang ZG, Zu XT, Huo Y. Effect of heating/cooling rate on the transformation temperatures in NiTiCu shape memory alloys. Thermochim Acta. 2005;436:153–5.
Nurveren K, Akdoğan A, Huang WM. Evolution of transformation characteristics with heating/cooling rate in NiTi shape memory alloys. J Mater Process Technol. 2008;196:129–34.
Wang G, Jiang XX, Nikanpour D. Measurement of specific heat, latent heat and phase transformation temperatures of shape memory alloys. High Temp High Press. 2008;37:91–107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nespoli, A., Besseghini, S. A complete thermo-mechanical study of a NiTiCu shape memory alloy wire. J Therm Anal Calorim 103, 821–826 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1042-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1042-z