Abstract
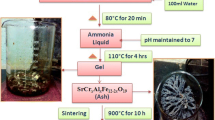
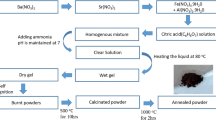
The nickel and cobalt substituted strontium aluminum hexaferrite Sr1-xNixAl2Fe10O19/Sr1-xCoxAl2Fe10O19 (x = 0.1, 0.2) were synthesized via the sol-gel auto-combustion technique using glycine fuel. The particles formed in the hexagonal crystal structure with space group P63/mmc. The crystallite size of the sample varied in the range of 49–58 nm. The field-emission scanning microscopy was adopted for morphological analysis, and the images revealed the plate-like formation of the particles. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirmed the presence and oxidation states of all the elements. The variation of magnetic parameters as magnetic saturation (33.96–41.54 emu/gm), coercivity (3681–7647 Oe), squareness ratio (0.6), and energy product values (0.23–0.40 MGOe) were studied through vibrating sample magnetometer. The electric studies disclosed the presence of relaxations in the system, which was interpreted through Koop and Maxwell-Wagner’s model. The synthesized samples are potential candidates for permanent magnet and magnetic recording media applications owing their remarkable magnetic properties.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
-
Conventional and economical sol-gel auto-combustion method was adopted for the synthesis procedure.
-
Double site substitution was performed to investigate the effect on magnetic and dielectric properties.
-
Substitution of Ni yielded a notable energy product value (BHmax) of 3.18 kJ/m3.
-
High dielectric constant values suggest sample’s potential application in microwave frequency range.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liaquat A, Anis-ur-Rehman M, ul Haq A (2020) Impact of Gd doping on the dielectric and magnetic properties of (Sr–Ba) Fe12O19 nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 822:153561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153561
Kumar A, Verma MK, Singh S et al. (2020) Electrical, magnetic and dielectric properties of cobalt-doped barium hexaferrite BaFe12−xCoxO19 (x = 0.0, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2) ceramic prepared via a chemical route. J Electron Mater 49:6436–6447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08364-8
Rehman MR, Akram MA, Gul IH (2022) Improved electrical properties of strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles by Co2+ substitutions. ACS Omega 7:43432–43439. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c03256
Chen N, Yang K, Gu M (2010) Microwave absorption properties of La-substituted M-type strontium ferrites. J Alloy Compd 490:609–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.10.116
Pullar RC (2012) Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog Mater Sci 57:1191–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.04.001
Vinnik DA, Trukhanov AV, Podgornov FV et al. (2020) Correlation between entropy state, crystal structure, magnetic and electrical properties in M-type Ba-hexaferrites. J Eur Ceram Soc 40:4022–4028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.04.036
VE Zhivulin, OV Zaitseva, EA Trofimovo, et al (2021) Anisotropy of the electrical properties of a single crystal of BaFe11.25Ti0.75O19 M-type barium hexaferrite. J Solid State Chem 298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122104
Buzinaro MAP, Macêdo MA, Costa BFO, Ferreira NS (2019) Disorder of Fe(2)O5 bipyramids and spin-phonon coupling in SrFe 12 O 19 nanoparticles. Ceram Int 45:13571–13574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.214
Saafan SA, Assar ST, Mansour SF (2012) Magnetic and electrical properties of Co1-xCaxFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by the auto combustion method. J Alloy Compd 542:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.07.050
Kishor G, Bhowmik RN, Sinha AK (2022) Structural phase stabilization via Ba site doping with bivalent Sr, Ca and Zn ions and Fe site doping with trivalent Cr and Ga ions in the BaFe12O19 hexaferrite and its magnetic modification. CrystEngComm 24:5269–5288. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ce00583b
G Han, R Sui, Y Yu, et al (2021) Structure and magnetic properties of the porous Al-substituted barium hexaferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 528:1–7.
