Abstract
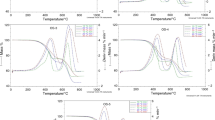
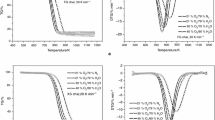
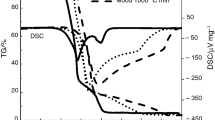
Oil shale semicoke, formed in retort furnaces, is a source of severe environmental pollution and is classified as a dangerous solid waste. For the industrial application of oil shale semicoke in combustion, this present work focused on the thermal analysis of its combustion characteristics. The pyrolysis and combustion experiments of semicoke were conducted in a Pyris thermogravimetric analyzer. From the comparison of pyrolysis curves with combustion curves, the ignition mechanism of semicoke samples prepared at different carbonization temperatures was deduced, and was found to be homogeneous for semicoke samples obtained at lower carbonization temperature, shifting to heterogeneous with an increase in the carbonization temperature. The effect of carbonization temperatures and heating rates on the combustion process was studied as well. At last, combustion kinetic parameters of semicoke were calculated with the binary linear regression method, showing that activation energy will increase with increasing the heating rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Y. Wang, Energy of China, Beijing, Metallurgical Industry Press, 1988, pp. 171–172. (in Chinese).
A. Trikkel, R. Kuusik and N. Maljukova, Oil Shale, 21 (2004) 227.
A. Paist, Oil Shale, 21 (2004) 181.
X. M. Jiang, D. C. Liu, H. P. Chen, C. G. Zheng and Y. K. Qin, Oil Shale, 18 (2001) 73.
J. O. Jaber and S. D. Probert, Appl. Energy, 58 (1997) 161.
X. M. Jiang, X. X. Han and Z. G. Cui, Energy, 32 (2007) 772.
M. V. Kök and A. G. Iscan, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 88 (2007) 657.
S. Yağmur and T. Durusoy, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 479.
X. M. Jiang, X. X. Han and Z. G. Cui, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 457.
A. Arenillas, F. Rubiera, B. Arias, J. J. Pis, J. M. Faundez, A. L. Gordon and X. A. Garcia, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 76 (2004) 603.
X. Y. Du, C. Gopalakrishnan and K. Annamalai, Fuel, 74 (1995) 487.
X. Y. Du and K. Annamalai, Combust. Flame, 97 (1994) 330.
T. F. Wall, D. Phong-Anant, V. S. Gururajan, L. J. Wibberley, A. Tate and J. Lucas, Combust. Flame, 72 (1988) 111.
X. X. Han, X. M. Jiang and Z. G. Cui, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 84 (2006) 631.
Q. Y. Zhu, G. B. Zhao, G. J. Ruan, Y. K. Qin and J. J. Tu, J. Eng. Therm. Power, 12 (1997) 332 (in Chinese, with English Abstract).
M. V. Kök, G. Pokol, C. Keskin, J. Madarász and S. Bagci, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 76 (2004) 247.
J. P. Vantelon, C. Breillat, F. Gaboriaud and A. Alaoui-Sosse, Fuel, 69 (1990) 211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X.X., Jiang, X.M. & Cui, Z.G. Study of the combustion mechanism of oil shale semicoke in a thermogravimetric analyzer. J Therm Anal Calorim 92, 595–600 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8659-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8659-6