Abstract
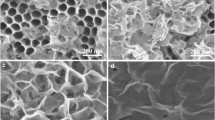
Semiconductor nano photocatalysis has considered a promising methodology for polluted water remediation. The electrons and holes’ high recombination rate and low reaction rate have obstructed their large-scale applications. Thus, heterogeneous nano photocatalysts are needed for promoting their practical applications. Herein, anatase nanoparticles (ANPs) are synthesized and heat-treated within two-time intervals of 1 h and 2 h at 300 °C by sol-gel method and doped with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) at room temperature (29 °C) owing to photocatalytic application. Vapor pressure scanning electron microscopy (VPSEM) shows the porous and granular localized homogeneous surface of Au-ANPs before and after heat treatment. The average nanoparticles diameter is calculated as 4.7 nm and after 2 h heat treatment it increased up to 4.9 nm. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method show that the Au-ANPs possessed low average surface roughness (Ra) ~ 3 nm, large surface area (SA) ~ 288 m2/g, and pore size distribution (PSD) 1.81 nm, respectively. Whereas Au-ANPs/2 h revealed Ra around 5 nm, SA ~ 145 m2/g, and PSD ~ 2.37 nm. All three nano photocatalysts exhibited thermal stability at ≤400 °C by thermogravimetric analysis. The Au-ANPs/2 h exhibited high photocatalytic activity with degradation of PR dye of 94% (k = 0.01 min−1, under ultraviolet radiation) after 280 min of reaction.

Graphical abstract
Highlight
-
Anatase nanoparticles (ANPs) doped with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) at room temperature owing to photocatalytic application.
-
Microscopic analysis shows the porous and granular localized homogeneous surface of nanocatalysts.
-
Thermally stable Au-ANPs/2h revealed roughness around 5 nm, surface area ~145 m2/g, and pore size distribution ~ 2.37 nm.
-
All three heterogeneous nano photocatalysts exhibited thermal stability at ≤400 °C.
-
The Au-ANPs/2h is exhibited high photocatalytic activity 94% and a rate constant 0.01 min−1.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oviedo LR, Muraro PCL, Pavoski G, Espinosa DCR, Ruiz YPM, Galembeck A, Rhoden CRB, da Silva WL (2022) Synthesis and characterization of nanozeolite from (agro)industrial waste for application in heterogeneous photocatalysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:3794–3807
Ribas LN, Bulhoes LOS, da Silva WL (2020) Study of the photocatalytic activity using silica-based materials doped with silver nanoparticles for degradation of rhodamine B dye. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:191
da Silva WL, Hamilton JWJ, Sharma PK, Dunlop PSM, Byrne JA, dos Santos JHZ (2021) Agro and industrial residues: Potential raw materials for photocatalyst development. J Photochemistry Photobiol, A: Chem 411:113184
Compagnoni M, Villa A, Bahdori E, Morgan DJ, Prati L, Dimitratos N, Rossetti I, Ramis G (2018) Surface probing by spectroscopy on titania-supported gold nanoparticles for a photoreductive application. Catalysts 8:623
da Silva WL, dos Santos JHZ (2017) Ecotechnological strategies in the development of alternative photocatalysts Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable. Chemistry 6:63–68
Hezam M, Qaid SMH, Bedja IM, Alharbi F, Nazeeruddin MK, Aldwayyan A (2019) Synthesis of pure brookite nanorods in a nonaqueous growth environment. Crystals 9:562
Wang J, Yang J, Hu J, Fu Y, Ye M (2020) D. Metal organic framework derivative-TiO2 composite as efficient and durable photocatalyst for the degradation of toluene. Appl Catal B 267:118667
Padikkaparambil S, Narayanan B, Yaakob Z, Viswanathan S, Tasirin SM (2013) Au/TiO2 reusable photocatalysts for dye degradation. Int J Photoenergy 752605:10. Article ID
Zhou M, Zhang J, Cheng B, Yu H (2012) Enhancement of visible-light photocatalytic activity of mesoporous Au–TiO2 nanocomposites by surface plasmon resonance. Int J Photoenergy 532843:10 pages.
