Abstract
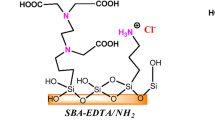
Herein we present silica (SiO2) and amino-functionalized SiO2 particles (NH2@SiO2) based on the Stöber method involving the reaction of hydrolysis and condensation of alkoxide precursors tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), 3- (trimethoxysilylpropyl) diethylenetriamine (DETA) and (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS) for specific and selective removal of heavy metal ions such as Lead (Pb2+), Chromium (Cr3+) and Mercury (Hg2+). The prepared SiO2 and NH2@SiO2 particles were characterized by Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), specific surface area (BET), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), zeta potential (ζ) measurements and potential titration measurements. We studied the adsorption efficiency toward heavy metal ions (Pb2+, Cr3+ and Hg2+) in model salt solutions. The adsorption process was evaluated in terms of adsorption efficiency, adsorption capacity, adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic parameters and desorption efficiency based on the result of the atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) measurements for Pb2+ and Cr3+ ions and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) measurements for Hg2+. The results showed the highest adsorption efficiency and capacity for heavy metal ions (Pb2+, Cr3+ and Hg2+) by NH2@SiO2 using APTMS. Furthermore, the adsorption efficiency was 99.3 % for Pb2+, 98.4 % in the case of Cr3+ ions and 88% for Hg2+. The adsorption process for Pb2+, Cr3+ and Hg2+ ions using non-functionalized SiO2 and NH2@SiO2 particles follows pseudo-second-order kinetics and is best described by the Langmuir adsorption model. The desorption results showed potential for reusing NH2@SiO2 particles with more than 91.8 % desorbed Pb2+ ions using 0.1 M HCl and 100% desorbed Hg2+ ions using 1.5 M C6H8O7.

Three alkoxide precursors (tetraethoxysilane (TEOS), 3-(trimethoxysilylpropyl), diethylenetriamine (DETA) and (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS)) were used in the one-pot synthesis of silica (SiO2) and amino-functionalized SiO2 (NH2@SiO2) particles. The prepared adsorbent materials were characterized and used for adsorption tests and desorption toward heavy metals ions (Pb2+, Cr3+ and Hg2+). Adsorption efficiency, adsorption capacity, adsorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic parameters were determined. Desorption efficiency was tested using 0.1 M HCl or 1.5 M C6H8O7.
Highlights
-
Silica (SiO2) particles and amino-functionalized SiO2 (NH2@SiO2) particles were synthesized and characterized.
-
APTMS precursor showed maximal adsorption efficiency.
-
Adsorption efficiency for Pb2+, Cr3+ and Hg2+ were 99.3%, 98.4%, and 88%, respectively.
-
Langmuir’s adsorption model describes the kinetics of pseudo-second-order for the adsorption process.
-
Desorption of 91.8% and 100% were achieved for Pb2+ and Hg2+ ions, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Community (2000) Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Parliament vol. L327, no. September 1996. pp. 1–82. https://doi.org/10.1039/ap9842100196
Gupta A, Singh MR (2017) Water Pollution-Sources,Effects and Control [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321289637
Enderlein U, Enderlein RE, Williams W (1997) Water Quality Requirements, Water Pollution Control - A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles. p. 29. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203477540
Verma R, Dwivedi P (2013) Heavy metal water pollution- A case study, Recent Res. Sci. Technol., vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 98–99, [Online]. Available: http://recent-science.com/
Gorito AM, Ribeiro AR, Almeida CMR, Silva AMT (2017) A review on the application of constructed wetlands for the removal of priority substances and contaminants of emerging concern listed in recently launched EU legislation. Environ Pollut 227:428–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.060
Escribano Francés G, Quevauviller P, San Martín González E, Vargas Amelin E (2017) Climate change policy and water resources in the EU and Spain. A closer look into the Water Framework Directive. Environ Sci Policy 69:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2016.12.006
The European Parlament and the Council of the European Union, (2013) Directives of 12 August 2013 amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Union. pp. 1–17, 2013, eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex:32013L0039
Kos Durjava M, Kolar B, Balk F, Peijnenburg W (2013) Water framework directive and specific pollutants in surface waters in Slovenia. Acta Hydrotechnica 45:61–69
Ministry of the Environment and Spatial Planning, “Rules on drinking water,” Slovenia, 2017. [Online]. Available: http://www.pisrs.si/Pis.web/pregledPredpisa?id=PRAV3713
Ministry of the Environment and Spatial Planning (2017) Decree on the discharge and treatment of urban wastewater. Slovenia. pp. 1–34
