Abstract
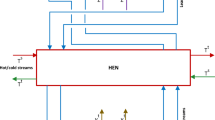
In this paper, a brief survey of hydrogen production methods is presented with a focus on S-I cycle. Based on heat duty data of sulfuric acid decomposition in S-I cycle, optimization models are developed to explore the minimum utility consumption and the minimum number of heat exchangers. Finally an optimal heat exchanger network for S-I thermochemical cycle is defined by a mixed integer optimization model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Energy Supply and Demand, Statistics Canada, Table 128-0009, Catalogue No: 57-003-x, 2007.
K. Tsunokawa and C. Hoban, Roads and Environment, A Handbook, The World Bank, Washington, D. G., 1997, p. 90.
Inventory of U. S. Greenhouse Gas Emission and Sinks: 1990–2006 (EPA 430-R-08-005), U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., 2008, p. ES–15.
Fuel Cell Vehicle World Survey 2003, Breakthrough Technologies Institute, Washington, D.C., 2004, pp. 55, 57, 82.
A. Tugnoli, G. Landucci and V. Cozzani, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 33 (2008) 4352.
Y. Z. Chen, Y. Z. Wang, H. Y. Xu and G. X. Xiong, Appl. Catal. B: Env., 80 (2008) 283.
J. Ivy, Summary of Electrolytic Hydrogen Production, Milestone Completion Report National Renewable Energy Laboratory, U.S. Department of Commence, Springfield VA, 2004, p. 8.
EN19 Efficiency of conventional thermal electricity production, European Environment Agency, 2007, p. 3.
J. S. Herring, J. E. O’Brien, C. M. Stoots, G. L. Hawkes, J. J. Hartvigsen and M. Shahnam, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 32 (2007) 441.
C. W. Forsberg, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 28 (2003) 1075.
S. Kasahara, S. Kubo, R. Hino, K. Onuki, M. Nomura and S. Nakao, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 32 (2007) 489.
B. Yidiz and M. S. Kazimi, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 31 (2006) 83.
P. M. Mathias, General Atomics and Sandia National Laboratories Modeling the Sulfur-Iodine, Aspen Plus Building Blocks and Simulation Models, AspenTech, Rev. 2, 2002, p. 4.
K. Schultz, Thermochemical Production of Hydrogen from Solar and Nuclear Energy, General Atomics, San Diego, 2003, pp. 7, 30.
B. Belaissaoui, R. Thery, X. M. Meyer, M. Meyer, V. Gerbaud and X. Joulia, Chem. Eng. Process., 47 (2008) 397.
L. C. Brown, G. E. Besenbruch, R. D. Lentsh, K. R. Schultz, J. F. Funk, P. S. Pickard, A. C. Marshall, S. K. Showalter, High Efficiency Generation of Hydrogen Fuels Using Nuclear Power, General Atomics, 2003, pp. iii, 3–7, 3–13, 3-, 3–16.
R. Turton, R. C. Bailie, W. B. Whiting and J. A. Shaeiwitz, Analysis Synthesis and Design of Chemical Processes, Second Edition, Prentice Hall PTR, New Jersey, 2007, pp. 464–477.
L. T. Biegler, I. E. Grossmann and A. W. Westerberg, Systematic Methods of Chemical Process Design, Prentice Hall PTR, New Jersey, 1997, pp. 527–566.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Kantor, I., Elkamel, A. et al. Optimal synthesis of heat exchanger network for thermochemical S-I cycle. J Therm Anal Calorim 96, 27–33 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9834-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9834-0