Abstract
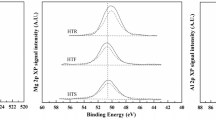
Hydrotalcites containing carbonate, vanadate and molybdate were prepared by coprecipitation. The resulting materials were characterized by XRD, and TG/DTA to determine the stability of the hydrotalcites synthesized. The thermal decomposition of carbonate hydrotalcites consist of two decomposition steps between 300 and 400°C, attributed to the simultaneous dehydroxylation and decarbonation of the hydrotalcite lattice. Water loss ascribed to dehydroxylation occurs in two decomposition steps, where the first step is due to the partial dehydroxylation of the lattice, while the second step is due to the loss of water interacting with the interlayer anions. Dehydroxylation results in the collapse of the hydrotalcite structure to that of its corresponding metal oxides, including MgO, Al2O3, MgAl2O4, NaMg4(VO4)3 and Na2Mg4(MoO4)5. The presence of oxy-anions proved to be beneficial in the stability of the hydrotalcite structure, shown by the delay in dehydroxylation of oxy-anion containing hydrotalcites compared to the carbonate hydrotalcite. This is due to the substantial amount of hydroxyl groups involved in a network of hydrogen bonds involving the intercalated anions. Therefore, the stability of the hydrotalcite structure appears to be dependent on the type of anion present in the interlayer. The order of thermal stability for the synthesized hydrotalcites in this study is Syn-HT-V>Syn-HT-Mo> Syn-HT-CO3-V>Syn-HT-CO3-Mo>Syn-HT-CO3. Carbonate containing hydrotalcites prove to be less stable than oxy-anion only hydrotalcites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. L. Frost, W. Martens, Z. Ding, J. T. Kloprogge and T. E. Johnson, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A: Molecular Biomolecular Spectrosc., 59A (2003) 291.
R. L. Frost, Z. Ding, W. N. Martens, T. E. Johnson and J. T. Kloprogge, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A: Molecular Biomolecular Spectrosc., 59A (2003) 321.
J. T. Kloprogge and R. L. Frost, J. Solid State Chem., 146 (1999) 506.
R. L. Frost, J. Kristóf, E. Horváth and J. T. Kloprogge, J. Raman Spectrosc., 32 (2001) 873.
J. M. Bouzaid, R. L. Frost, A. W. Musumeci and W. N. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 745.
R. L. Frost and Z. Ding, Thermochim. Acta, 405 (2003) 207.
R. L. Frost and K. L. Erickson, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 76 (2004) 217.
R. L. Frost and K. L. Erickson, Thermochim. Acta, 421 (2004) 51.
R. L. Frost, W. Martens and M. O. Adebajo, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 81 (2005) 351.
R. L. Frost, W. Martens, Z. Ding and J. T. Kloprogge, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 71 (2003) 429.
R. L. Frost, A. W. Musumeci, T. Bostrom, M. O. Adebajo, M. L. Weier and W. Martens, Thermochim. Acta, 429 (2005) 179.
R. L. Frost, A. W. Musumeci, J. T. Kloprogge, M. L. Weier, M. O. Adebajo and W. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 205.
Y.-H. Lin, M. O. Adebajo, R. L. Frost and J. T. Kloprogge, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 81 (2005) 83.
H. C. B. Hansen and C. B. Koch, Appl. Clay Sci., 10 (1995) 5.
E. Horváth, J. Kristóf, R. L. Frost, N. Heider and V. Vágvölgyi, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 78 (2004) 687.
R. L. Frost, M. L. Weier and K. L. Erickson, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 76 (2004) 1025.
R. L. Frost and K. L. Erickson, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 78 (2004) 367.
E. Horváth, J. Kristóf, R. L. Frost, A. Redey, V. Vágvölgyi and T. Cseh, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 71 (2003) 707.
J. Kristóf, R. L. Frost, J. T. Kloprogge, E. Horváth and E. Makó, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 69 (2002) 77.
F. Rey, V. Fornes and J. M. Rojo, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 88 (1992) 2233.
M. Valcheva-Traykova, N. Davidova and A. Weiss, J. Mater. Sci., 28 (1993) 2157.
G. Lichti and J. Mulcahy, Chem. Australia, 65 (1998) 10.
Y. Seida and Y. Nakano, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 34 (2001) 906.
Y. Roh, S. Y. Lee, M. P. Elless and J. E. Foss, Clays Clay Miner., 48 (2000) 266.
Y. Seida, Y. Nakano and Y. Nakamura, Water Res., 35 (2001) 2341.
J. T. Kloprogge, D. Wharton, L. Hickey and R. L. Frost, Am. Mineral., 87 (2002) 623.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palmer, S.J., Frost, R.L. & Nguyen, T. Thermal decomposition of hydrotalcite with molybdate and vanadate anions in the interlayer. J Therm Anal Calorim 92, 879–886 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8642-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8642-2