Abstract
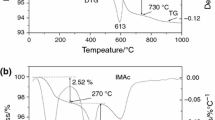
The desorption of benzoic acid and stearic acid from sodium and calcium montmorillonites has been studied using thermogravimetric and differential thermogravimetric analysis. Desorption of benzoic acid from sodium montmorillonites occurs at 140 °C and from calcium montmorillonites at 179 °C. This increase in temperature is attributed to the benzoic acid bonding to the calcium in the interlayer. A lowering of the dehydroxylation temperature of montmorillonites is observed with acid adsorption. Stearic acid desorbs at 218 °C as observed by the DTG curves. The desorption pattern differs between the sodium montmorillonites and the calcium montmorillonites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy MJ, Pevear DR, Hill RJ. Mineral surface control of organic carbon in black shale. Science. 2002;295:657–60.
Greene-Kelly R. Sorption of aromatic organic compounds by montmorillonite. I. Orientation studies. Trans Faraday Soc. 1955;51:412–24.
Greenland DJ, Laby RH, Quirk JP. Adsorption of amino acids and peptides by montmorillonite and illite. I. Cation exchange and proton transfer. Trans Faraday Soc. 1965;61:2013–23.
Heller-Kallai L, Aizenshtat Z, Miloslavski I. The effect of various clay minerals on the thermal decomposition of stearic acid under ‘bulk flow’ conditions. Clay Miner. 1984;19:779–88.
Sieskind O, Ourisson G. Clay-organic matter interactions. Formation of complexes between montmorillonite and stearic and behenic acids. Comptes Rendus des Seances de l’Academie des Sciences, Serie C: Sciences Chimiques. 1971;272:1885–8.
Yan L-G, Wang J, Yu H-Q, Wei Q, Du B, Shan X-Q. Adsorption of benzoic acid by CTAB exchanged montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci. 2007;37:226–30.
Yariv S, Lapides I. The effect of mechanochemical treatments on clay minerals and the mechanochemical adsorption of organic materials onto clay minerals. J Mater Synth Process. 2000;8:223–33.
Adu-Wusu K, Whang JM, McDevitt MF. Modification of clay-based waste containment materials, Conference proceedings—international containment technology conference, St. Petersburg, FL, Feb 9–12, 1997. p. 665–671.
Akcay G, Yurdakoc K. Removal of various phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicides from water by organo-clays. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol. 2000;28:300–4.
Alther GR. Organoclay filtration technology for oil removal. Adv Filtr Sep Technol. 1999;13B:945–52.
Alther GR. Organoclays remove humic substances from water. Spec Publ R Soc Chem. 2000;259:277–88.
Alther G. Soil and groundwater remediation with organoclay. Contam Soils. 2001;6:225–31.
Bhatt J, Bhalala BT. Use of organo-clay for decolorizing colored wastewater from the textile industry. Vijnana Parishad Anusandhan Patrika. 1995;38:249–54.
Alther GR. Stormwater treatment. Water Environ Technol. 2001;13:31–4.
Alther GR. Removal of emulsified oil from wastewater. Fluid/Part Sep J. 2000;13:146–51.
Srinivasan KR, Fogler HS. Use of inorgano-organo-clays in industrial wastewater treatment. Organohalogen Compd. 1990;3:417–20.
Springman K, Mayura K, McDonald T, Donnelly KC, Kubena LF, Phillips TD. Organoclay adsorption of wood-preserving waste from groundwater. Analytical and toxicological evaluations. Toxicol Environ Chem. 1999;71:247–59.
Brixie JM, Boyd SA. Treatment of contaminated soils with organoclays to reduce leachable pentachlorophenol. J Environ Qual. 1994;23:1283–90.
Cruz-Guzman M, Celis R, Hermosin MC, Cornejo J. Sorption of the herbicide simazine by biomolecule-modified clays, Pesticide in Air, Plant, Soil & Water System, Proceedings of the Symposium Pesticide Chemistry, 12th, Piacenza, Italy, June 4–6, 2003. p. 185–191.
Carrizosa MJ, Hermosin MC, Koskinen WC, Cornejo J. Use of organosmectites to reduce leaching losses of acidic herbicides. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 2003;67:511–7.
Sand ID, Piner RL, Gilmer JW, Owens JT. Organoclays as processing aids for plasticized thermoplastics. USA: U.S. Eastman Chemical Company, Us; 2003. 8 pp.
Rafailovich M, Si M, Goldman M. Flame retardant and UV absorptive polymethylmethacrylate nanocomposites. PCT Int. Appl. USA: The Research Foundation of State University of New York; Wo, 2003. 34 pp.