Choudhary BC, Paul D, Gupta T, Tetgure SR, Garole VJ, Borse AU, Garole DJ (2017) Photocatalytic reduction of organic pollutant under visible light by green route synthesized gold nanoparticles. J Environ Sci 55:236–246
Ahmad A, Wei Y, Syed F, Imran M, Khan ZUH, Tahir K (2015) Size dependent catalytic activities of green synthesized gold nanoparticles and electro-catalytic oxidation of catechol on gold nanoparticles modified electrode. RSC Adv 5:99364–99377
Islam MT, Jing H, Yang T, Zubia E, Goos AG, Bernal RA, Botez CE, Narayan M, Chan C, Noveron JC (2018) Fullerene stabilized gold nanoparticles supported on titanium dioxide for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Environ Chem Eng 6(4):3827–3836
Alshoaibi A, Islam S (2021) Thermally stable ZnO doped SiO2-TiO2 nanocomposite based Opto-chemical sensor. Mater Chem Phys 267:124687
Islam S, Rahman RA, Othaman Z, Riaz S, Saeed MA, Naseem S (2013) Preparation, and characterization of crack-free sol–gel based SiO2–TiO2 hybrid nanoparticle film. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 68:162–168
Nguyen VN, Nguyen MV, Nguyen THT, Doan MT, Ngoc LLT, Janssens E, Yadav A, Lin Pin-C, Nguyen MS, Hoang NH (2020) Surface-modified titanium dioxide nanofibers with gold nanoparticles for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. Catalysts 10:261
Oliveira GV, da Silva WL, de Oliveira ER, Lansarin MA, dos Santos JHZ (2016) Foundry sands as supports for heterogeneous photocatalysts. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:373
Figueiredo VM, Lourenço JB, de Vasconcellos NJS, da Silva WL (2020) Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of activated charcoal from microalgae for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye. Ceramica 66:367–372
Ghorbani V, Dorranian D (2016) Properties of TiO2/Au nanocomposite produced by pulsed laser irradiation of mixture of individual colloids. Appl Phys A 122:1019
Islam S, Bakhtiar H, Aziz M, Riaz S, Naseem S (2021) Effect of pH on phenolphthalein immobilized gold nanoparticles/nanostructures for pH sensing evaluations: sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 100:192–204
Islam S, Bakhtiar H, Aziz M, Riaz S, Naseem S (2019) Mesoporous anatase based opto-chemical sensor. Mater Sci Semiconductor Process 100:236–244
Muraro PCL, Mortari SR, Vizzotto BS, chuy G, Santos CD, Brum LFW, da Silva WL (2020) iron oxide nanocatalyst with titanium and silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity on the degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Sci Rep 10:3055
Islam S, Bidin N, Riaz S, Rahman AR, Naseem S, Marsin MF (2015) Mesoporous SiO2-TiO2 nanocomposite for pH sensing. Se5ns Actuators B 221:993–1002
Mahlambi MM, Mishra AK, Mishra SB, Krause RW, Mamba BB, Raichur AM, Calorim TA (2012) Comparison Rhodamine B Degrad UV Irradiat Two Phases Titania Nano-Photocatal 110:847–855
Islam S, Aziz MS, Bakhtiar H, Alshoaibi A, Harun SW, Riaz S, Naseem S (2021) Optically functionalized hierarchical hematite assembled silica-titania nanocomposites for hydrocarbon detection: Fiber optic chemical sensor. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 326:111398
da Costa ML, Pavoski G, Espinosa DCR, de Vasconcellos NJS, da Silva WL (2022) Potential application of alternative materials for organic pollutant removal. Water Air Soil Pollut 233:65
Rehman G, Tahir M, Goh PS, Ismail AF, Khan IU (2019) Controlled synthesis of reduced graphene oxide supported magnetically separable Fe3O4@rGO@AgI ternary nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of phenol. Powder Technol 356:547–558
Ros M-C, Socaci C, F-Avram V, Borodi G, Pogacean F, Coros M, Magerus L, Pruneanu S (2016) Photocatalytic performance of graphene/TiO2-Ag composites on amaranth dye degradation. Mater Chem Phys 179(15):232–241
Wu XQ, Shao ZD, Liu Q, Xie Z, Zhao F, Zheng YM (2019) Flexible and porous TiO2/SiO2/carbon composite electrospun nanofiber mat with enhanced interfacial charge separation for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 553:156–166
Rohani N, Bamoharram FF, Marijani A, Heravi MM (2017) Gold nanoparticles Wells-Dawson heteropolyacid nanocomposite film as an effective nanocatalyst in photocatalytic removal of azo dyes from wastewaters. J Nanostruct Chem 7:171–178
An L, Wang G, Cheng Y (2015) Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of visible-light-driven TiO2/Bi2O3 nanocomposite photocatalysts: characterization, properties and azo dye removal application. Res Chem Intermed 41:7449–7461
Ayati A, Ahmadpour A, Bamoharram FF, Tanhaei B, Manttari M, Lahtinen M, Sillanpaa M (2014) Novel Au NPs/Preyssler Acid/TiO2 nanocomposite for the photocatalytic removal of Azo dye. Sep Purif Technol 133(8):415–420
Funding
This work was supported through the Annual Funding track by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia [Project No. 152].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshoaibi, A., Islam, S. Heating influence on atomic site structural changes of Mesoporous Au supported Anatase nanocomposite for photocatalytic progression. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 104, 225–238 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05892-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05892-z