Trusov LA, Gorbachev EA, Lebedev VA et al. (2018) Ca-Al double-substituted strontium hexaferrites with giant coercivity. Chem Commun 54:479–482. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc08675j
XM Ma, J Liu, SZ Zhu, HG Shi (2016) Tuning of magnetic properties of aluminium-doped strontium hexaferrite powders. Chin Phys B 25: https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/25/12/126102
Irshad Z, Bibi I, Ghafoor A et al. (2022) Results in physics Ni doped SrFe12O19 nanoparticles synthesized via micro-emulsion route and photocatalytic activity evaluation for the degradation of crystal violet under visible light irradiation. Results Phys 42:106006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2022.106006
V Dixit, SG Kim, J Park, YK Hong (2017) Effect of ionic substitutions on the magnetic properties of strontium hexaferrite: a first principles study. AIP Adv 7. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995309
Alna’washi GA, Alsmadi AM, Bsoul I et al. (2021) Investigation on X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, structural and low temperature magnetic properties of Ni-Ti co-substituted M-type strontium hexaferrites prepared by ball milling technique. Results Phys 28:104574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104574
Godara SK, Singh M, Kaur V et al. (2021) Effect of calcium solubility on structural, microstructural and magnetic properties of M-type barium hexaferrite. Ceram Int 47:20399–20406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.048
Godara SK, Kaur V, Narang SB et al. (2021) Tailoring the magnetic properties of M-type strontium ferrite with synergistic effect of co- substitution and calcinations temperature. J Asian Ceram Soc 9:686–698. https://doi.org/10.1080/21870764.2021.1911059
Sharma A, Jasrotia R, Kumari N et al. (2022) Tailoring the structural and magnetic traits of copper modified BaFe12O19 nanostructured hexaferrites for recording media application. J Magn Magn Mater 564:170124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.170124
R Jasrotia, N Kumari, R Verma, et al. (2023) Effect of rare earth (Nd3+) metal doping on structural, morphological, optical and magnetic traits of Zn–Mg nano-ferrites. J Rare Earths https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2022.08.015
Godara SK, Kaur V, Chuchra K et al. (2021) Impact of Zn2+-Zr4+ substitution on M-type Barium Strontium Hexaferrite’s structural, surface morphology, dielectric and magnetic properties. Results Phys 22:103892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.103892
Godara SK, Kaur V, Narang SB et al. (2019) Tunable M-type nano barium hexaferrite material by Zn2+/Zr4+ co-doping. Mater Res Express 6:116111
Kumar S, Kaur T, Kumar S, Srivastava AK (2015) Effect of heat treatment on properties of Sr0.7Nd0.3Co0.3Fe11.7O19. J Supercond Nov Magn 28:2935–2940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3105-7
Godara SK, Dhaka RK, Kaur N et al. (2021) Synthesis and characterization of Jamun pulp-based M-type barium hexaferrite via sol–gel auto-combustion. Results Phys 22:103903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.103903
Zahid M, Siddique S, Anum R et al. (2021) M-type barium hexaferrite-based nanocomposites for EMI shielding application: a review. J Supercond Nov Magn 34:1019–1045
Joshi H, Kumar AR (2022) Investigations and correlations of structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of M-type barium hexaferrite (BaFe12O19) for hard magnet applications. J Supercond Nov Magn 35:2435–2451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06203-x
Yang Y, Wang F, Shao J et al. (2019) Structural, spectral, magnetic, and electrical properties of Gd–Co-co-substituted M-type Ca–Sr hexaferrites synthesized by the ceramic method. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 125:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2339-1
Rashad MM, Rasly M, El-Sayed HM et al. (2013) Controlling the composition and the magnetic properties of hexagonal Co2Z ferrite powders synthesized using two different methods. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 112:963–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7456-7
SK Godara, M Singh, V Kaur, et al (2022) Effect of calcium solubility on structural, microstructure and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19. Phys B Condens Matter 628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2021.413560.
