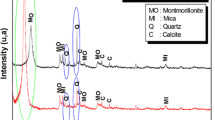
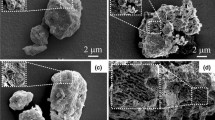
Abstract
Pristine and purified Argel sodium bentonites were organically modified with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium surfactants by ion exchange reaction in order to investigate the effect of the chemical identity of the surfactant and of the clay purification procedure in the intercalation process, final structure and thermal stability of organobentonites. The bentonites were characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis, thermogravimetric analysis and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The bentonite purification treatment and, especially, the chemical structure of surfactant affected the thermal behavior of the organobentonites. The phosphonium modified bentonites were thermally more stable than those modified with ammonium, particularly the purified bentonite. These results seem to be promising regarding to the potential application of phosphonium modified Argel bentonites for the melt processing preparation of nanocomposites with polymeric matrices requiring high processing temperatures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grim RE, Güven N. Bentonites, geology, mineralogy, properties and uses, development in sedimentology, vol. 24. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1978.
Xi YF, Zhou Q, Frost RL, He HP. Thermal stability of octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide modified montmorillonite organoclay. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007;311:347–53.
Zidelkheir B, Abdelgoad M. Effect of surfactant agent upon the structure of montmorillonite X-ray diffraction and thermal analysis. J Therm Anal Cal. 2008;94:181–7.
Chen D, Zhu JX, Yuan P, Yang SJ, Chen T-H, He HP. Preparation and characterization of anion–cation surfactants modified montmorillonite. J Therm Anal Cal. 2008;94:841–8.
Utracki LA. Clay-containing polymeric nanocomposites, vol. 1. UK: Rapra; 2004.
Bottino FA, Di Pasquale G, Fabbri E, Orestano A, Pollicino A. Influence of montmorillonite nano-dispersion on polystyrene photo-oxidation. Polym Degrad Stab. 2009;94:369–74.
Olson CG, Thompson ML, Wilson MA. Phyllosilicates. In: Summer ME, editor. Handbook of soil science. New York: CRC Press; 1993.
Xi Y, Ding Z, Hongping H, Frost RL. Infrared spectroscopy of organoclays synthesized with the surfactant octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide. Spectrochim Acta A. 2005;61:515–25.
Tabak A, Afsin B, Aygun SF, Koksal E. Structural characteristics of organo-modified bentonites of different origin. J Therm Anal Cal. 2007;87:377–82.
Markarian J. Mineral modifiers take on new roles. Plast Addit Compound. 2005;7:18.
Paiva LB, Morales AR, Valenzuela-Díaz FR. Organoclays: properties, preparation and applications. Appl Clay Sci. 2008;42:8–24.
Ray SS, Okamoto M. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: a review from preparation to processing. Prog Polym Sci. 2003;28:1539–1641.
Kurose T, Yudin VE, Otaigbe JU, Svetlichnyi VM. Compatibilized polyimide (R-BAPS)/BAPS-modified clay nanocomposites with improved dispersion and properties. Polymer. 2007;48:7130–8.
Costache MC, Heidecker MJ, Manias E, Gupta RK, Wilkie CA. Benzimidazolium surfactants for modification of clays for use with styrenic polymers. Polym Degrad Stab. 2007;92:1753–62.
Önal M, Sarkaya Y. Thermal characterization of methyltributylammonium-smectites. J Therm Anal Cal. 2008;91:835–9.
Huskić M, Žagar E, Žigon M, Brnardić I, Macan J, Ivanković M. Modification of montmorillonite by cationic polyesters. Appl Clay Sci. 2009;43:420–4.
Xie W, Gao Z, Liu K, Pan W, Vaia R, Hunter D, et al. Thermal characterization of organically modified montmorillonite. Thermochim Acta. 2001;367:339–50.
Fethi K. Thermal stability investigation of organo-acid-activated clays by TG-MS and in situ XRD techniques. Thermochim Acta. 2009;486:71–6.
Ramos Vianna MMG, Dweck J, Kozievitch VFJ, Valenzuela-Diaz FR, Büchler PM. Characterization and study of sorptive properties of differently prepared organoclays from a Brazilian natural bentonite. J Therm Anal Cal. 2005;82:595–602.
Shah RK, Paul DR. Organoclay degradation in melt processed polyethylene nanocomposites. Polymer. 2006;47:4075–84.
Chigwada G, Wang D, Wilkie CA. Polystyrene nanocomposites based on quinolinium and pyridinium surfactants. Polym Degrad Stab. 2006;91:848–55.
Costache MC, Heidecker MJ, Manias E, Wilkie CA. Preparation and characterization of poly(ethylene terephtalate)/clay nanocomposites by melt blending using thermally stable surfactants. Polym Adv Technol. 2006;17:764–71.
Xie W, Xie R, Pan WP, Hunter D, Koene B, Tan LS, et al. Thermal stability of quaternary phosphonium modified montmorillonites. Chem Mater. 2002;14:4837–45.
Patel HA, Somani RS, Bajaj HC, Jasra RV. Preparation and characterization of phosphonium montmorillonite with enhanced thermal stability. Appl Clay Sci. 2007;35:194–200.
