Abstract
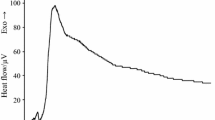
The microcalorimetric method has been used to study the effects of cefpiramide and ceftizoxime sodium on the E. coli growth. The results revealed that these two cephalosporins may alter the metabolic way of the E. coli. Moreover, the lethal doses of cefpiramide and ceftizoxime sodium are 2.000 and 0.2000 μg mL−1, respectively. Combining with the relationships between growth rate constant (k), the maximum power output (P m ), the time corresponding to the maximum power output (t m ) and cephalosporins concentration (C), one can draw the conclusion that the ceftizoxime sodium has a stronger inhibition effects on the growth of E. coli than that of cefpiramide and they both have the possibility to induce the drug fever.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu JC, Li CH, Liu Y, Zhang ZH, Hou AX, Qu SS. A microcalorimetric study of the action of mercuric chloride on the metabolism of mitochondria isolated from Cyprinus carpio liver tissue. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;83:181–6.
Wadsö I, Gomez F, Sjohölm I, Rocculi P. Effect of tissue wounding on the results from calorimetric measurements of vegetable respiration. Thermochim Acta. 2004;422:89–93.
Yao J, Wang F, Tian L, Zhou Y, Chen HL, Chen K, et al. Studying the toxic effect of cadmium and hexavalent chromium on microbial activity of a soil and pure microbe. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95:517–24.
Zheng D, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Chen XJ, Shen YF. Microcalorimetric investigation of the toxic action of Cr(VI) on the metabolism of Tetrahymena thermophila BF5 during growth. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006;22:121–7.
Yan D, Han YM, Wei L, Xiao XH. Effect of berberine alkaloids on Bifidobacterium adolescentis growth by microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95:495–9.
Trampuz A, Salzmann S, Antheaume J, Daniels AU. Microcalorimetry: a novel method for detection of microbial contamination in platelet products. Transfusion. 2007;47:1643–50.
Yang LN, Xu F, Sun LX, Zhao ZB. A microcalorimetric study of the toxicity of two cobalt compounds on Escherichia coli DH5α growth. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:583–8.
Ma J, Qi WT, Yang LN, Yu WT, Xie YB, Wang W, et al. Microcalorimetric study on the growth and metabolism of microencapsulated microbial cell culture. J Microbiol Meth. 2007;68:172–7.
Liu Y, Deng FJ, Zhao RM, Shen XS, Wang CX, Qu SS. Microcalorimetric studies of the toxic action of La3+ in mitochondria isolated from Star-cross 288 chicken heart tissue cells. Chemosphere. 2000;40:851–4.
Liu W, Chaspoul F, Berge Lefranc D, Decome L, Gallice P. Microcalorimetry as a tool for Cr(VI) toxicity evaluation of human dermal fibroblasts. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;89:21–4.
Barry AL, Jones RN, Thornsberry C, Fuchs PC, Ayers LW, Gavan TL, et al. Cefpiramide: comparative in-vitro activity and β-lactamase stability. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985;16:315–25.
Nakagawa K, Koyama M, Matsui H, Ikeda C, Yano K, Nakatsuru N, et al. Pharmacokinetics of cefpiramide (SM-1652) in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984;25:221–5.
Bharathi C, Prasad CS, Bharathi DV, Shankar R, Rao VJ, Dandala R, et al. Structural identification and characterization of impurities in ceftizoxime sodium. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007;43:733–40.
Roy K, Saha A, De K, Sengupta C. Evaluation of probucol as suppressor of ceftizoxime induced lipid peroxidation. Acta Pol Pharm. 2002;59:231–4.
Yang LN, Qiu SJ, Xu F, Sun LX, Zhao ZB, Liang JG, et al. Microcalorimetric investigation of the growth of the Escherichia coli DH5α in different antibiotics. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007;89:875–9.
Wadsö I. Isothermal microcalorimetry in applied biology. Thermochim Acta. 2002;394:305–11.
Yang LN, Xu F, Sun LX, Tan ZC, Tan HD, Zhao ZB, et al. Study on interaction between antibiotics and Escherichia coli DH5α by microcalorimetric method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;85:807–10.
Xie CL, Tang HK, Song ZH, Qu SS, Liao YT, Liu HS. Microcalorimetric study of bacterial growth. Thermochim Acta. 1988;123:33–41.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China for financial support to this work under Grant No. 50671098, 20473091 and 20573112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L.N., Sun, L.X., Xu, F. et al. Inhibitory study of two cephalosporins on E. coli by microcalorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim 100, 589–592 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0222-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0222-1