Official Journal of the European Union (2013) (Legislative acts) Directives, 2013/39/EU OF THE European Parliament and Of the Council of 12 August 2013 amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2013:226:0001:0017:EN:PDF
Arunakumara KKIU, Zhang X (2007) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and toxicity with special reference to microalgae J Ocean Univ China 7(no. 1):60–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0060-y
Diaz S, MartinGonzalez A, Gutierrez JC (2006) Evaluation of heavy metal acute toxicity and bioaccumulation in soil ciliated protozoa. Environ Int 32(no. 6):711–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.03.004
Mohamed K, Morad L, Al-blewi Fawzia F, Nadjet R, Reda AM, Messali M, Rachid T (2016) Liquid-liquid extraction of metal ions, DFT and TD-DFT analysis of some 1,2,4-triazole Schiff Bases with high selectivity for Pb(II) and Fe(II). J Mol Struct 1113:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.02.046
de Luna MDG, Bellotindos LM, Asiao RN, Lu MC (2015) Removal and recovery of lead in a fluidized-bed reactor by crystallization process. Hydrometallurgy 155:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.03.009
Bolto BA, Pawčpwski L (1987) Waste Water Treatment by Ion Exchange. New York: Chapman and Hall
Bauman M, Košak A, Lobnik A, Petrinić I, Luxbacher T (2013) Nanofiltration membranes modified with alkoxysilanes: Surface characterization using zeta-potential. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 422:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.01.005
Da’na E (2017) Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 247:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.03.050
Qu X, Alvarez PJJ, Li Q (2013) Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res. 47(no. 12):3931–3946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.058
Mende M, Schwarz D, Steinbach C, Boldt R, Schwarz S (2016) Simultaneous adsorption of heavy metal ions and anions from aqueous solutions on chitosan—Investigated by spectrophotometry and SEM-EDX analysis Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng Asp 510:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.08.033
Salem Attia TM, Hu XL, Yin DQ (2013) Synthesized magnetic nanoparticles coated zeolite for the adsorption of pharmaceutical compounds from aqueous solution using batch and column studies. Chemosphere 93(no. 9):2076–2085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.046
Burakova AE, Galunina EV, Burakovaa IV, Kucherovaa AE, Agarwalb S, Tkacheva AG, Gupta VK (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.034
Smith L, Ibn-Mohammed T, Koh SCL, Reaney IM (2018) Life cycle assessment and environmental profile evaluations of high volumetric efficiency capacitors. Appl Energy 220:496–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.03.067
Yong WYD, Zhang Z, Cristobal G, Chin WS (2014) One-pot synthesis of surface functionalized spherical silica particles. lloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 460:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.03.039
Viltužnik B, Lobnik A, Košak A (2015) The removal of Hg(II) ions from aqueous solutions by using thiol-functionalized cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol, 74(1):199–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3596-x
Amin MT, Alazba AA, Manzoor U (2014) A review of removal of pollutants from water/wastewater using different types of nanomaterials. vol. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/825910
Bogush GH, Tracy MA, Zukoski CF (1988) Preparation of monodisperse silica particles: Control of size and mass fraction. J Non Cryst Solids 104(no. 1):95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(88)90187-1
Singh LP, Bhattacharyya SK, Ahalawat S, Kumar R, Mishra G, Sharma U, Sing G (2014) Sol-Gel processing of silica nanoparticles and their applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 214:17–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.10.007
Kango S, Kalia S, Celli A, Njuguna J, Habibi Y, Kumar R (2013) Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic-inorganic nanocomposites - A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 38(no. 8):1232–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.02.003
Milea CA, Bogatu C (2011) The influence of parameters in silica sol-gel process. Bull Transilv Univ Brasov Eng Sci 4(no. 1):59–66
Liu S, Han MY (2010) Silica-coated metal nanoparticles. Chem - An Asian J 5(no. 1):36–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.200900228
Vansant EF, Van Der Voort P, Vrancken KC (1995) Characterization and chemical modification of the silica surface. Vol. 93 Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0444819282
Brinker C, Scherer GW (1990) Sol-gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. 1st Edition. Academic Press. London. ISBN 9780080571034
Branda F (2011) The sol-gel route to nanocomposites. Adv Nanocomposites- Synth Characterisation Ind. Appl. 14:323–340. https://doi.org/10.5772/15454
Košak A, Lobnik A, Bauman M (2015) Adsorption of mercury(II), lead(II), cadmium(II) and zinc(II) from aqueous solutions using mercapto-modified silica particles. Int J Appl Ceram Technol 12(no. 2):461–472. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.12180