Meincke O, Hoffmann B, Dietrich C, Friedrich C. Viscoelastic properties of polystyrene nanocomposites based on layered silicates. Macromol Chem Phys. 2003;204:823–30.
Maiti P, Yamada K, Okamoto M, Ueda K, Okamoto K. New polylactide/layered silicate nanocomposites: role of organoclays. Chem Mater. 2002;14:4654–61.
Chaiko D. Preparation of organoclays with improved dispersibility from smectites and kaolin clays by coating clays with water-soluble polymer. PCT Int. Appl. USA: University of Chicago; Wo, 2002. 24 pp.
Nzengung VA, Organoclays as sorbents for organic contaminants in aqueous and mixed-solvent systems. GA: Georgia Institute Technology, FIELD URL; 1993. 191 pp.
Soule NM, Burns SE. Effects of organic cation structure on behavior of organobentonites. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng. 2001;127:363–70.
Earnest CM. Characterization of smectite clay minerals by differential thermal analysis and thermogravimetry. Part I. Montmorillonite. Perkin-Elmer Thermal Analysis Application Study 31, Pt. 1; 1980. 8 pp.
Yariv S. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) in the study of thermal reactions of organo-clay complexes. Natural and Laboratory-Simulated Thermal Geochemical Processes; 2003. p. 253–296.
Yariv S. The role of charcoal on DTA curves of organo-clay complexes: an overview. Appl Clay Sci. 2004;24:225–36.
Yariv S, Ovadyahu D, Nasser A, Shuali U, Lahav N. Thermal analysis study of heat of dehydration of tributylammonium smectites. Thermochim Acta. 1992;207:103–13.
Pramoda KP, Liu T, Liu Z, He C, Sue H-J. Thermal degradation behavior of polyamide 6/clay nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab. 2003;81:47–56.
Carmody O, Frost R, Xi Y, Kokot S. Selected adsorbent materials for oil-spill cleanup. A thermoanalytical study. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;91:809–16.
Frost RL, Locke A, Martens WN. Thermogravimetric analysis of wheatleyite Na2Cu2+ (C2O4)2 · 2H2O. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:993–7.
Frost RL, Locke AJ, Hales MC, Martens WN. Thermal stability of synthetic aurichalcite. Implications for making mixed metal oxides for use as catalysts. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:203–8.
Frost RL, Locke AJ, Martens W. Thermal analysis of beaverite in comparison with plumbojarosite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:887–92.
Frost RL, Wain D. A thermogravimetric and infrared emission spectroscopic study of alunite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;91:267–74.
Hales MC, Frost RL. Thermal analysis of smithsonite and hydrozincite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;91:855–60.
Palmer SJ, Frost RL, Nguyen T. Thermal decomposition of hydrotalcite with molybdate and vanadate anions in the interlayer. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:879–86.
Vagvoelgyi V, Daniel LM, Pinto C, Kristof J, Frost RL, Horvath E. Dynamic and controlled rate thermal analysis of attapulgite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:589–94.
Vagvoelgyi V, Hales M, Frost RL, Locke A, Kristof J, Horvath E. Conventional and controlled rate thermal analysis of nesquehonite Mg(HCO3)(OH) · 2(H2O). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:523–8.
Vagvolgyi V, Daniel LM, Pinto C, Kristof J, Frost RL, Horvath E. Dynamic and controlled rate thermal analysis of attapulgite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:589–94.
Vagvolgyi V, Frost RL, Hales M, Locke A, Kristof J, Horvath E. Controlled rate thermal analysis of hydromagnesite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:893–7.
Vagvolgyi V, Hales M, Martens W, Kristof J, Horvath E, Frost RL. Dynamic and controlled rate thermal analysis of hydrozincite and smithsonite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92:911–6.
Zhao Y, Frost RL, Vagvolgyi V, Waclawik ER, Kristof J, Horvath E. XRD, TEM and thermal analysis of yttrium doped boehmite nanofibres and nanosheets. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:219–26.
Kristof J, Frost RL, Kloprogge JT, Horvath E, Mako E. Detection of four different OH-groups in ground kaolinite with controlled-rate thermal analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2002;69:77–83.
Acknowledgements
The financial and infra-structure support of the Queensland University of Technology Inorganic Materials Research Program is gratefully acknowledged. The Australian Research Council (ARC) is thanked for funding the Thermal Analysis Facility. Financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China through Grant Nos: 40672085 and 40872089) is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Frost, R.L. & Cai, J. Desorption of benzoic and stearic acid adsorbed upon montmorillonites: a thermogravimetric study. J Therm Anal Calorim 99, 377–384 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0125-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0125-1