Abstract
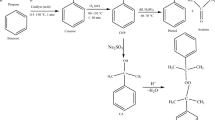
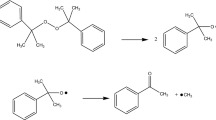
Organic peroxides have caused many serious explosions and fires that were promoted by thermal instability, chemical pollutants, and even mechanical shock. Cumene hydroperoxide (CHP) has been employed in polymerization and for producing phenol and dicumyl peroxide (DCPO). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) has been used to assess the thermal hazards associated with CHP contacting sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Thermokinetic parameters, such as exothermic onset temperature (T 0), peak temperature (T max), and enthalpy (ΔH) were obtained. Experimental data were obtained using DSC and curve fitting using thermal safety software (TSS) was employed to obtain the kinetic parameters. Isothermal microcalorimetry (thermal activity monitor, TAM) was used to investigate the thermal hazards associated with storing of CHP and CHP mixed with NaOH under isothermal conditions.
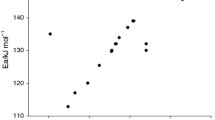
TAM showed that in the temperature range from 70 to 90°C an autocatalytic reaction occurs. This was apparent in the thermal curves. Depending on the operating conditions, NaOH may be one of the chemicals or catalysts incompatible with CHP. When CHP was mixed with NaOH, the T 0 is lower and reactions become more complex than those associated with assessment of the decomposition of the pure peroxide. The data by curve fitting indicated that the activation energy (E a) for the induced decomposition is smaller than that for decomposition of CHP in the absence of hydroxide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. W. Wang, C. M. Shu, Y. S. Duh and C. S. Kao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 40 (2001) 1125.
H. Y. Hou, Y. S. Duh, W. H. Lin and C. M. Shu, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 85 (2006) 145.
H. Y. Hou, C. M. Shu and Y. S. Duh, AIChE J., 47 (2001) 1893.
Y. S. Duh, C. S. Kao, C. Lee and S. W. Yu, Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng., 75 (1997) 73.
T. Ando, Y. Fujumeta and S. Morisaki, Safety Document of the Japan Research Institute of Industrial Safety, 1987, RIIS-SD-87.
Y. S. Duh, C. C. Hsu, C. S. Kao and S. W. Yu, Thermochim. Acta, 285 (1996) 67.
United Nations, Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, 14th Revised Ed., 205 (2005) USA.
NFPA 43B, National Fire Protection Association, Quincy, MA, USA.
R. A. Porob, S. Z. Khan, S. C. Mojumdar and V. M. S. Verenkar, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 605.
M. Day, A. V. Nawaby and X. Liao, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 623.
K. L. Singfield and N. B. Djogbenou, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 631.
D. Fessas, M. Signorelli and A. Schiraldi, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 82 (2005) 691.
C. C. Liao, S. H. Wu, T. S. Su, M. L. Shyu and C. M. Shu, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 85 (2006) 65.
The Isothermal Calorimetric Manual for Thermometric AB, Jarfalla, Sweden 1998.
A. Kossoy and T. Hofelich, Process Saf. Prog., 22 (2003) 235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, Y.P., Huang, J.Y., Tseng, J.M. et al. Reaction hazard analysis for the thermal decomposition of cumene hydroperoxide in the presence of sodium hydroxide. J Therm Anal Calorim 93, 275–280 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8833-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8833-x