Witucki GL (1993) A silane primer: chemistry and applications of alkoxy silanes. J. Coatings Technol. 65(no. 822):57–60. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.109.028449
Bauman M, Košak A, Lobnik A, Petrinić I, Luxbacher T (2013) Nanofiltration membranes modified with alkoxysilanes: Surface characterization using zeta-potential. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 422:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.01.005
Li X, Shi B, Wang Y, Li M, Liu Y, Gao LI, Mao L (2015) Preparation of monodispersed mesoporous silica particles and their applications in adsorption of Au3+ and Hg2+ after mercapto-functionalized treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 214:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.04.033
Heidari A, Younesi H, Mehraban Z (2009) Removal of Ni(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) from a ternary aqueous solution by amino functionalized mesoporous and nano mesoporous silica. Chem Eng J 153(no. 1–3):70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.06.016
Pandey S, Singh N, Shukla S, Tiwari M (2017) Removal of Lead and Copper from Textile Wastewater Using Egg Shells. Iranian (Iranica) J Energy Environ 8(3):202–209. https://doi.org/10.5829/ijee.2017.08.03.04
Gautam K, Markandeya Singh NB, Shukla SP, Mohan D (2020) Lead removal efficiency of various natural adsorbents (Moringa oleifera, Prosopis juliflora, peanut shell) from textile wastewater. Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2:288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2065-0
Ilyas M, Ahmad A, Saeed M (2013) Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using peanut shell as adsorbent. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 35(3):760–768
Zhu Y, Zhang H, Zeng H, Liang M, Lu R (2012) Adsorption of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by the iron (III)-impregnated sorbent prepared from sugarcane bagasse. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:463–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0043-9
Su M, Fang Y, Li B, Yin W, Gu J, Liang H, Li P, Wu J (2019) Enhanced hexavalent chromium removal by activated carbon modified with micro-sized goethite using a facile impregnation method. Sci. Environ. 647:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.372
Kushwaha S, Sodaye S, Padmaja P (2008) Equilibrium, kinetics and termodynamic studies for adsorption of Hg (II) on palm shell powder. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 19:597–603
Solis KL, Nam Go-Un, Hong Y (2016) Effectiveness of gold nanoparticle-coated 199silica in the removal of inorganic mercury in aqueous systems: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Environ Eng Res 21(no. 1):99–107. Crossref. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2015.126. †Korean Society of Environmental Engineering,
Faulconer EK, von Reitzenstein NVH, Mazyck DW (2012) Optimization of magnetic powdered activated carbon for aqueous Hg (II) removal and magnetic recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 199–200:9–14
Yusmaniar A, Purwanto EA, Putri, Rosyidah D (2017) Adsorption of Pb(II) using silica gel composite from rice husk ash modified 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES)-activated carbon from coconut shell. AIP Conf. Proc. 1823:no. Ii. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4978107
Sertsing S, Chukeaw T, Pengpanich S, Pornchuti B (2018) Adsorption of Nickel and Chromium Ions by Amine-Functionalized Silica Aerogel. MATEC Web Conf. 156:4–7. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201815603014
Soltani RDC, Khorramabadi GS, Khataee AR, Jorfi S (2014) Silica nanopowders/alginate composite for adsorption of lead (II) ions in aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45(no. 3):973–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.09.014
Zhao J, Niu Y, Ren B, Chen H, Zhang S, Jin J, Zhang Y (2018) Synthesis of Schiff base functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4composites for effective removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution Chem Eng J 347:574–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.151. no. March
Lai X, Sun D, Hou Y, Zuo Y, Li Y, Zhang L (2018) Amino-Functionalized Multilayer Core–Shell Mesoporous Organosilica Nanospheres for Cr(VI) Removal. Adv. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 5, no. 18. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201800630
Bogush GH, Et-zukoski CF (1991) Studies of the kinetics of the precipitation of uniform silica particles through the hydrolysis and condensation of silicon alkoxides. J Colloid Interface Sci. 142:1
La Mer VK (1952) Nucleation in phase transitions. Ind Eng Chem 44:1270–1277. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50510a027
Look JL, Bogush GH, Zukoski CF (1990) Colloidal interactions during the precipitation of uniform submicrometre particles. Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 40:345