Hedley CB, Yuan G, Theng BKG. Thermal analysis of montmorillonites modified with quaternary phosphonium and ammonium surfactants. Appl Clay Sci. 2007;35:180–8.
Avalos F, Ortiz JC, Zitzumbo R, López-Manchado MA, Verdejo R, Arroyo M. Effect of montmorillonite intercalant structure on the cure parameters of natural rubber. Appl Clay Sci. 2008;43:27–32.
Wang D, Wilkie CA. A stibonium-modified clay and its polystyrene nanocomposite. Polym Degrad Stab. 2003;82:309–15.
Davis CH, Mathias LJ, Gilman JW, Schiraldi DA, Shields JR, Trulove P, et al. Effects of melt-processing conditions on the quality of poly(ethylene terephthalate) montmorillonite clay nanocompósitos. J Polym Sci B. 2002;40:2661–6.
Gilman JW, Awad WH, Davis RD, Shields J Jr, Harris RH, Morgan AB, et al. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites from thermally stable trialkylimidazolium-treated montmorillonite. Chem Mater. 2002;14:3776–85.
Wang M, Chung TC, Gilman JW, Manias E. Melt-processable syndiotactic polystyrene/montmorillonite nanocompósitos. J Polym Sci B. 2003;41:3173–87.
Phelps GW, Harris Amer DL. Methylene blue surface area method to correlate with specific soil properties. Ceram Soc Bull. 1968;47:1146–50.
Araujo PER, Araújo SS, Raposo CMO, Silva SML. Poly(ethylene terephthalate)(PET)/layered silicate nanocomposites. Effect of bentonite purification on morphology/behaviour relationship. The Polymer Processing Society 23rd Annual Meeting, 2007.
Silva SML, Araujo PER, Ferreira KRM, Canedo EL, Carvalho LH, Raposo CMO. Effect of clay/water ratio during bentonite clay organophilization on the characteristics of the organobentonites and its polypropylene nanocompósitos. Polym Eng Sci. 2009. doi:10.1002/pen.21399
Moore DM, Reynolds RC. Clay minerals. New York: Oxford University Press; 1997.
Lee SY, Kim SJ. Delamination behavior of silicate layers by adsorption of cationic surfactants. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2002;248:231–8.
Bray HJ, Redfem SAT. Kinetics of dehydration of Ca-montmorillonite. Phys Chem Miner. 1999;26:591–600.
Colthup NB, Daly LH, Wiberlay SE. Introduction to infrared and Raman spectroscopy. 3rd ed. New York: Academic Press; 1990.
Spratt HJ, Palmer SJ, Frost RL. Thermal decomposition of synthesised layered double hydroxides based upon Mg/(Fe,Cr) and carbonate. Thermochim Acta. 2008;479:1–6.
Marras SI, Tsimpliaraki A, Zuburtikudis I, Panayiotou C. Thermal and colloidal behavior of amine-treated clays: the role of amphiphilic organic cation concentration. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007;315:520–7.
Xi YF, Ding Z, He HP, Frost RL. Structure of organoclays—an X-ray diffraction and thermogravimetric analysis study. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2004;277:116–20.
Xi Y, Frost RL, He H. Modification of the surfaces of Wyoming montmorillonite by the cationic surfactants alkyl trimethyl, dialkyl dimethyl, and trialkyl methyl ammonium bromides. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007;305:150–8.
Venkataraman NV, Vasudevan S. Conformation of methylene chains in an intercalated surfactant bilayer. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:1805–12.
Zhu JX, He HP, Zhu LZ, Wen XY. Characterization of organic phases in the interlayer of montmorillonite using FTIR and 13C NMR. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;292:239–44.
Fornes T, Yoon P, Paul D. Polymer matrix degradation and color formation in melt processed nylon 6/clay nanocomposites. Polymer. 2003;44:7545–56.
Kiliaris P, Papaspyrides CD, Pfaendner R. Influence of accelerated aging on clay-reinforced polyamide 6. Polym Degrad Stab. 2009;94:389–96.
Ramos Filho FG, Melo TJA, Rabello MS, Silva SML. Thermal stability of nanocomposites based on polypropylene and bentonite. Polym Degrad Stab. 2005;89:383–92.
Madejová J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib Spectrosc. 2003;31:1–10.
Xu X, Ding Y, Qian Z, Wang F, Wen B, Zhou H, et al. Degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/clay nanocomposites during melt extrusion: effect of clay catalysis and chain extension. Polym Degrad Stab. 2009;94:113–23.
Zhong Y, Zhu Z, Wang S. Synthesis and rheological properties of polystyrene/layered silicate nanocomposite. Polymer. 2005;46:3006–13.
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Bentonit União Nordeste (BUN) for donating the Argel bentonite clay and to CNPq and RENAMI for the financial support through grants # 478451/2006-7; PRONEX FAPESQ/MCT/CNPq 03/04 term #8 and RENAMI # 555212/2005-0. CNPq fellowships on behalf of Itamara Farias Leite (D), Laura H. de Carvalho (PQ), Oscar M. Loureiro Malta (PQ) and Suédina M. L. Silva (PQ) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leite, I.F., Soares, A.P.S., Carvalho, L.H. et al. Characterization of pristine and purified organobentonites. J Therm Anal Calorim 100, 563–569 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0265-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0265-3