Gupta A, Kar M, Roy PK (2022) Substitutional effect of Ni-Al in electromagnetic properties of Sr-hexaferrite based non-rare earth magnet with high energy density for motor applications. Mater Chem Phys 292:126842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126842
Verma S, Singh A, Sharma S et al. (2023) Magnetic and structural analysis of BaZnxZrxFe12–2xO19 (x = 0.1–0.7) hexaferrite samples for magnetic applications. J Alloy Compd 930:167410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167410
Mehmood S, Anis-ur-Rehman M (2020) Association of structural strains and dielectric relaxation in Co-doped Sr-Hexaferrites. Phys B Condens Matter 582:412003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.412003
Gupta A, Roy PK (2021) Synthesis and tuning the electro-magnetic properties of Co-Cr substituted Sr-hexaferrite towards diverse usages. Mater Sci Eng B Solid State Mater Adv Technol 263:114815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114815
Sriramulu G, Maramu N, Reddy BR et al. (2022) Structural, magnetic and electromagnetic properties of microwave-hydrothermally synthesized Sr(Zr-Mn)2xFe12-2xO19 hexaferrites. Mater Res Bull 149:111732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2022.111732
S Thakur, B Raina, KK Bamzai (2022) Investigations on structural, spectroscopic and magnetic properties of yttrium barium orthoferrite and nickel doped strontium hexaferrite composites. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05399-y
T Yener, İ Araz, A Kırsoy, et al (2022) Electromagnetic properties in the structure of cerium-copper substituted barium hexaferrite. J Mol Struct 1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133752
VE Zhivulin, EA Trofimov, OV Zaitseva, et al (2022) Effect of configurational entropy on phase formation, structure, and magnetic properties of deeply substituted strontium hexaferrites. Ceram Int https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.082
Tang R, Jiang C, Qian W et al. (2015) Dielectric relaxation, resonance and scaling behaviors in Sr3Co2Fe24O41 hexaferrite. Sci Rep. 5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13645
Rusevich LL, Kotomin EA, Zvejnieks G et al. (2022) Effects of Al Doping on Hydrogen Production Efficiency upon Photostimulated Water Splitting on SrTiO3Nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 126:21223–21233. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c05993
Anantharamaiah PN, Shashanka HM, Srinivasan S et al. (2022) Structural, magnetic, and magnetostriction properties of flexible, nanocrystalline CoFe2O4 films made by chemical processing. ACS Omega 7:43813–43819. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c04943
Joshi H, Kumar AR (2021) Scrutiny and correlations of structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of M-type strontium hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) for permanent magnet applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32:4331–4346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05176-8
Dagar S, Hooda A, Khasa S, Malik M (2020) Structural refinement, investigation of dielectric and magnetic properties of NBT doped BaFe12O19 novel composite system. J Alloy Compd 826:154214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154214
Pandey R, Kumar Pradhan L, Kumari S et al. (2020) Surface magnetic interactions between Bi0.85La0.15FeO3 and BaFe12O19 nanomaterials in (1-x)Bi0.85La0.15FeO3-(x)BaFe12O19 nanocomposites. J Magn Magn Mater 508:166862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166862
Basha DB, Kumar NS, Kumar GR, et al (2022) Structural, electrical, and magnetic properties of nano Sr1-XLaXFe12O19 (X = 0. 2 - 0. 8)
Z Li, V Koval, A Mahajan, et al (2020) Room-temperature multiferroic behavior in layer-structured Aurivillius phase ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 117. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0017781
A Hilczer, K Pasińska (2022) Dielectric response of Sr0.95Nd0.05Fe12-xScxO19 hexaferrites nanoceramics as dependent on crystal and microstructure and ceramic heterogeneity. J Alloys Compd 893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162303
MR Rehman, MA Akram, IH Gul (2022) Improved electrical properties of strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles by Co2+ substitutions. ACS Omega https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c03256
Khadhraoui S, Triki A, Hcini S et al. (2014) Variable-range-hopping conduction and dielectric relaxation in Pr 0.6Sr0.4Mn0.6Ti0.4O 3±δ perovskite. J Magn Magn Mater 371:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.07.044
Rahmouni H, Smari M, Cherif B et al. (2015) Conduction mechanism, impedance spectroscopic investigation and dielectric behavior of La0.5Ca0.5-xAgxMnO3 manganites with compositions below the concentration limit of silver solubility in perovskites (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.2). Dalton Trans 44:10457–10466. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5dt00444f
Lobo LS, Kalainathan S, Kumar AR (2015) Investigation of electrical studies of spinel FeCo2O4 synthesized by sol-gel method. Superlattices Microstruct 88:116–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2015.09.010
Thansanga L, Shukla A, Kumar N, Choudhary RNP (2020) Study of effect of Dy substitution on structural, dielectric, impedance and magnetic properties of bismuth ferrite. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31:10006–10017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03545-x
Tanwar K, Gyan DS, Gupta P et al. (2018) Investigation of crystal structure, microstructure and low temperature magnetic behavior of Ce4+ and Zn2+ co-doped barium hexaferrites (BaFe12O19). RSC Adv 8:19600–19609. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA02455C
Almessiere MA, Unal B, Slimani Y et al. (2019) Results in physics electrical and dielectric properties of Nb 3 + ions substituted Ba-hexaferrites. Results Phys 14:102468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102468
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge VIT management for the facilities provided for this work. The authors also would like to convey their gratefulness to all the lab members.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, and investigation, Writing—original draft preparation: HJ; Writing—review and editing, Supervision: ARK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, H., Ruban Kumar, A. Effect of Ni2+and Co2+ substitution on the characteristics of the strontium aluminum hexaferrite (SrAl2Fe10O19). J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 109, 32–55 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06245-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06245-0