Tabatabaei S, Shukohfar A, Aghababazadeh R, Mirhabibi A (2006) Experimental study of the synthesis and characterisation of silica nanoparticles via the sol-gel method. J Phys Conference Series 26(no. 1):371–374. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/26/1/090
Huang H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Niu Z, Li X (2020) Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater. Open Chem. 18(no. 1):97–107. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2020-0009
Dąbrowski A (2001) Adsorption — from theory to practice. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 93(no. 1):135–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-8686(00)00082-8
Dabbaghian MA, Babalou AA, Hadi P, Jannatdoust E (2010) A Parametric Study of the Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles via Sol-Gel Precipitation Method. International Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 6(no. 2):104–113
Hadela A (2020) Novel reusable functionalized magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles as oil adsorbent. Adsor Sci Technol 0(0):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617420922014
Drew Myers, (1999) “Surfaces, Interfaces, and Colloids: Principles and Applications”, Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., ISBNs: 0-471-33060-4
Michael W, McKittrick (2003) Toward single-site functional materials preparation of amine-functionalized surfaces exhibiting site-isolated behavior. Chem Mater 15:1132–1139
Manyangadze M, Chikuruwo NMH, Narsaiah TB, Chakra CS, Charis G, Danha G, Mamvura TA (2020) Adsorption of lead ions from wastewater using nano silica spheres synthesized on calcium carbonate templates Heliyon 6(no. 11):e05309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05309
Rekondo A, Irusta L, Fernández-Berridi M (2010) Characterization of silanized poly(ether-urethane) hybrid systems using thermogravimetric analysis (TG). J Therm Anal Calorim 101:331–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-0674-3
Kulkarni SA, Ogale SB, Vijayamohanan KP (2008) Tuning the hydrophobic properties of silica particles by surface silanization using mixed self-assembled monolayers. Colloid Interface Sci 318:372
Chan CCP, Choudhury NR, Majewski P (2011) Fabrication and characterisation of self-assembled monolayers of N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]diethylenetriamine on silica particles. Colloids Surf: Physicochem Eng Aspects 377:20–27
Pérez-Quintanilla D, del Hierro I, Fajardo M, Sierra I (2006) Mesoporous silica functionalized with 2-mercaptopyridine: synthesis, characterization and employment for Hg (II) adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 89:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.10.012
Pérez-Quintanilla D, del Hierro I, Fajardo M, Sierra I (2006) 2-Mercaptothiazoline modified mesoporous silica for mercury removal from aqueous media. J Hazard Mater 134(30. P.):245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.004
Pérez-Quintanilla D, del Hierro I, Fajardo M, Sierra I (2006) Preparation of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole-derivatized mesoporous silica and removal of Hg (II) from aqueous solution. J Environ Monit 8:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1039/B507983G
Liang R, Zou H (2020) Removal of aqueous Hg (II) by thiol-functionalized nonporous silica microspheres prepared by one-step sol–gel method. RSC Adv 10(31):18534–18542. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra02759f
IUPAC (1982) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems. Pure Appl Chem 54(no. 11):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
ZemljičL F, Čakara D, Michaelis N, Heinze T, Kleinschek KS (2011) Protonation behavior of 6-deoxy-6-(2-aminoethyl)amino cellulose: a potentiometric titration study. Cellulose 18(no. 1):33–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9467-x
Erdem E, Karapinar N, Donat R (2004) The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 280(2):309–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.028.15533402
Jiang Y, Pang H, Liao B (2009) Removal of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution by modified bagasse. J Hazard Mater 164(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.107.18790566
Sing KSW (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem 57:603–619
Yong Jae Suh (2015) Role of chemical hardness in the adsorption of hexavalent chromium species onto metal oxide nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 273:401–405
Parr RG, Pearson RG (1983) Absolute hardness: companion parameter to absolute electronegativity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105:7512
Yokoi T, Yoshitake H, Tatsumi T (2004) Synthesis of amino-functionalized MCM-41 via direct co-condensation and post-synthesis grafting methods using mono-, di- and tri-amino-organoalkoxysilanes. J Mater Chem 14:951–957
Manu V, Haresh MM, Bajaj HC, Jasra RV (2009) Adsorption of Cu2+ on amino functionalized silica gel with different loading. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:8954–8960
