Abstract
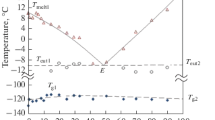
To reveal the denaturation mechanism of lysozyme by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), thermal stability of lysozyme and its preferential solvation by DMSO in binary solutions of water and DMSO was studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and using densities of ternary solutions of water (1), DMSO (2) and lysozyme (3) at 298.15 K. A significant endothermic peak was observed in binary solutions of water and DMSO except for a solution with a mole fraction of DMSO (x 2) of 0.4. As x 2 was increased, the thermal denaturation temperature T m decreased, but significant increases in changes in enthalpy and heat capacity for denaturation, ΔH cal and ΔC p, were observed at low x 2 before decreasing. The obtained amount of preferential solvation of lysozyme by DMSO (∂g 2/∂g 3) was about 0.09 g g−1 at low x 2, indicating that DMSO molecules preferentially solvate lysozyme at low x 2. In solutions with high x 2, the amount of preferential solvation (∂g 2/∂g 3) decreased to negative values when lysozyme was denatured. These results indicated that DMSO molecules do not interact directly with lysozyme as denaturants such as guanidine hydrochloride and urea do. The DMSO molecules interact indirectly with lysozyme leading to denaturation, probably due to a strong interaction between water and DMSO molecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Jozwiak, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 93 (2008) 701.
B. Marongiu, A. Piras, S. Porcedda and E. Tuveri, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 90 (2007) 909.
F. Franks and D. Eagland, CRC Critical Reviews in Biochemistry, 3 (1975) 165.
H. Uedaira and H. Uedaira, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 53 (1980) 2451.
C. F. Lau, P. T. Wilson and D. V. Fenby, Aust. J. Chem., 23 (1970) 1143.
J. M. G. Cowie and P. M. Toporowski, Can. J. Chem., 39 (1961) 2240.
R. N. Havemeyer, J. Pharm. Sci., 55 (1966) 851.
H. K. Schachman and M. A. Lauffer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 71 (1949) 536.
E. F. Casassa and H. Eisenberg, Adv. Protein Chem., 19 (1964) 287.
S. N. Timasheff, J. C. Lee, E. P. Pittz and N. Tweedy, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 55 (1976) 658.
S. N. Timasheff, Acc. Chem. Res., 3 (1970) 62.
J. C. Lee and S. N. Timasheff, Biochemistry, 13 (1974) 257.
V. Prakash, C. Loucheux, S. Scheufele, M. J. Gorbunoff, and S. N. Timasheff, Arc. Biol. Biophys., 210 (1981) 455.
S. E. Radford, C. M. Dobson and P. A. Evans, Nature, 358 (1992) 302.
W. Pfeil and P. L. Privalov, Biophys. Chem., 4 (1976) 23.
A. Zielenkiewicz and W. Zielenkiewicz, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 90 (2007) 941.
T. Kamiyama, T. Matsusita and T. Kimura, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 48 (2003) 1301.
T. Kamiyama, M. Morita and T. Kimura, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 49 (2004) 1350.
T. Kamiyama, M. Morita and T. Kimura, J. Solution Chem., 37 (2008) 27.
H. Johannesson, V. P. Denisov and B. Halle, Protein Sci., 6 (1997) 1756.
S. C. Mande and M. E. Sbhia, Protein Eng., 13 (2000) 133.
M. S. Lehmann and R. F. D. Stansfield, Biochemistry, 28 (1989) 7028.
J. M. Sturtevant, Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem., 38 (1987) 463.
S. Kidokoro, Comprehensive Handbook of Calorimetry and Thermal Analysis, Wiley (2004) p. 200.
K. Gekko and H. Noguchi, J. Phys. Chem., 83 (1979) 2706.
S. N. Timasheff, Protein-Solvent Interactions, R. B. Gregory, Ed., Marcel Dekker, 1995, p. 445.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamiyama, T., Liu, H.L. & Kimura, T. Preferential solvation of lysozyme by dimethyl sulfoxide in binary solutions of water and dimethyl sulfoxide. J Therm Anal Calorim 95, 353–359 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9232-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-008-9232-7