Lee J, Kim JH, Choi K, Kim HG, Park JA, Cho SH, Hong SW, Lee JH, Lee JH, Lee S, Lee SY, Choi JW (2018) Investigation of the mechanism of chromium removal in (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilane functionalized mesoporous silica. Sci Rep 8:12078. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29679-x
Gascón V, Arencibia A, Arsuaga JM (2019) Aqueous heavy metals removal by removal on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica”. Desalination Water Treatment 146:210–226
Zhang L, Yu C, Zhao W, Hua Z, Chen H, Li L, Shi J (2007) Preparation of multi-amine-grafted mesoporous silicas and their application to heavy metal ions adsorption. J Non-Cryst Solids 353:4055–4061
Dindar MH, Yaftian MR, Rostamnia S (2015) Potential of functionalized SBA-15 mesoporous materials for decontamination of water solutions from Cr(VI), As(V) and Hg(II) ions. J Environ Chem Eng 3:986–995
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156(no. 1):2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Langmuir Freundlich Temkin AOD, Dubinin–Radushkevich (2012) Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn 2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. IOSR J Appl Chem 3(no. 1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-0313845
Gogoi S, Chakraborty S, Saikia MD (2018) Surface modified pineapple crown leaf for adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) ions from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 6(no. 2):2492–2501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.03.040
Kothalawala N, Blitz JP, Gun’ko VM, Jaroniec M, Grabicka B, Semeniuc RF (2013) Post-synthesis surface-modified silicas as adsorbents for heavy metal ion contaminants Cd(II), Cu(II), Cr(III), and Sr(II) in aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 392(no. 1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.10.037
Zhuravlev LT (2000) The surface chemistry of amorphous silica. Zhuravlev model. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 173(no. 1–3):1–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(00)00556-2
Lue L (2009) Chemical thermodynamics. Ventus Publishing Aps. ISBN 978-87-7681-497-7
Saha P, Chowdhury S (2011) Insight into adsorption thermodynamics. Thermodynamics https://doi.org/10.5772/13474
Ali Khan AS (2012) Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption on sand from Temkin adsorption isotherm. Turkish J. Chem. 36(no. 3):437–443. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1108-34
Idris SAM (2015) Adsorption, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for manganese extraction from aqueous medium using mesoporous silica. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 440:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.10.022
Kushwaha AK, Gupta N, Chattopadhyaya MC (2017) Adsorption behavior of lead onto a new class of functionalized silica gel. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 10:S81–S89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.06.010
Hayati B, Maleki A, Najafi F, Daraei H, Gharibi F, McKay G (2017) Adsorption of Pb2 +, Ni2 +, Cu2 +, Co2 + metal ions from aqueous solution by PPI/SiO2 as new high performance adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic studies
Flores-Cano JV, Leyva-Ramos R, Carrasco-Marin F, Aragón-Piña A, Salazar-Rabago JJ, Leyva-Ramos S (2016) Adsorption mechanism of Chromium(III) from water solution on bone char: effect of operating conditions. Adsorption 22(no. 3):297–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-016-9771-3
Tytłak A, Oleszczuk P, Dobrowolski R (2015) Sorption and desorption of Cr(VI) ions from water by biochars in different environmental conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22(no. 8):5985–5994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3752-4
Bernardo Garcia-ReyesRefugio, Rene Rangel-MendezJose, Catalina Alfaro-DelaTorreMa (2009) Chromium (III) uptake by agro-waste biosorbents: Chemical characterization, sorption-desorption studies, and mechanism. J Hazard Mater 170(no. 2–3):845–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.046
Acknowledgements
The result presented is performed with financial support from the GMOS-Train Program European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement no. 860497. The work is co-funded by the project HMRecycle from the Eurostars-2 joint programme. We express our gratitude to the national funding organisation Slovenian Ministry of Education, Science and Sport (www.mizs.gov.si/en) for additional co-financing of this work. The results were created within the Research program Design of new properties of (nano) materials & applications, No. P2-0424 and authors acknowledge the financial support from the Slovenian Research Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, A.F.P.A.M., Krajnc, S., Bauman, M. et al. Removal of Pb2+, Cr3+ and Hg2+ ions from aqueous solutions using SiO2 and amino-functionalized SiO2 particles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 103, 290–308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05830-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05830-z